Romania, a vibrant nation at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe, is undergoing a remarkable economic transformation. Once primarily known for its rich history and breathtaking landscapes, it is now rapidly emerging as a dynamic hub for technology, shared services, and advanced manufacturing. For professionals both within and outside its borders, this evolution raises a critical question: What does it truly mean to build a career in Romania today, and what level of compensation can one expect?
This guide is designed to be your definitive resource for understanding the salary landscape in Romania in 2024. We will move far beyond a single, simplistic "average salary" figure. Instead, we will dissect the intricate factors that shape your earning potential—from your specific industry and years of experience to the city you call home. Having worked with international teams and analyzed compensation data across Europe for over a decade, I've seen firsthand how a country's economic narrative directly impacts individual careers. I remember a conversation with a young software developer from Cluj-Napoca who, in just five years, saw his earning potential triple, a testament not just to his skill but to the explosive growth of Romania's tech sector. His story is a microcosm of the opportunity that this dynamic market represents.
Whether you are a Romanian graduate planning your first career move, an experienced local professional seeking to maximize your earnings, or an expatriate considering a relocation, this article will provide you with the data, context, and strategic advice needed to navigate the Romanian job market with confidence.
### Table of Contents
- [Understanding the Romanian Job Market: An Overview](#understanding-the-romanian-job-market-an-overview)
- [The Average Salary in Romania 2024: A Deep Dive](#the-average-salary-in-romania-2024-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Your Salary in Romania](#key-factors-that-influence-your-salary-in-romania)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth in Romania](#job-outlook-and-career-growth-in-romania)
- [How to Land a Job in Romania: A Guide for Locals and Expats](#how-to-land-a-job-in-romania-a-guide-for-locals-and-expats)
- [Conclusion: Is a Career in Romania Right for You?](#conclusion-is-a-career-in-romania-right-for-you)
Understanding the Romanian Job Market: An Overview

Before diving into specific numbers, it's essential to understand the structure and culture of the Romanian workplace. The country's job market is a fascinating blend of traditional industries and hyper-modern, internationalized sectors. Fueled by EU membership, foreign direct investment, and a highly skilled, often multilingual workforce, Romania has become a critical destination for multinational corporations (MNCs).
The core of the modern Romanian economy rests on several key pillars:
1. Information Technology (IT) & Software Development: This is the undisputed engine of growth. Cities like Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, and Iași have become major European tech hubs, hosting R&D centers and development offices for global giants like Oracle, Microsoft, Amazon, and IBM, alongside a thriving ecosystem of homegrown startups like the unicorn UiPath.
2. Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) & Shared Service Centers (SSCs): Romania's strong language skills (especially in English, French, German, and Italian) have made it a leader in this field. Companies centralize their finance, HR, procurement, and customer support operations here, creating thousands of jobs for multilingual professionals.
3. Automotive & Manufacturing: Romania has a long-standing industrial tradition, now modernized. It's a key manufacturing hub for major automotive players like Dacia (part of Renault Group) and Ford, along with a vast network of parts suppliers.
4. Agriculture and Food Production: A historically vital sector that remains a significant employer, particularly in rural areas.
5. Finance & Banking: A robust and modernizing sector concentrated in Bucharest, with all major European banking groups having a significant presence.
### A "Day in the Life" of a Mid-Level Software Engineer in Bucharest
To make this more tangible, let's imagine a day for "Andrei," a 30-year-old software engineer working for a multinational tech company in Bucharest.
- 8:45 AM: Andrei arrives at his modern office in the Aurel Vlaicu district, a major business hub. He grabs a coffee from the high-end machine provided by the company, greeting colleagues in a mix of Romanian and English—the official language of the office.
- 9:00 AM: Daily stand-up meeting with his agile team. The team includes members in Bucharest, a project manager in London, and a QA specialist in India. They discuss progress on the current sprint and any blockers.
- 9:30 AM - 1:00 PM: Deep work session. Andrei focuses on coding a new feature for a cloud-based enterprise application. He collaborates with a colleague via Slack to troubleshoot a complex API integration.
- 1:00 PM: Lunchtime. Andrei uses his company-provided meal vouchers (`tichete de masă`) to buy lunch at one of the many restaurants in the office park. He joins colleagues on a terrace, and the conversation shifts from tech to plans for a weekend trip to the mountains.
- 2:00 PM - 4:00 PM: Code review and a planning meeting for the next sprint. He provides feedback on a junior developer's code and participates in a technical design discussion for an upcoming project.
