Nursing is a cornerstone of the healthcare industry, offering a career path that is not only personally fulfilling but also financially rewarding and exceptionally stable. As you consider entering this dynamic field, one of the most common questions is about earning potential: What is the salary difference between a Registered Nurse (RN) with an Associate's Degree and one with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)?
While both paths lead to becoming a licensed RN, the choice of degree can have a significant impact on your career trajectory and, importantly, your salary. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for all Registered Nurses was $86,070 in May 2023. However, data from salary aggregators reveals that nurses with a BSN consistently out-earn their counterparts with an Associate's Degree.
This article provides a data-driven breakdown of the RN vs. BSN salary landscape, exploring the key factors that influence your earning potential in this vital profession.
What Does a Registered Nurse Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the role. A Registered Nurse, regardless of their degree, is a licensed healthcare professional responsible for a wide range of patient care duties. At the bedside, the day-to-day responsibilities of an RN with an Associate's Degree of Nursing (ADN) and an RN with a BSN can be very similar.
Core responsibilities include:
- Assessing patients' conditions and recording medical histories.
- Administering medications and treatments.
- Developing and implementing patient care plans.
- Operating and monitoring medical equipment.
- Educating patients and their families about health conditions.
- Collaborating with doctors and other healthcare professionals.
The primary difference is that a BSN curriculum provides a deeper education in areas like nursing theory, research, leadership, and public health. This advanced training is what opens the door to higher-level roles and, consequently, higher pay.
Average RN vs. BSN Salary
It's crucial to clarify a common point of confusion: "RN" is a license, not a degree. To become an RN, you must earn either an Associate's Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and then pass the NCLEX-RN licensure exam. The salary comparison, therefore, is between an ADN-prepared RN and a BSN-prepared RN.
While the BLS groups all RNs into a single category with a median pay of $86,070 per year, other sources show a clear financial advantage for BSN holders.
- According to a 2024 report from Payscale, RNs with an ADN earn an average base salary of approximately $77,000 per year.
- In contrast, RNs holding a BSN earn an average base salary of around $95,000 per year.
This represents a potential salary increase of nearly $18,000 annually for nurses who invest in a bachelor's degree. Salary ranges also reflect this gap. Data from Salary.com shows that the typical range for a Registered Nurse (Level I) is $68,665 to $88,299, but this can climb well over $100,000 for senior or specialized BSN-prepared nurses.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your degree is a significant factor, but it's not the only one. Several elements combine to determine your total earning potential as a nurse.
### Level of Education
As established, holding a BSN is one of the most direct ways to increase your salary. The reasoning goes beyond just the degree itself. Many leading healthcare institutions, particularly those with "Magnet" status—a prestigious designation for nursing excellence—have policies that require or strongly prefer BSN-prepared nurses.
The landmark 2010 Institute of Medicine report (now the National Academy of Medicine) recommended that 80% of the nursing workforce hold a BSN by 2020. This initiative has shifted hiring practices, making a BSN a prerequisite for many of the best-paying hospital jobs. Furthermore, a BSN is the gateway to management roles (like Nurse Manager or Clinical Lead) and is a mandatory stepping stone for pursuing even higher-paying Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) careers, such as Nurse Practitioner (NP) or Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA), where salaries can easily exceed $128,000 per year (BLS, 2023).
### Years of Experience
Experience pays. As you accumulate years of hands-on practice, develop clinical skills, and prove your reliability, your value to an employer increases.
- Entry-Level (0-1 year): An entry-level RN might start in the $65,000 to $75,000 range, depending on location and institution.
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): With solid experience, an RN can expect to earn closer to the national median and beyond, often in the $85,000 to $95,000 range.
- Experienced (10+ years): Senior nurses with extensive experience, especially those in specialized or leadership roles, can command salaries well over $100,000. Payscale notes that an experienced RN with 20+ years on the job can earn an average of $101,000 or more.
