Nursing is a career defined by compassion, skill, and immense professional opportunity. It's also a field with significant earning potential. As of 2023, the median salary for Registered Nurses (RNs) stands at an impressive $86,070 per year, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. However, one of the most common questions aspiring nurses ask is: "How much more will I make with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)?"
The answer is crucial for anyone planning their educational and professional future. While both an Associate's Degree in Nursing (ADN) and a BSN can lead to an RN license, the BSN is increasingly becoming the key that unlocks higher salaries, greater responsibilities, and advanced career paths. This article will break down the salary differences, the factors that influence your pay, and the long-term value of investing in your nursing education.
What Does a Registered Nurse (RN) Do?

A Registered Nurse is a licensed healthcare professional who provides and coordinates patient care, educates patients and the public about various health conditions, and offers emotional support to patients and their families. Their responsibilities are both broad and critical, including:
- Assessing patient conditions and recording medical histories and symptoms.
- Administering medications and treatments.
- Developing and implementing patient care plans.
- Operating and monitoring medical equipment.
- Collaborating with a team of doctors, specialists, and other healthcare professionals.
- Educating patients and their families on managing illness or injury.
While these core duties are shared by all RNs, the complexity of these tasks and the level of autonomy can vary significantly based on education, experience, and work setting.
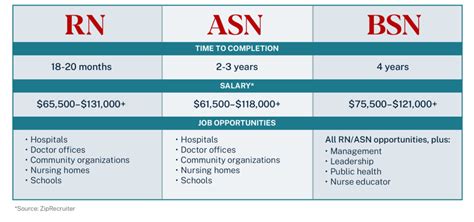
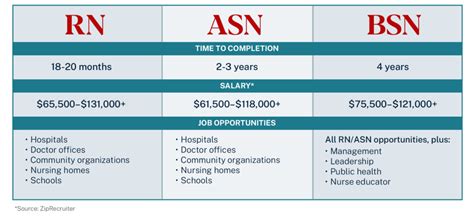
Average RN Salary: The ADN vs. BSN Difference
To understand the salary landscape, it's essential to first look at the overall picture and then drill down into the impact of education.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports the median annual wage for all Registered Nurses was $86,070 in May 2023. The salary range is wide, with the lowest 10 percent earning less than $63,720 and the highest 10 percent earning more than $132,680.
This figure includes RNs with all levels of education. When we isolate for the degree, the financial benefit of a BSN becomes clear. While the BLS doesn't separate salary data by degree type, salary aggregators that collect real-world data provide valuable insight:
- Payscale reports that as of late 2023, an RN with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) earns an average salary of approximately $93,000 per year.
- In contrast, an RN with an Associate's Degree in Nursing (ADN) earns an average of around $76,000 per year.
This reflects an average salary premium of $17,000 per year for BSN-prepared nurses—a significant difference that can amount to hundreds of thousands of dollars over a career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your degree is a foundational factor, but it's not the only variable that determines your paycheck. Several key elements combine to shape your earning potential as an RN.
### Level of Education
This is the central point of the "RN vs. BSN" salary debate. A BSN degree typically commands a higher salary for several reasons. BSN programs provide a more in-depth education in areas like evidence-based practice, community health, nursing theory, and leadership. This advanced training makes BSN-prepared nurses more valuable to employers, especially in complex healthcare settings.
Furthermore, many top-tier hospitals and healthcare systems, particularly those seeking or holding Magnet Recognition from the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), are required to have a higher percentage of BSN-prepared nurses on staff. This high demand directly translates to higher starting salaries and better opportunities for BSN graduates. A BSN is also the required stepping stone for pursuing even higher-paying advanced practice roles, such as Nurse Practitioner (NP), Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS), or Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA).
### Years of Experience
Experience is a powerful driver of salary growth in nursing. As you gain clinical skills, confidence, and specialized knowledge, your value to an employer increases.
- Entry-Level RN (0-1 year): An RN with little to no experience can expect to earn closer to the lower end of the salary range, though this is still competitive.
- Mid-Career RN (5-9 years): With solid experience, nurses can see a significant jump in their earnings and may take on charge nurse or preceptor roles.
- Experienced RN (10-20+ years): Senior nurses with decades of experience, particularly those with specialized certifications, command the highest salaries in non-management clinical roles. Payscale data shows an experienced RN with over 20 years of experience can earn well over the average, often approaching or exceeding six figures depending on other factors.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Nursing salaries vary dramatically by state and even by metropolitan area due to differences in cost of living, demand, and union presence.
According to the BLS (May 2023 data), the top-paying states for Registered Nurses are:
1. California: $137,690
2. Hawaii: $119,710
3. Oregon: $110,060
4. Washington: $107,720
5. Alaska: $106,770
Conversely, states in the South and Midwest tend to have lower average salaries, though the cost of living in those areas is also significantly lower.
### Company Type
The type of facility where you work is another major factor. Nurses in fast-paced, high-acuity environments often earn more.
The BLS identifies the top-paying industries for RNs as:
- Nonscheduled Air Transportation: $112,630
- Pharmaceutical and Medicine Manufacturing: $105,990
- Federal Executive Branch (Government): $102,150
- Outpatient Care Centers: $97,340
- General Medical and Surgical Hospitals: $92,160
Working for a large, urban research hospital will typically pay more than a small, rural clinic or a nursing home.
### Area of Specialization
Generalizing about "nurse salary" is difficult because specialization has a massive impact. Gaining skills and certifications in a high-demand area can dramatically increase your earning potential.
Some of the most lucrative nursing specializations include:
- Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA): An advanced practice role with an average salary exceeding $200,000. Requires a master's or doctoral degree.
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Nurse: These nurses work in high-stakes environments and are compensated accordingly.
- Operating Room (OR) / Perioperative Nurse: A highly skilled role that often comes with higher pay and on-call stipends.
- Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) Nurse: Specializing in the care of newborns requires advanced skills and often yields higher pay.
- Nursing Informatics: This growing field combines nursing with information technology and is one of the highest-paying non-bedside roles, often requiring a BSN or higher.
Job Outlook

The future for Registered Nurses is incredibly bright. The BLS projects that employment for RNs will grow by 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth will result in about 177,400 openings for registered nurses each year, on average, over the decade. This demand is fueled by an aging population requiring more healthcare services, a retiring nursing workforce, and an increased emphasis on preventive care. This robust job market ensures strong job security and continued salary competitiveness for years to come.
Conclusion

Navigating the path to a nursing career involves important educational choices. While an ADN provides a faster route to becoming a licensed RN, the data clearly shows that a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is a powerful investment in your long-term financial and professional growth.
Key Takeaways:
- Clear Salary Advantage: On average, BSN-prepared nurses earn significantly more per year than their ADN-prepared counterparts.
- Greater Career Mobility: A BSN is the gateway to leadership, management, and high-paying advanced practice roles.
- Higher Demand: Top hospitals and healthcare systems, especially Magnet facilities, prefer or require a BSN, giving you a competitive edge in the job market.
- Strong Future: With a robust job outlook, nursing remains a secure and rewarding profession, and a BSN positions you to maximize its potential.
Whether you are just starting your journey or are an existing ADN-RN considering an RN-to-BSN program, understanding these salary dynamics is the first step toward building a successful and prosperous career in nursing.