Choosing a career in medicine is a significant commitment of time, energy, and finances. It is a path driven by a desire to heal and make a profound impact on people's lives. Beyond the intrinsic rewards, a career as a physician also offers substantial financial stability and earning potential. While the journey is long, the compensation often reflects the high level of skill, responsibility, and dedication required.
Physician salaries are not monolithic; they vary dramatically based on a number of critical factors. The average physician's salary in the United States comfortably exceeds $200,000 per year, but top specialists in high-demand fields can earn upwards of $600,000 or more. This guide will break down the complex landscape of physician compensation, exploring how specialty, location, experience, and other factors shape a doctor's earnings.
What Does a Physician Do?

At its core, a physician's role is to maintain and restore human health through the practice of medicine. Their responsibilities are vast and vary significantly by specialty, but generally include:
- Diagnosing Illnesses: Interviewing patients, taking detailed medical histories, conducting physical examinations, and ordering diagnostic tests.
- Developing Treatment Plans: Analyzing test results to create and implement personalized treatment strategies, which may include prescribing medication, performing procedures, or recommending lifestyle changes.
- Patient Care and Counseling: Providing ongoing care, monitoring patient progress, and educating patients and their families about health conditions, treatments, and preventive care.
- Collaboration: Working as part of a larger healthcare team, consulting with other specialists, and coordinating care to ensure the best possible patient outcomes.
From the fast-paced environment of an emergency room to the long-term patient relationships in primary care, a physician's daily work is intellectually stimulating, demanding, and deeply impactful.
Average Physician Salary
When discussing physician salaries, it's essential to look at multiple sources to get a complete picture. Government data provides a solid baseline, while industry reports offer a more detailed look at compensation, including bonuses and incentives.
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that the median annual wage for physicians and surgeons was $229,300 as of May 2022. This figure represents the midpoint, with half of all physicians earning more and half earning less.
- Industry-specific reports, which often survey physicians directly and include production bonuses and other incentives, show significantly higher averages. The Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 found that the average overall physician compensation (for both primary care and specialists) was $352,000.
A typical salary range for a physician in the United States spans from approximately $180,000 for early-career primary care doctors in lower-paying regions to over $700,000 for experienced, top-earning specialists in private practice.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Compensation is not a single number but a spectrum. Several key variables determine where a physician will fall on this spectrum.
### Level of Education
All physicians must complete a four-year undergraduate degree, followed by four years of medical school to earn either a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree. While the type of medical degree itself has a negligible impact on salary, the subsequent training—residency and fellowships—is the most critical educational factor.
- Residency: This hands-on training lasts from three to seven years, and its length and focus directly correlate with earning potential. A three-year residency in Family Medicine or Pediatrics leads to a different salary outcome than a five-year Orthopedic Surgery residency.
- Fellowship: This is an optional, additional one to three years of highly specialized training after residency. A cardiologist who completes fellowships in interventional cardiology or electrophysiology, for example, will have a significantly higher earning potential than a general cardiologist.
### Years of Experience
Like most professions, compensation for physicians increases with experience. Early in their careers, physicians are focused on establishing their practice and building a patient base. As they become more efficient and their reputation grows, so does their income. According to Payscale, an entry-level physician earns about 8% less than the national average, while a late-career physician (with over 20 years of experience) can earn 15% or more above the average. This growth is especially pronounced for physicians who become partners in a private practice.