- 4:00 PM - 5:30 PM: Andrei dedicates the last part of his day to professional development. The company offers a subscription to online learning platforms, and he spends time on a course about advanced Kubernetes orchestration to keep his skills sharp.
- 5:45 PM: Andrei heads home, taking the metro. Some days he might stay for a company-sponsored social event or use his subsidized gym membership, another common perk.
This snapshot illustrates a work environment that is global, technologically advanced, and comes with a benefits package designed to attract and retain top talent—a reality for many professionals in Romania's leading sectors.
The Average Salary in Romania 2024: A Deep Dive
When discussing salaries in Romania, it's crucial to distinguish between gross salary (`salariu brut`) and net salary (`salariu net`). The gross salary is the amount before taxes and social contributions, while the net salary is the actual take-home pay. The difference is significant, as contributions for pension, health, and income tax are substantial.
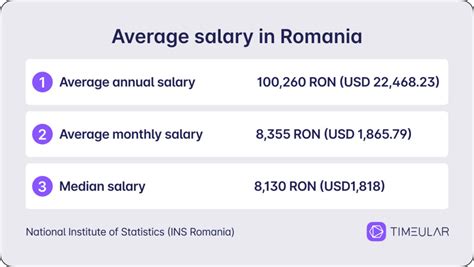
As of early 2024, the latest data from the Romanian National Institute of Statistics (INSSE) provides the most authoritative figures.
- Average Gross Salary: According to the INSSE report for January 2024 (published in March 2024), the average gross nominal earning was 8,436 RON per month.
- Average Net Salary: The corresponding average net nominal earning was 5,185 RON per month.
*Source: Institutul Național de Statistică (INSSE), Câștigul salarial mediu, January 2024.*
It is critical to understand that this is a national average across all sectors and experience levels. It includes both a high-earning IT manager in Bucharest and a minimum-wage worker in a rural area. Therefore, this figure should only be a starting point.
A more practical view comes from salary aggregators that capture real-world, user-submitted data. According to Salario, the salary comparison tool from the leading Romanian job portal eJobs.ro, the median net salary in Romania is approximately 5,000 RON per month as of 2024. This median figure is often more representative than the average, as it is less skewed by extremely high salaries. The eJobs data also reveals that most net salaries fall between 3,000 RON and 7,500 RON.
### Salary Brackets by Experience Level
Salary growth in Romania is closely tied to experience. The leap from an entry-level position to a senior role can be dramatic, especially in high-demand fields.
| Experience Level | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (RON) | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (EUR)* | Description |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level (0-2 years) | 3,000 - 4,500 RON | €600 - €900 | Positions for recent graduates or those new to the workforce. Often includes internships or junior roles. |
| Mid-Career (3-8 years) | 4,500 - 8,000 RON | €900 - €1,600 | Professionals with established skills and some level of independence. This is the largest segment of the workforce. |
| Senior/Expert (8+ years) | 8,000 - 15,000 RON | €1,600 - €3,000 | Highly experienced specialists, team leads, and technical experts with deep domain knowledge. |
| Management/Executive| 15,000 - 30,000+ RON| €3,000 - €6,000+ | Department heads, C-level executives, and senior managers with significant responsibility for budget and personnel. |
*Note: Conversion to EUR is approximate (1 EUR ≈ 5 RON) and for illustrative purposes. Actual salaries are paid in RON.*
*Source: Aggregated data from eJobs.ro (Salario), Glassdoor, and professional recruitment agency reports for 2023-2024.*
### Beyond the Paycheck: Understanding Total Compensation
In Romania, especially within multinational corporations, the compensation package extends far beyond the net salary. These benefits are a crucial part of the overall value proposition and can significantly impact your financial well-being and lifestyle.
- Meal Vouchers (`Tichete de Masă`): This is one of the most common and valued benefits. Employees receive a monthly allowance on a dedicated card to be used for food purchases at supermarkets and restaurants. As of 2024, the maximum tax-free value is around 40 RON per workday, translating to over 800 RON/month.
- Private Health Insurance: While Romania has a public healthcare system, many medium-to-large companies offer private health insurance packages. These provide access to a network of private clinics and hospitals, allowing for faster appointments and often a higher standard of care.
- Performance Bonuses: Annual or semi-annual bonuses tied to individual and company performance are standard in many sectors, particularly in sales, finance, and IT. These can range from one extra month's salary to significantly more for high-achievers.
