South Korea, a global economic powerhouse known for its technological innovation and vibrant culture, presents a compelling landscape for ambitious professionals. From world-leading tech giants to a booming entertainment industry, the "Miracle on the Han River" offers dynamic career opportunities. But what can one expect to earn?
Navigating the salary landscape of a new country is a critical step in career planning. The average salary in South Korea is competitive, often ranging from ₩45,000,000 to ₩68,000,000 (approx. $33,000 to $50,000 USD) annually. However, this figure is just the starting point. Your actual earning potential is shaped by a unique blend of your background, industry, and strategic career choices.
This guide will break down the average salary in South Korea, explore the key factors that influence it, and provide an outlook on the job market to help you map your professional journey.
What Drives the South Korean Economy and Workforce?
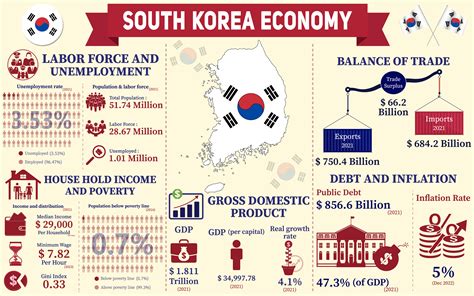
Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the context. The "average salary" in South Korea is a reflection of a highly dynamic, competitive, and sophisticated economy. The workforce is among the most educated in the world, with a strong emphasis on technology, manufacturing, and professional services.
Key industries that anchor the South Korean economy and offer high-paying jobs include:
- Technology & Semiconductors: Home to giants like Samsung and SK Hynix.
- Automotive & Heavy Industry: Dominated by global players like Hyundai and Kia.
- Finance & Banking: A robust sector centered in Seoul.
- Biotechnology & Healthcare: A rapidly growing field with significant government investment.
- Digital Content & Entertainment: The global force of K-pop, K-drama, and gaming.
A professional's role within these sectors, combined with the factors below, will ultimately determine their place on the salary spectrum.
Average Salary in South Korea

