When you think of trusted television personalities in major media markets, names like Dallas Raines often come to mind. As the long-serving Chief Meteorologist for KABC-TV in Los Angeles, he has become a household name, known for his expertise and engaging on-air presence. This prominence naturally leads to questions about his compensation.
While the exact salary of a specific individual is private, industry data allows us to build a comprehensive picture. A top-tier Chief Meteorologist in a major market like Los Angeles can command an impressive salary, often ranging from $200,000 to over $800,000 annually. This article will break down the salary expectations for a meteorologist, the factors that drive these high earnings, and the career path required to reach such a level.
What Does a Chief Meteorologist Like Dallas Raines Do?
The role of a Chief Meteorologist extends far beyond simply pointing at a map and predicting rain. It is a senior-level position that blends science, communication, and leadership.
A Chief Meteorologist is responsible for:
- Leading a Weather Team: They manage and mentor a team of other meteorologists and weather producers at the station.
- Advanced Data Analysis: They interpret complex meteorological data from satellites, radar, and weather models to create accurate, localized forecasts.
- On-Air Presentation: They are the primary on-air weather anchor for the station's most-watched newscasts, responsible for clearly and effectively communicating weather information, especially during severe weather events.
- Brand Ambassadorship: As a highly visible figure, the Chief Meteorologist is a key face of the news station, participating in community events and building trust with the audience.
- Developing Graphics and Content: They work with production teams to create compelling and easy-to-understand weather graphics for television and digital platforms.
Essentially, they are the final authority on weather for the station and a trusted scientific expert for millions of viewers.
Average Meteorologist Salary
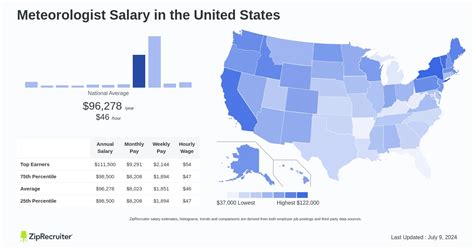
Salary potential in broadcast meteorology varies dramatically based on role and location. Dallas Raines represents the pinnacle of the profession, but the journey to that level involves starting in smaller roles and markets.
- Entry-Level Meteorologist (Small Market): Meteorologists starting their careers in smaller cities or on weekend shifts can expect to earn between $45,000 and $70,000.
- Mid-Career Meteorologist (Medium/Large Market): With several years of experience, a meteorologist in a mid-sized to large market might earn between $75,000 and $150,000.
- Chief Meteorologist (Major Market): For top talent like Dallas Raines in a major market (e.g., Los Angeles, New York, Chicago), the salary range widens significantly. According to data from salary aggregators like Salary.com and industry reports, a Chief Meteorologist's salary typically falls between $150,000 and $400,000+. The most famous and tenured personalities in the very top markets can push this figure even higher, into the $500,000 to $800,000+ range, which is where a figure like Dallas Raines is widely estimated to be.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for atmospheric scientists, including meteorologists, was $104,810 in May 2022. However, the BLS notes that broadcast announcers working in television can have vastly different pay scales, and this figure does not fully capture the high earning potential of top-tier on-air talent.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Reaching a six-figure salary as a meteorologist is not guaranteed. Several critical factors determine earning potential.
###
Level of Education & Certifications
A bachelor's degree in meteorology or atmospheric science is the standard requirement. However, to stand out and command a higher salary, many top professionals pursue advanced credentials. The most prestigious is the Certified Broadcast Meteorologist (CBM) designation from the American Meteorological Society (AMS). Earning a CBM seal demonstrates a high level of scientific competency and is often a prerequisite for lead roles in major markets.
###
Years of Experience & On-Air Presence
Experience is paramount. A broadcast meteorologist's career is built by moving up through progressively larger markets. A long and successful track record, like Dallas Raines' decades-long tenure at KABC-TV, builds credibility and trust, which is invaluable to a news station. Beyond experience, on-air "talent"—a combination of charisma, clarity, and trustworthiness—is a major X-factor that separates high earners from the rest.
###
Geographic Location (Market Size)
This is arguably the most significant factor in broadcast meteorology. Salaries are directly tied to the Nielsen Designated Market Area (DMA) or "market size." A meteorologist in Glendive, Montana (Market #210) will earn a fraction of what a meteorologist in Los Angeles (Market #2) earns. Larger markets have more viewers, which translates to higher advertising revenue for stations, allowing them to pay top dollar for premier talent.
###
Company Type (Station & Network Affiliation)
The station itself plays a huge role. A station owned and operated by a major network (like ABC, NBC, or CBS) in a top-10 market will have a much larger budget for talent than an independent station or a station in a smaller market. The Chief Meteorologist role at a flagship station is one of the highest-paid positions in the newsroom.
###
Area of Specialization & Role
Within a station, the Chief Meteorologist earns the most. Morning, weekend, and staff meteorologists have different responsibilities and correspondingly lower salaries. Furthermore, those who develop a reputation for specializing in critical areas—such as hurricane tracking in the Southeast or tornado analysis in the Midwest—can become regional experts, increasing their value and earning potential.
Job Outlook

According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for atmospheric and space scientists is projected to grow 4 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
However, the outlook for broadcast meteorology is more nuanced. While the need for qualified meteorologists remains strong, especially with increasing severe weather events, the number of on-air positions is limited and highly competitive. The most coveted jobs—the Chief Meteorologist roles in top-20 markets—are exceptionally rare, with very low turnover.
Opportunities are also growing in the private sector, with meteorologists working in aviation, agriculture, energy, and climate risk consulting.
Conclusion

The career of a broadcast meteorologist can be both professionally and financially rewarding, and Dallas Raines' success exemplifies the peak of this profession. While his estimated salary is at the highest end of the spectrum, it serves as a powerful benchmark for what is possible.
For those aspiring to a similar path, the key takeaways are clear:
- Build a Strong Foundation: A degree in meteorology and professional certifications like the AMS CBM are essential.
- Climb the Market Ladder: Be prepared to start in smaller markets to gain invaluable on-air experience.
- Cultivate Your On-Air Presence: Your ability to communicate clearly and connect with an audience is just as important as your scientific knowledge.
- Recognize the Competition: The path to becoming a Chief Meteorologist in a major city is a highly competitive marathon, not a sprint.
For those with a passion for weather science and the charisma for communication, it is a challenging but ultimately achievable career with significant earning potential.