### Geographic Location
Where you practice medicine matters immensely. This variation is driven by supply and demand; rural and underserved areas often offer higher salaries and significant loan repayment incentives to attract qualified physicians.
According to the Doximity 2023 Physician Compensation Report, the metropolitan areas with the highest average physician compensation include:
1. Charlotte, NC: $430,890
2. St. Louis, MO: $426,370
3. Oklahoma City, OK: $425,097
Conversely, metropolitan areas with historically higher concentrations of physicians and academic centers, often on the coasts, may have lower average salaries (though this is often offset by a higher cost of living). Examples include Washington, D.C., Boston, MA, and Baltimore, MD.
### Practice Setting / Employer Type
The type of organization a physician works for is a major determinant of their salary and overall compensation package.
- Physician-Owned Private Practice: Offers the highest earning potential, as physicians can become partners and share in the profits. However, this model also comes with the greatest financial risk and administrative burden.
- Hospital or Healthcare System: This is the most common employment model today. It provides a stable, predictable salary, robust benefits, and relief from administrative tasks like billing and staffing.
- Academic Medical Center: Salaries in academic medicine are often lower than in private practice. However, this is compensated by benefits such as teaching opportunities, research funding, prestige, and often better work-life balance.
- Government: Physicians working for government entities like the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) or public health services typically earn less than their private-sector counterparts but receive excellent benefits, job security, and a pension.
### Area of Specialization
This is arguably the single most significant factor influencing a physician's salary. The gap between procedural, surgery-based specialties and cognitive, primary-care-based specialties can be substantial.
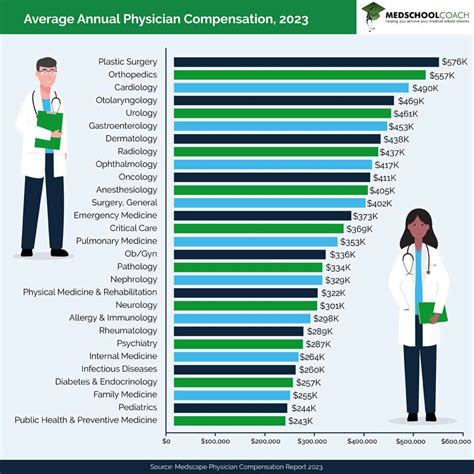
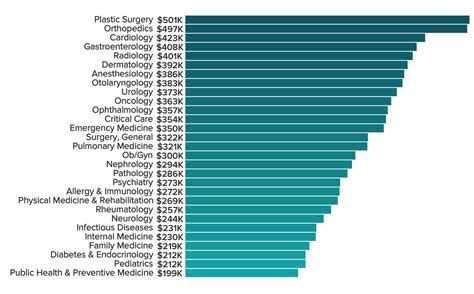
The following data from the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 highlights the vast differences in average annual compensation:
#### Top-Earning Physician Specialties
1. Plastic Surgery: $619,000
2. Orthopedics: $573,000
3. Cardiology: $507,000
4. Urology: $506,000
5. Gastroenterology: $501,000
6. Otolaryngology (ENT): $485,000
7. Radiology: $483,000
8. Oncology: $463,000
9. Anesthesiology: $448,000
10. Dermatology: $443,000
#### Lower (But Still High-Earning) Physician Specialties
1. Internal Medicine: $273,000
2. Family Medicine: $255,000
3. Pediatrics: $251,000
4. Public Health & Preventive Medicine: $249,000
It is crucial to note that while these fields are on the lower end of the physician salary spectrum, they still represent highly lucrative and rewarding careers.
Job Outlook

The demand for physicians and surgeons remains strong and is projected to grow. According to the BLS, employment for this profession is projected to grow 3 percent from 2022 to 2032.
This steady growth is fueled by several factors, including the nation's growing and aging population, which will require more medical care, and the projected retirement of a significant number of practicing physicians. The BLS anticipates that this will result in about 24,700 openings for physicians and surgeons each year, on average, over the decade. This ensures a high degree of job security for those entering the medical field.
Conclusion

A career in medicine is a noble and challenging pursuit that offers immense personal and financial rewards. While the overall average salary for physicians is high, actual earnings are a product of personal and professional choices. The path you choose—from your specialty and the years you dedicate to fellowship training to where you decide to practice—will fundamentally shape your career and compensation.
For prospective medical students and residents, it is vital to balance passion and interest with a clear understanding of the financial landscape. By carefully considering these factors, you can build a career that is not only emotionally fulfilling and intellectually stimulating but also financially secure and prosperous.