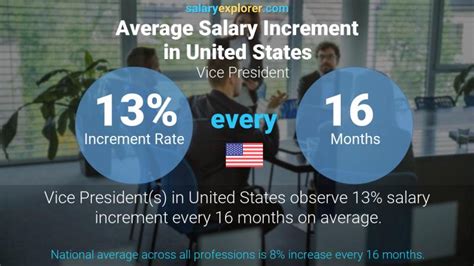
The title "Vice President" represents a significant milestone in a professional's career, signifying leadership, strategic influence, and substantial responsibility. Naturally, this level of seniority comes with significant financial rewards. A Vice President's salary in the United States typically lands well into the six figures, with total compensation packages often soaring higher thanks to bonuses, stock options, and other incentives.
If you have your sights set on the executive track, understanding the compensation landscape is a critical step. This guide breaks down the salary expectations for a Vice President, the key factors that influence earnings, and the career outlook for this prestigious role.
What Does a Vice President Do?

A corporate Vice President (VP) is a senior executive responsible for overseeing a specific department or function within an organization. While the President or C-suite executives (CEO, COO, CFO) set the overall company vision, VPs are the strategic leaders tasked with translating that vision into actionable plans for their respective areas.
Key responsibilities often include:
- Strategic Planning: Developing and executing long-term strategies for their department (e.g., marketing, sales, engineering, human resources).
- Leadership and Management: Leading large teams, mentoring directors and managers, and fostering a productive work culture.
- Budgetary Oversight: Creating, managing, and being accountable for the departmental budget.
- Performance Measurement: Setting key performance indicators (KPIs) and ensuring the department meets its goals.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Working closely with other VPs and executive leaders to ensure cohesive company operations.
- Reporting: Providing regular updates on departmental performance to the C-suite and board of directors.
Average Vice President Salary
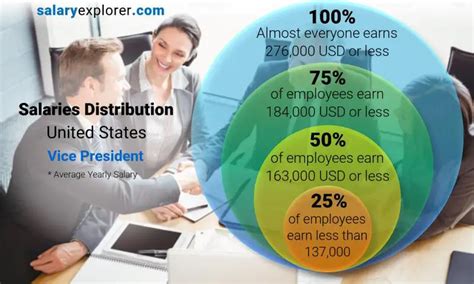
A Vice President's compensation is more than just a base salary; it's a comprehensive package. This package typically includes a base salary, annual bonuses, and, often, long-term incentives like stock options or profit sharing.
Here’s a look at what you can expect, based on data from leading salary aggregators:
- Median Base Salary: According to Salary.com, the median base salary for a Vice President in the United States is approximately $250,561 as of early 2024. The typical range falls between $190,443 and $328,958.
- Total Compensation: This figure is arguably more important for executive roles. Payscale reports an average base salary of around $165,000, but notes that with bonuses reaching up to $50,000 and profit sharing up to $35,000, the total pay package can be significantly higher.
- Glassdoor places the average total pay for a Vice President at $263,000 per year, combining an average base salary of around $179,000 with substantial additional pay from cash bonuses and stock options.
It's clear that while the base salary is robust, performance-based incentives make up a major portion of a VP's earnings.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your compensation as a VP isn't a single, fixed number. It's influenced by a dynamic interplay of your personal qualifications, your company's profile, and your specific role.
### Level of Education
While extensive experience is paramount for a VP role, education provides a crucial foundation. A bachelor's degree is typically the minimum requirement. However, a Master of Business Administration (MBA) or another advanced degree in a relevant field (e.g., finance, engineering) is highly common and often expected at this level. An MBA from a top-tier business school can not only increase earning potential but also provide the strategic framework and professional network necessary to excel in an executive position.
### Years of Experience
Experience is perhaps the single most significant factor. The path to a VP role is long and requires a proven track record of success.
- New VP (10-15 years of experience): A professional recently promoted to VP from a Director-level role will likely earn on the lower end of the salary spectrum.
- Experienced VP (15-20 years of experience): With several years in the role, a VP has a demonstrated ability to drive results, leading to higher base salaries and larger performance bonuses.
- Senior VP / Veteran (20+ years of experience): Senior Vice Presidents or those with decades of industry experience command the highest compensation packages, often with significant equity stakes in the company.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for VPs are significantly higher in major metropolitan areas with a high cost of living and a high concentration of corporate headquarters.
According to data from salary calculators like Salary.com, a VP working in San Francisco, CA, or New York, NY, can expect to earn 20-35% more than the national average. Conversely, salaries in smaller cities or regions with a lower cost of living will likely be closer to or slightly below the national median.
### Company Type
The size, industry, and structure of a company heavily impact executive pay.
- Company Size: A VP at a Fortune 500 company will almost always earn more in base salary and have a more structured bonus plan than a VP at a small to medium-sized business (SMB).
- Public vs. Private: VPs at publicly traded companies often receive a significant portion of their compensation in stock options or restricted stock units (RSUs), tying their earnings directly to the company's market performance. Private companies may offer profit sharing or equity that is less liquid.
- Startup vs. Established Company: A VP role at a startup might come with a lower base salary but offer a substantial equity stake, which could lead to a massive payday if the company is successful (e.g., through an IPO or acquisition). This is a high-risk, high-reward scenario.
### Area of Specialization
Not all VP roles are compensated equally. The department a VP leads directly impacts their earning potential, often based on its proximity to revenue generation and technical complexity.
- VP of Sales: Often among the highest-paid VPs, as their compensation is heavily tied to sales quotas and revenue generated.
- VP of Engineering / IT: In the tech industry, these roles command very high salaries due to the specialized technical skills and the critical importance of product development and infrastructure.
- VP of Marketing: Compensation is strong, especially for those who can demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI) for marketing campaigns.
- VP of Human Resources: While historically paid less than their revenue-facing counterparts, the increasing strategic importance of talent acquisition, retention, and culture has raised compensation for top HR executives.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups Vice Presidents under the category of "Top Executives." According to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook, employment for top executives is projected to grow 3 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
The BLS anticipates about 305,500 openings for top executives each year, on average, over the decade. While the growth isn't explosive, the demand for skilled, experienced, and effective leaders remains constant as companies navigate complex market dynamics. Competition for these positions is, and will remain, extremely intense.
Conclusion

Ascending to the rank of Vice President is a testament to years of hard work, proven leadership, and strategic acumen. The financial rewards reflect this high level of responsibility, with total compensation packages regularly exceeding a quarter of a million dollars.
For professionals aspiring to this level, the key takeaways are:
- Aim for Total Compensation: Focus not just on the base salary, but on the entire package, including bonuses and equity.
- Experience is King: Build a strong, quantifiable track record of success in your field.
- Specialize Wisely: Roles in sales, engineering, and other revenue-adjacent functions often offer the highest earning potential.
- Be Strategic About Location and Company: Your choice of where you work and for what type of company will have a major impact on your earnings.
The path to a VP position is a marathon, not a sprint. By continually developing your skills, delivering results, and building your professional network, you can position yourself to reach this rewarding and influential career peak.