- The 13th (and sometimes 14th) Salary: While less common than in some other European countries, some companies, particularly in manufacturing and retail, offer a guaranteed "13th salary" typically paid out before Christmas or summer holidays.
- Flexible Work and Remote Options: The pandemic accelerated this trend. Many companies, especially in tech, now offer fully remote or hybrid work models, providing flexibility and saving employees commuting time and costs.
- Professional Development Budget: A dedicated budget for courses, certifications, conferences, and training is a key perk in knowledge-based industries to ensure employees' skills remain current.
- Other Perks: Depending on the company, you might also find gym memberships (e.g., 7card), transport allowances, company cars (for senior/sales roles), and stock option plans (especially in tech startups and MNCs).
When evaluating a job offer in Romania, it is essential to consider the value of this entire package, not just the net salary figure.
Key Factors That Influence Your Salary in Romania
Your potential salary is not a single number but a variable determined by a powerful combination of factors. Understanding these levers is the key to maximizing your earning potential throughout your career in Romania.
###
Level of Education and Certifications
While a bachelor's degree is the standard entry requirement for most professional roles, the impact of education on salary is nuanced.
- Bachelor's vs. Master's Degree: A master's degree can provide an edge and a slightly higher starting salary, particularly in specialized fields like finance, law, or engineering. For instance, a Master's in Finance might open doors to higher-paying roles in investment banking or analysis. However, in the fast-moving IT sector, demonstrable skills and experience often outweigh a master's degree after the first few years.
- University Prestige: Graduating from a top-tier Romanian university like the University of Bucharest, Babeș-Bolyai University in Cluj-Napoca, or the Polytechnic University of Bucharest can provide a networking advantage and may be viewed more favorably by some traditional employers.
- Professional Certifications: This is where education has the most direct and significant impact on salary, especially in IT. Industry-recognized certifications act as proof of specialized, in-demand skills.
- IT & Cloud: Certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Google Cloud Professional, or Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator can add 15-30% to a developer's or systems administrator's salary.
- Project Management: A Project Management Professional (PMP) or PRINCE2 certification is highly valued and can be a prerequisite for senior project management roles, commanding salaries in the 10,000 - 18,000 RON (net) range.
- Finance & Accounting: Certifications like ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants) or CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) are a golden ticket to the highest-paying roles in finance and audit.
###
Years of Experience
As shown in the table above, experience is arguably the single most powerful driver of salary growth in Romania. The progression is not linear; it often occurs in significant jumps.
- 0-2 Years (Junior): The focus is on learning and execution. Salaries are at the lower end as companies invest in training. A junior software developer might start at 4,000-5,000 RON net.
- 3-5 Years (Mid-Level): This is the sweet spot for the first major salary leap. Professionals have proven their competence and can work independently. They are highly sought after. That junior developer can now expect 7,000-10,000 RON net. Changing jobs at this stage often results in a significant pay bump.
- 6-10+ Years (Senior): At this stage, you are an expert. You not only execute tasks but also mentor juniors, design systems, and lead projects. Your value is in your strategic contribution. Senior developers, engineers, or financial controllers can command salaries from 12,000 RON upwards to 20,000 RON or more.
- Leadership/Management: Transitioning from a senior individual contributor to a team lead or manager marks another significant salary increase. Managerial roles add responsibility for people and budgets, with compensation reflecting this.
###
Geographic Location
There is a stark salary divide in Romania between major economic hubs and the rest of the country. Your postal code is a major determinant of your paycheck.
- Tier 1 Cities (The Powerhouses): Bucharest and Cluj-Napoca.
- Bucharest: As the capital and largest city, it has the highest concentration of corporate headquarters, government institutions, and the highest salaries on average across almost all sectors. It is the undisputed center for finance, BPO, and large-scale IT operations.
- Cluj-Napoca: The heart of Transylvania's "Silicon Valley." It has a hyper-competitive IT market that sometimes pushes tech salaries to levels matching or even exceeding Bucharest. The cost of living, particularly rent, is also very high.
- Tier 2 Cities (Major Hubs): Timișoara and Iași.
- Timișoara: A strong industrial and automotive hub with a significant German influence and a rapidly growing IT sector. Salaries are very competitive, often close to Tier 1 levels.
- Iași: A major university city that has become a key center for IT and BPO in the eastern part of the country. While salaries may be 10-15% lower than in Bucharest, the lower cost of living can make it an attractive option.
