California's dynamic economy offers a wealth of opportunities for skilled professionals in roles classified as "exempt." While this term might seem like legal jargon, understanding it is crucial for anyone navigating the state's professional landscape. It dictates not just your eligibility for overtime pay but also reflects a certain level of professional standing and earning potential.
For 2024, the legal minimum salary for most exempt employees in California has risen to $66,560 per year. However, this is merely the starting line. Many professional roles that fall under this classification command significantly higher salaries, with experienced specialists in high-demand fields often earning well into the six-figure range. This guide will break down the legal requirements and explore the real-world factors that shape the salaries of exempt professionals across the Golden State.
What Does "Exempt Employee" Mean in California?
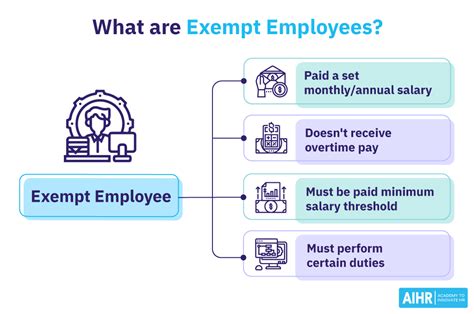
First, it's essential to clarify that "exempt employee" is not a job title but a legal classification under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and California Labor Code. An employee classified as "exempt" is not entitled to overtime pay, minimum wage, or meal and rest breaks.
To be legally classified as exempt in California, an employee must meet three stringent criteria:
1. Salary Basis Test: The employee must be paid a predetermined, fixed salary that is not subject to reduction because of variations in the quality or quantity of work performed.
2. Salary Level Test: The employee must earn a salary that is at least two times the state's minimum wage for full-time employment.
3. Duties Test: The employee’s primary duties must involve executive, administrative, or professional tasks as defined by state law. There are also specific exemptions for computer professionals and outside salespersons.
Common examples of jobs that are often classified as exempt include Marketing Managers, Software Engineers, Human Resources Directors, Senior Accountants, and Management Consultants.
The California Exempt Salary Threshold for 2024
In California, the minimum salary required for an employee to be considered exempt is directly tied to the state minimum wage. As of January 1, 2024, the state minimum wage increased to $16.00 per hour for all employers.
The formula for the exempt salary threshold is:
(State Minimum Wage x 2) x 40 hours per week x 52 weeks per year
For 2024, the calculation is:
($16.00 x 2) x 40 x 52 = $66,560 per year (or $5,546.67 per month).
This is the absolute minimum an employer must pay for most executive, administrative, and professional exemptions.
Special Exemption for Computer Professionals: California has a separate, higher salary threshold for certain computer software professionals. For 2024, this rate has been adjusted to $115,763.35 per year (or a minimum hourly rate of $55.58), according to the California Department of Industrial Relations.
Key Factors That Influence Actual Salary

While the $66,560 figure is the legal floor, it is not a typical salary for most exempt professionals. Actual compensation is determined by a combination of powerful market factors.
### Level of Education
A strong educational background is often the foundation for an exempt-level career. While a bachelor's degree is a common requirement, advanced degrees can significantly increase earning potential. For example, a data scientist with a master's degree or Ph.D. will command a much higher salary than one with only a bachelor's, as their specialized knowledge is in high demand. According to a 2022 report from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), individuals with a master's degree earn a median of 16% more than those with a bachelor's degree.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. Companies pay a premium for professionals who have a proven track record of delivering results.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals just starting may earn closer to the state minimum exempt salary or slightly above, typically in the $70,000 to $90,000 range, depending on the role.
- Mid-Career (5-10 years): With substantial experience, professionals like project managers or senior engineers can expect to earn between $110,000 and $160,000.
- Senior/Lead (15+ years): Top-level directors and principal engineers with extensive experience can command salaries of $180,000 to $250,000+, as reported by salary aggregators like Salary.com for senior management roles in California.
### Geographic Location
In a state as large and diverse as California, where you work matters tremendously. Cost of living and competition for talent create vast salary disparities between metropolitan areas.
- San Francisco Bay Area (including San Jose): This region consistently has the highest salaries in the state due to the concentration of the tech industry. A Software Engineer in San Francisco has an average base salary of around $164,000, according to 2024 data from Glassdoor.
- Los Angeles Metropolitan Area: A major economic hub, Los Angeles offers competitive salaries, though typically lower than the Bay Area. A Marketing Manager in Los Angeles can expect an average salary of approximately $125,000, per Salary.com.
- San Diego: With a growing biotech and defense industry, San Diego's salaries are strong, often falling between those in L.A. and the Bay Area.
- Sacramento and the Central Valley: While still robust, salaries in these areas are generally lower to reflect a lower cost of living. Expect salaries to be 15-25% lower than in the Bay Area for comparable roles.
### Company Type
The size, industry, and financial health of a company heavily influence its compensation strategy.
- Large Tech Corporations (e.g., Google, Apple, Meta): These companies offer top-tier salaries, lucrative stock options, and comprehensive benefits to attract the best talent.
- Startups: While early-stage startups may offer lower base salaries, they often provide significant equity (stock options) as a major part of the compensation package, representing high potential future earnings.
- Non-Profit and Government: These sectors typically offer lower base salaries than the private sector but often compensate with excellent benefits, retirement plans, and strong job security.
### Area of Specialization
Within any profession, certain specializations are more lucrative than others. For example, in the field of information technology:
- An IT professional specializing in Cybersecurity or Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning will earn significantly more than a generalist IT Support Manager due to overwhelming market demand and a shortage of skilled talent. According to Payscale, the average salary for a Cybersecurity Engineer in California is approximately $136,000, with senior roles easily exceeding $180,000.
Job Outlook for Exempt-Level Professions

The job outlook for the types of professional and managerial roles typically classified as exempt is very strong. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment in management occupations is projected to grow 8 percent from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations. Similarly, computer and information technology occupations are projected to grow 15 percent, adding hundreds of thousands of new jobs.
This robust growth is driven by technological innovation, the need for advanced data analysis, and the increasing complexity of global business operations. This signals sustained demand for skilled, exempt-level professionals in California and nationwide.
Conclusion

Understanding the "California exempt employee salary" for 2024 requires looking beyond the legal minimum. While the $66,560 threshold is a critical compliance number for employers, it is not representative of the true earning potential for skilled professionals in the state.
For individuals pursuing or advancing in a professional career path, the key takeaways are:
- Know Your Value: Your actual salary will be determined by your experience, education, location, industry, and specialization.
- Invest in Growth: Continuous learning, gaining experience in high-demand specializations, and pursuing advanced education can dramatically increase your lifetime earnings.
- Location Matters: Be aware of the significant salary differences across California's diverse regions.
The prospects for exempt-level careers in California remain exceptionally bright. By focusing on building valuable skills and strategically navigating your career, you can move far beyond the minimum threshold and achieve a highly rewarding and prosperous professional life in the Golden State.