Determining a single average salary requires looking at data from multiple authoritative sources, as methodologies can differ.
According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the average annual wage in South Korea was USD 48,922 in 2022 (the latest full-year data). At a recent exchange rate (approx. 1,350 KRW to 1 USD), this translates to approximately ₩66,000,000 KRW per year. The OECD figure is a strong benchmark as it considers the total wages paid divided by the average number of employees.
Salary aggregator data, which often relies on user-submitted information, provides a slightly different but equally valuable perspective:
- Payscale reports an average base salary of ₩52,000,000 KRW per year (as of early 2024).
- Salary Expert, a subsidiary of ERI, indicates an average salary of ₩55,478,545 KRW per year.
Considering these sources, a realistic salary range for a professional in South Korea looks like this:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years' experience): ₩35,000,000 – ₩48,000,000
- Mid-Career (5-10 years' experience): ₩50,000,000 – ₩75,000,000
- Senior/Managerial Level (10+ years' experience): ₩80,000,000 – ₩120,000,000+
*Note: Salary data is subject to change, and currency conversions are approximate and fluctuate.*
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your individual earning potential can vary significantly from the national average. Here are the most critical factors that determine salary in South Korea.
###
Level of Education
South Korea is a society that places an immense value on education, and this is directly reflected in compensation. A higher level of education from a prestigious university is a powerful salary driver.
- Bachelor's Degree: This is typically the minimum requirement for most professional (or "white-collar") jobs.
- Master's Degree/PhD: Holding an advanced degree, particularly in a specialized field like AI, engineering, or finance, can lead to significantly higher starting salaries and faster career progression. Graduates from top-tier "SKY" universities (Seoul National University, Korea University, and Yonsei University) often command the highest starting offers.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is a universal factor, but it has a unique weight in South Korea. While Western companies have largely moved to performance-based pay, many traditional Korean companies still incorporate elements of a seniority-based pay system (*hobongje*, 호봉제).
- Entry-Level (0-3 Years): Professionals are focused on learning and proving their value. Salaries are at their lowest point but can increase steadily with proven performance.
- Mid-Career (4-9 Years): With demonstrable expertise and a track record of success, professionals can expect significant salary jumps, either through promotions or by moving to a competitor.
- Senior Level (10+ Years): These professionals are valued for their deep industry knowledge, leadership skills, and strategic insight. They command the highest salaries and often hold managerial or executive titles.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work in South Korea has a massive impact on your salary and cost of living. The country's economy is highly centralized.
- Seoul Capital Area (Seoul, Gyeonggi, Incheon): This region is the undisputed economic, political, and cultural hub. It hosts the headquarters of nearly all major corporations and offers the highest salaries in the country—often 10-25% higher than in other regions. However, it also has the highest cost of living.
- Other Major Metropolitan Cities (Busan, Daegu, Daejeon): These cities have strong regional economies, particularly in manufacturing, logistics (Busan), and R&D (Daejeon). Salaries are competitive but generally lower than in Seoul.
- Rural Areas: Salaries are significantly lower in rural provinces, reflecting the concentration of agricultural and smaller-scale industrial jobs.
###
Company Type
The type of company you work for is arguably one of the most significant factors in determining your compensation package.
- Chaebols (재벌): These family-owned industrial conglomerates (e.g., Samsung, Hyundai, LG, SK Group) are the most coveted employers. They are known for offering the highest salaries, exceptional benefits, bonuses, and unparalleled job security.
- Foreign/Multinational Corporations (MNCs): International companies often offer salaries competitive with Chaebols to attract top talent. They may also provide a more performance-oriented culture and better work-life balance, appealing to many professionals.
- Public/State-Owned Corporations: Jobs in this sector are known for extreme stability and excellent pensions, though salaries may not reach the highest peaks seen at top Chaebols.
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs / 중소기업): SMEs are the backbone of the Korean economy, employing the majority of the workforce. However, salaries and benefits are typically lower than at larger corporations.
- Startups: The startup scene is vibrant, especially in tech. Salaries can be highly variable. Some may offer lower base pay but compensate with stock options, offering high-risk, high-reward potential.
###
Area of Specialization
As in any country, your industry and specific role are paramount. In-demand skills command premium salaries.
- Top-Tier Fields:
- IT/Software Engineering (AI, Cloud, Cybersecurity): ₩60M - ₩120M+
- Finance (Investment Banking, Asset Management): ₩70M - ₩150M+
- Semiconductor Engineering: ₩65M - ₩130M+
- Management Consulting: ₩70M - ₩140M+
- Strong, Competitive Fields:
- Marketing & Sales (at major brands): ₩50M - ₩90M
- Automotive Engineering: ₩55M - ₩100M
- Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals: ₩50M - ₩95M
- Standard Fields:
- Human Resources & Administration: ₩40M - ₩70M
- Education: ₩40M - ₩65M
*(Salary ranges are approximate and vary based on experience and company type).*
Job Outlook

The economic and job market outlook for South Korea is stable, with projected modest growth. While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not cover South Korea, reports from the Bank of Korea and the IMF highlight key trends.
The nation faces challenges like an aging population and intense competition for desirable "good" jobs. However, the government is actively fostering growth in future-oriented industries. The strongest job prospects are in:
- Digital Transformation: AI specialists, data scientists, and cloud engineers are in extremely high demand.
- Green Energy: Roles related to renewable energy, battery technology, and sustainable development are expanding.
- Advanced Technology: The national focus on dominating the global semiconductor market ensures continued demand for skilled engineers.
- Healthcare & Biotech: An aging population and a focus on R&D create a robust job market for healthcare professionals and researchers.
Conclusion

South Korea offers a challenging yet highly rewarding professional environment. While the national average salary provides a useful benchmark, your personal earning potential is a story you write yourself. The key takeaways for any professional considering a career in South Korea are clear:
- Aim for High-Growth Industries: Focus on technology, finance, and specialized engineering sectors where demand outstrips supply.
- Location Matters: Target the Seoul Capital Area for the highest earning potential, but be prepared for a higher cost of living.
- Company Choice is Crucial: Aiming for a position at a Chaebol or a leading multinational corporation will put you in the top salary bracket.
- Never Stop Learning: Continuous upskilling and a potential advanced degree are powerful levers for salary negotiation and career advancement in a highly educated society.
For those with the right skills, ambition, and understanding of the market, South Korea is more than just a place to work—it's a place to build a prosperous and globally competitive career.
