Decoding the Dollars: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Resident Salaries

Embarking on a career in medicine is a monumental achievement, marked by years of intense study and dedication. The final, critical phase of this journey before becoming a fully independent physician is the residency program. While the long hours and immense responsibility are well-known, a common and practical question on the minds of many aspiring doctors is: "What can I expect to earn as a resident?"
This article provides a data-driven look at the average salary for a medical resident in the United States. While resident pay is modest compared to that of a fully licensed physician, it is a stable, salaried position that supports you through your advanced training. The national average salary for a medical resident is approximately $67,400 per year, but this figure can vary significantly. Let's explore the details of the role and the key factors that influence your earnings during this pivotal career stage.
What Does a Medical Resident Do?

A medical resident is a physician who has graduated from medical school with an M.D. or D.O. degree and is now undergoing supervised, hands-on training in a specific medical specialty. This period, known as graduate medical education (GME), can last anywhere from three to seven years or more.
Think of residency as a medical apprenticeship. Residents are doctors who practice in hospitals and clinics under the direct supervision of senior physicians (attendings). Their core responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing and treating patients.
- Developing patient care plans.
- Performing medical procedures.
- Responding to medical emergencies.
- Working long hours, including nights, weekends, and on-call shifts.
- Rotating through various departments to gain comprehensive experience.
The primary goal of residency is to transform a medical school graduate into a competent, confident, and skilled specialist ready for independent practice.
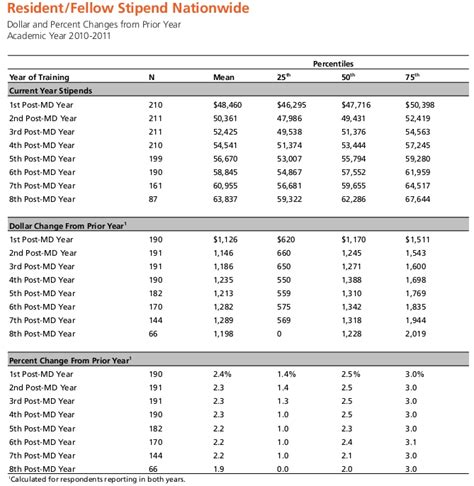
Average Medical Resident Salary
A resident's compensation is typically referred to as a "stipend" or salary, which is standardized across an institution and increases incrementally each year.
According to the Medscape Resident Salary & Debt Report 2023, the average salary for medical residents in the U.S. is $67,400. This figure represents a steady increase in recent years as institutions work to provide more competitive compensation.
Salary aggregators provide a similar range:
- Salary.com reports a typical range for a first-year resident (intern) between $61,718 and $68,891, with an average of $64,369 as of late 2023.
- Glassdoor places the average total pay for a "Resident Physician" at around $71,000 per year, which includes base salary and potential additional pay.
It is crucial to understand that this is not an hourly wage. Given that residents often work 60-80 hours per week, the effective hourly rate is quite low. However, the true compensation is the invaluable training and experience that paves the way for a lucrative and impactful career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While institutions try to standardize pay, several factors can affect a resident's annual salary.
### Post-Graduate Year (PGY) and Experience
This is the single most significant factor in determining a resident's salary. "PGY" stands for Post-Graduate Year and indicates how many years a resident has been in training. Institutions have a set pay scale that increases with each PGY level to reflect growing experience and responsibility.
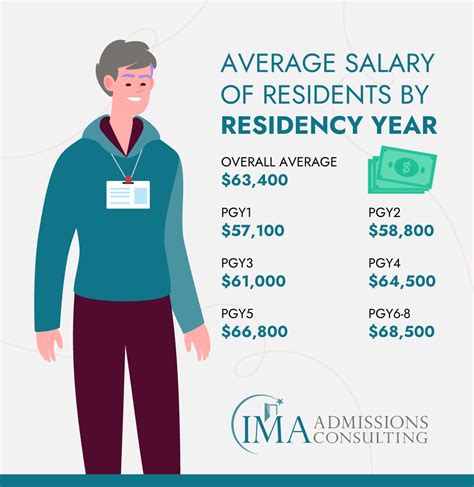
Based on the Medscape 2023 report, the progression looks like this:
- PGY-1 (Interns): $61,000
- PGY-2: $63,000
- PGY-3: $65,500
- PGY-4: $68,500
- PGY-5: $71,000
- PGY-6 to PGY-8 (Fellows/Senior Residents): $74,500 - $79,000
A resident in a longer program like surgery (5-7 years) will eventually earn more per year than a resident in a shorter program like family medicine (3 years) simply by advancing to higher PGY levels.
### Geographic Location
Where you complete your residency matters. Hospitals in regions with a higher cost of living typically offer higher salaries to help offset expenses. According to various residency program databases, stipends are often highest in the Northeast (New York, Massachusetts) and on the West Coast (California). Conversely, salaries may be lower in the South and parts of the Midwest, where the cost of living is also generally lower. However, a higher salary in a major metropolitan area may not translate to more take-home pay after accounting for rent, taxes, and other living expenses.
### Company Type (Hospital or Institution)
The type of institution hosting the residency program can influence pay and benefits.
- Academic Medical Centers: University-affiliated hospitals are the most common training sites. Their salaries are often well-documented and follow a rigid PGY structure.
- Community Hospitals: Both private and non-profit community hospitals may offer slightly higher salaries to attract top candidates and compete with prestigious academic centers.
- Government Hospitals: Institutions like those run by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offer competitive, federally-funded salaries and excellent benefits.
### Area of Specialization
During residency itself, the choice of specialty has a minimal direct impact on your salary. A PGY-1 in neurosurgery will likely earn the same as a PGY-1 in pediatrics *at the same institution*.
However, specialization has two major indirect effects:
1. Length of Training: A general surgery residency (5 years) means you'll reach the higher PGY-5 salary, while a family medicine residency (3 years) concludes at the PGY-3 salary level.
2. Future Earning Potential: This is the most critical point. While your resident salary is modest, it's a stepping stone. The salary for a fully licensed cardiologist, anesthesiologist, or surgeon is significantly higher than that of a primary care physician. Therefore, the choice of specialty dramatically impacts your lifelong earning potential *after* residency is complete.
Job Outlook

The future for physicians and surgeons in the United States is bright. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for physicians and surgeons is projected to grow 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
This demand is driven by several factors, including:
- An aging population requiring more medical care.
- Continued advancements in medical technology and treatments.
- An increased focus on preventative care.
Completing a residency program is the mandatory pathway to becoming a licensed physician, so the demand for residents will remain strong and aligned with the overall demand for doctors.
Conclusion

Becoming a medical resident is the culmination of a decade of hard work and the beginning of a rewarding career. While the salary—averaging around $67,400 per year—is modest for a doctor, it's important to view it as a paid, multi-year investment in your future.
Here are the key takeaways for anyone considering this path:
- Expect Incremental Growth: Your salary is primarily determined by your PGY level, increasing steadily each year you are in training.
- Location Matters: Higher cost-of-living areas typically offer higher stipends to compensate.
- Focus on the Future: The real financial reward comes after residency. Your choice of specialty will be the ultimate driver of your long-term earning potential.
- It's a Secure Path: The demand for physicians remains robust, ensuring excellent job security upon completion of your training.
Residency is a challenging but temporary phase. The skills, experience, and professional network you build during these years will form the foundation for a successful, impactful, and financially rewarding career in medicine.