### Geographic Location
Where you work is arguably the single largest determinant of your salary. Nursing pay varies dramatically by state and even by metropolitan area, largely due to differences in cost of living, demand, and the presence of unions.
According to the BLS (May 2023 data), the top-paying states for Registered Nurses are:
1. California: $137,690 (Annual Mean Wage)
2. Hawaii: $129,590
3. Oregon: $115,440
4. Washington: $113,630
5. Alaska: $113,440
In contrast, states with a lower cost of living, such as South Dakota ($71,590) and Alabama ($71,830), have lower average nursing salaries.
### Company Type (Work Setting)
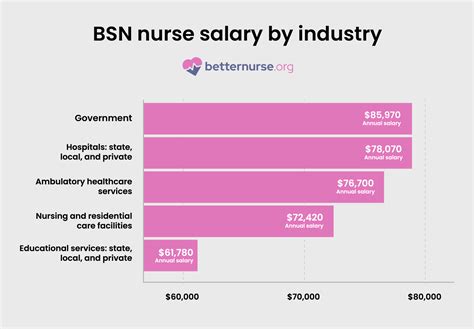
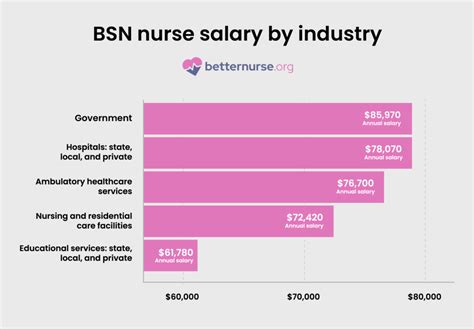
Your work environment also plays a role in compensation. The BLS reports salary variations across different healthcare settings for RNs:
- Outpatient Care Centers: $97,340 (Annual Mean Wage)
- General Medical and Surgical Hospitals: $95,270
- Government (Federal, State, and Local): $94,990
- Offices of Physicians: $80,180
- Educational Services (e.g., School Nurses): $73,340
Nurses in outpatient centers or specialized surgical hospitals often earn more due to the focused, high-skill nature of the work.
### Area of Specialization
Developing expertise in a high-demand specialty can significantly boost your income. BSN-prepared nurses are often better positioned to enter these fields. Certifications in these specialties can further increase pay.
Some of the higher-paying BSN-level specializations include:
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) / Critical Care: These nurses handle the most critically ill patients and are compensated for their high-level skills.
- Operating Room (OR) / Perioperative Nursing: Assisting in surgeries requires specialized knowledge and precision.
- Labor and Delivery: A consistently in-demand and well-compensated specialty.
- Nursing Informatics: This growing field combines nursing with information technology to manage health data, and Glassdoor reports average salaries around $103,000.
Job Outlook

The future for Registered Nurses is exceptionally bright. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment for RNs will grow by 6% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth translates to approximately 177,400 job openings for RNs each year, on average, over the decade. This demand is driven by an aging population, a greater focus on preventive care, and the need to replace a large number of nurses who are retiring. This robust demand ensures long-term job security for those entering the profession.
Conclusion

For anyone considering a career in nursing, the outlook is promising. While an ADN provides a fast and effective route to becoming a licensed RN, the data is clear: investing in a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is a strategic move for your financial future.
Key Takeaways:
- BSN Earns More: A BSN-prepared RN consistently earns a higher salary than an ADN-prepared RN, with the gap often reaching $15,000-$20,000 or more per year.
- BSN Opens Doors: A BSN is often required for jobs in top hospitals (especially Magnet facilities) and is essential for leadership, research, and public health roles.
- Multiple Factors at Play: Your ultimate salary will be a combination of your education, experience, geographic location, work setting, and specialty.
- A Secure Future: Nursing remains a high-demand, stable, and financially rewarding career path with strong projected growth.
Choosing to pursue a BSN is not just about a higher starting salary; it's an investment in a wider range of career opportunities and a lifetime of professional and financial growth.