- Tier 3 Cities (Emerging Hubs): Brașov, Sibiu, Oradea. These cities offer a great quality of life and are developing their own tech and manufacturing niches. Salaries are generally lower than in Tiers 1 and 2 but are rising as more companies establish offices there to tap into local talent pools.
- Rural Areas & Smaller Cities: Outside of these major hubs, job opportunities are more limited to local industries, agriculture, and public sector roles. Salaries are significantly lower, often at or near the national minimum wage.
Illustrative Net Monthly Salary Comparison by City (Mid-Level Role)
| Role | Bucharest/Cluj | Timișoara/Iași | Brașov/Sibiu | Smaller City |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Software Developer | 9,000 - 12,000 RON | 8,000 - 10,000 RON | 7,000 - 9,000 RON | 4,500 - 6,000 RON |
| Accountant | 6,000 - 7,500 RON | 5,500 - 6,500 RON | 5,000 - 6,000 RON | 3,500 - 4,500 RON |
| Marketing Specialist| 5,500 - 7,000 RON | 5,000 - 6,000 RON | 4,500 - 5,500 RON | 3,000 - 4,000 RON |
*Source: Market analysis based on data from local job portals and recruitment agencies.*
###
Company Type & Size
The type of organization you work for has a profound impact on your compensation and work environment.
- Multinational Corporations (MNCs): Generally the highest payers. They have large budgets, structured salary bands, and extensive benefits packages (private health, meal vouchers, bonuses). They are the primary employers in IT, BPO, and finance.
- Romanian Tech Companies & Unicorns (e.g., UiPath): These companies compete directly with MNCs for top talent and often offer very competitive salaries, along with potentially lucrative stock options. The culture may be more dynamic and less bureaucratic.
- Startups: Compensation can be a mixed bag. Early-stage startups may offer lower base salaries but compensate with significant equity (stock options). The risk is higher, but the potential reward is greater if the company succeeds.
- Local Romanian Companies (Non-Tech): Traditional Romanian companies in sectors like retail, construction, or food production typically offer lower salaries and less extensive benefit packages compared to MNCs.
- Government & Public Sector: Public sector jobs (e.g., in administration, education, healthcare) offer high job security but have notoriously lower salaries than the private sector for comparable qualifications. A complex, grid-based salary system (`grilă de salarizare`) determines pay, with less room for negotiation.
###
Industry & Area of Specialization
This is where we see the most significant variations. Your career choice is paramount. The INSSE itself reports that the highest net salaries are in Information Technology and Communications (averaging over 11,000 RON net), while the lowest are in Hospitality (around 3,000 RON net).
Let's break down some key sectors with more granular data.
1. Information Technology (IT)
The undisputed king of salaries in Romania. There is a huge talent deficit, which drives wages up continuously.
| IT Role | Experience Level | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (RON) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Junior Software Developer | Entry-Level | 4,500 - 6,500 |
| Mid-Level Software Developer | Mid-Career | 8,000 - 13,000 |
| Senior Software Developer/Architect | Senior | 14,000 - 25,000+ |
| DevOps / Cloud Engineer | Mid-Senior | 12,000 - 22,000 |
| QA Engineer (Automation) | Mid-Senior | 8,000 - 14,000 |
| IT Project Manager | Senior | 10,000 - 18,000 |
| Data Scientist / ML Engineer | Mid-Senior | 12,000 - 25,000 |
2. Finance & Banking
A stable, high-paying sector, concentrated in Bucharest.
| Finance Role | Experience Level | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (RON) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Accountant | Mid-Career | 5,500 - 7,500 |
| Financial Controller | Senior | 9,000 - 15,000 |
| Financial Analyst | Mid-Career | 7,000 - 11,000 |
| Auditor (Big 4) | Mid-Senior | 8,000 - 13,000 |
| Private Banker / Relationship Mgr | Senior | 10,000 - 16,000 + Bonus |
3. BPO / Shared Service Centers (SSCs)
Characterized by multilingual requirements. Base salary is often augmented by a "language bonus."
| BPO/SSC Role | Experience Level | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (RON) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Customer Support (English) | Entry-Level | 3,500 - 4,500 |
| Customer Support (German/French/Nordic)| Entry-Mid | 4,500 - 6,500 (incl. language bonus)|
| Accounts Payable/Receivable | Mid-Career | 5,000 - 7,000 |
| Team Leader | Senior | 7,000 - 10,000 |
4. Engineering & Manufacturing
Strong in automotive and industrial centers like Timișoara, Brașov, and Pitești.
| Engineering Role | Experience Level | Typical Net Monthly Salary Range (RON) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Mechanical/Electrical Engineer | Mid-Career | 6,000 - 9,000 |
| Process Engineer | Mid-Senior | 7,000 - 11,000 |
| Quality Engineer (Automotive) | Senior | 8,000 - 12,000 |
| Production Manager | Senior | 10,000 - 16,000 |
###
In-Demand Skills
Beyond your job title, specific skills can make you a more valuable and thus higher-paid candidate.
