The Salary of a Public Servant: How Much Do City Council Members Earn?

Serving on a city council is a unique and impactful career path, placing you at the forefront of community leadership and local governance. But beyond the call to public service, prospective candidates often have a practical question: What is the salary for a city council member? The answer is incredibly varied, ranging from a modest annual stipend in small towns to a six-figure income in major metropolitan areas. This article will break down the compensation you can expect and the key factors that determine it.
What Does a City Council Member Do?
Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the role. A city council member is an elected legislator for a municipality. Their primary duty is to represent the interests of their constituents by creating and voting on local laws, known as ordinances.
Key responsibilities include:
- Approving the City Budget: Allocating funds for essential services like policing, firefighting, public works, and parks.
- Developing Policy: Proposing, debating, and voting on legislation that affects everything from zoning and land use to public health and safety.
- Constituent Services: Acting as a liaison between residents and the city government, helping to solve problems and address concerns.
- Oversight: Overseeing the performance of city departments and administrative staff to ensure they are operating effectively and efficiently.
In smaller communities, this may be a part-time role requiring attendance at evening meetings. In large cities, it is a demanding, full-time job with a dedicated staff.
Average City Council Member Salary
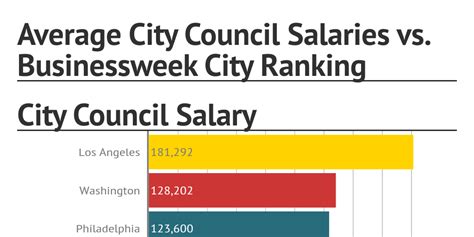
Unlike traditional professions, there isn't a single, straightforward salary for a city council member. Compensation is determined by the municipality itself and varies dramatically across the United States.
According to data from Salary.com, the average salary for a City Council Member in the United States is approximately $55,930 as of 2024. However, the typical salary range is vast, generally falling between $45,390 and $71,780.
It's crucial to understand this range in context:
- Low End: In many small towns and rural communities, serving on the city council is considered a civic duty rather than a career. Council members may only receive a small stipend—sometimes just a few hundred to a few thousand dollars per year—to compensate them for their time and travel to meetings.
- High End: In major cities like Los Angeles, New York, or Chicago, being a city council member is a full-time, high-pressure job. Salaries in these locations can easily exceed $150,000 or even $200,000 annually, reflecting the immense responsibility and high cost of living.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Compensation for a city council member is not determined by a corporate pay scale but by a specific set of factors tied to the community they serve.
### Geographic Location & City Size
This is the single most significant factor. The size of a city's population and the complexity of its economy directly correlate with council member pay.
- Large Metropolitan Areas: A council member in a city with millions of residents and a multi-billion dollar budget (e.g., Los Angeles) has far greater responsibilities than one in a town of 5,000. Their salary reflects this, often making them some of the highest-paid municipal legislators in the country.
- Small Towns & Rural Areas: In smaller municipalities, the issues are often less complex and the budget is smaller. The role is typically part-time, and the salary is structured as a stipend.
- Cost of Living: Regions with a higher cost of living generally offer higher salaries to ensure that public service is a viable option for qualified individuals.
### Years of Experience & Leadership Roles
While there isn't a standard "senior-level" pay bump, experience and tenure play a role. A seasoned council member is more likely to be elected to leadership positions, which often come with additional compensation. For example, the City Council President, Mayor Pro Tem, or a committee chair may receive a higher salary or an extra stipend in recognition of their added duties and responsibilities.
### Level of Education
There are generally no formal educational requirements to be elected to a city council. However, a relevant educational background can make a candidate more effective and electable, indirectly influencing their career trajectory. Degrees in Public Administration (MPA), Law (J.D.), Urban Planning, or Finance equip a candidate with valuable skills for policymaking and budget analysis, potentially leading to influential committee assignments and leadership roles more quickly.
### City Governance Structure & Budget
A city's own laws and financial health dictate pay. Council salaries are set by city charter or by a vote of the council itself, and are often reviewed by independent salary-setting commissions to avoid conflicts of interest.
- Council-Manager vs. Strong Mayor Systems: The structure of the city government can influence the council's power and, consequently, its pay. In systems where the council holds more legislative and administrative authority, compensation may be higher.
- City Budget: Ultimately, a city can only pay what it can afford. The size of the city's tax base and its overall economic health are the ultimate foundation for all municipal salaries.
### Area of Specialization (Committee Leadership)
In a municipal context, "specialization" translates to leadership on key council committees. Chairing a powerful committee like Budget & Finance, Public Safety, or Land Use & Zoning requires deep subject matter expertise and significant time commitment. In many cities, these chairmanships come with an additional stipend to compensate for the expanded workload, directly increasing a member's total earnings.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups city council members under the broader category of "Legislators." The number of these positions is relatively fixed, as a city or state has a set number of legislative seats.
The BLS projects little to no change in the overall employment of legislators from 2022 to 2032. However, this statistic doesn't reflect the reality of opportunities. Openings arise consistently due to term limits, retirements, and incumbents being defeated in elections. Therefore, while the number of jobs isn't growing, turnover ensures that opportunities for new candidates are always present. Competition for these roles, especially in well-compensated, full-time positions, is typically very high.
Conclusion

Pursuing a role on a city council is a decision driven by a passion for public service and community improvement. While the financial compensation can be substantial in large cities, it is often modest in smaller communities.
Key Takeaways:
- Salary is Hyper-Local: A council member's salary is determined almost entirely by the size, wealth, and governance structure of the city they serve.
- It's a Spectrum: The role can be a part-time volunteer position with a small stipend or a full-time, high-stakes career with a six-figure salary.
- Impact is the Real Reward: Regardless of pay, the true value of the role lies in the ability to enact meaningful change and improve the lives of your fellow residents.
For anyone considering this path, research your specific municipality's charter and compensation structure. Understand that while the salary varies, the opportunity to lead and serve your community is a constant and profound reward.