- Language Skills: Fluency in languages other than English is a major asset, especially in the BPO/SSC sector. German, French, Dutch, and Nordic languages can add a bonus of 1,500 - 3,500 RON to a monthly salary.
- Technical Skills (IT): Proficiency in high-demand programming languages (Python, Go, Rust), cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), cybersecurity frameworks, and data science/AI/ML technologies will always command a premium.
- Soft Skills: In an increasingly collaborative and global work environment, skills like leadership, communication, strategic thinking, and stakeholder management are what separate senior professionals from mid-level ones and are critical for accessing management-level salaries.
Job Outlook and Career Growth in Romania
The long-term career prospects in Romania are promising, albeit with some challenges. The country's economy has shown remarkable resilience and is projected to continue its growth trajectory, outpacing many of its EU peers.
### Economic Outlook and Job Growth
According to the European Commission's Winter 2024 Economic Forecast, Romania's GDP is projected to grow by 2.9% in 2024 and 3.2% in 2025. This growth is expected to be driven by strong private consumption, increased investment (partially funded by the EU's Recovery and Resilience Facility), and a robust export sector.
This positive macroeconomic outlook translates directly into a healthy job market. While there isn't a direct equivalent to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) 10-year projection, data from job platforms and economic analyses point to several clear trends:
- Sustained, High Demand in IT: This is not a temporary boom. The global trend of digitalization ensures that the demand for software developers, cybersecurity experts, cloud engineers, and data scientists will continue to grow much faster than the available talent pool. This sector will remain the primary driver of high-wage job creation.
- Growth in High-Value Services: The BPO sector is evolving into Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO). Companies are moving more complex functions to Romania, such as financial analysis, R&D, and engineering design. This creates higher-skilled, better-paying jobs.
- Green Transition and Energy: With significant EU funding allocated for the green transition, there will be substantial growth in jobs related to renewable energy (wind, solar), energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure. This will create a new wave of opportunities for engineers, project managers, and specialized technicians.
- Modernization of Infrastructure: Ongoing projects to upgrade Romania's highways, railways, and public utilities will continue to fuel demand in the construction and engineering sectors.
### Emerging Trends and Future Challenges
Navigating a career in Romania also means being aware of the key trends and potential headwinds:
- The War for Talent: The biggest challenge for employers is finding and retaining skilled labor. This gives skilled professionals significant leverage in salary negotiations and job choices.
- Inflation and Wage Pressure: While wage growth has been strong, it has been battling high inflation. A key challenge for the economy is to ensure that wage increases remain sustainable and translate into real purchasing power gains.
- Demographics and Brain Drain: Romania faces a demographic challenge with an aging population and a history of skilled professionals leaving for Western Europe. While this trend has slowed, and some are returning ("re-pats"), it remains a long-term concern. For those who stay, it reduces competition for senior roles.
- Automation and AI: As in the rest of the world, AI and automation will reshape the job market. Repetitive roles in areas like data entry, basic customer support, and some manufacturing processes are at risk. Roles that require creativity, critical thinking, and complex problem-solving will become even more valuable.
### How to Stay Relevant and Advance Your Career
To thrive in this dynamic environment, professionals must be proactive and strategic.
1. Embrace Lifelong Learning: The single most important factor for long-term career success is continuous skill development. Use company-provided resources, take online courses, and pursue new certifications in your field. In tech, you must learn or you will be left behind.
2. Develop "T-Shaped" Skills: Gain deep expertise in one core area (the vertical bar of the "T") but also develop a broad understanding of related fields (the horizontal bar). A developer who understands business principles and marketing will be more valuable than one who only knows how to code.
3. Master English and a Second Foreign Language: English is the non-negotiable language of business in Romania's high-paying sectors. Adding German or French opens up a vast number of additional opportunities and can directly increase your salary.
4. Build a Professional Network: Actively use LinkedIn. Attend industry meetups, conferences