Climbing the corporate ladder to a Vice President (VP) position is a significant career milestone, representing a pinnacle of leadership, strategic influence, and, consequently, substantial financial reward. For professionals aiming for the executive suite, the role offers a compelling compensation package, with average total earnings often soaring well into the six-figure range and frequently exceeding $300,000 annually.
This guide will break down the complexities of a Vice President's salary in the United States, exploring the core responsibilities of the role, the key factors that dictate earning potential, and the future job outlook for this esteemed position.
*(Note: This article focuses on the corporate title of "Vice President" within companies in the United States. For those curious about the Vice President of the United States of America, that is a singular, publicly-funded role with a salary set by Congress. As of 2024, the salary for the Vice President of the USA is $235,100 per year.)*
What Does a Corporate Vice President Do?
A Corporate Vice President is a senior executive responsible for the management and strategic direction of a specific department or business unit. They act as a critical link between the C-suite (CEO, COO, CFO) and the senior management who handle day-to-day operations.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Strategic Planning: Developing and executing long-term strategies for their department that align with the company's overall goals.
- Leadership and Management: Leading large teams, mentoring senior managers, and fostering a productive and innovative culture.
- Budgetary Oversight: Managing significant departmental budgets, ensuring financial accountability, and driving profitability.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Working closely with other VPs and executive leaders to ensure cohesive business operations.
- Reporting: Presenting performance reports, strategic plans, and financial results to the C-suite and board of directors.
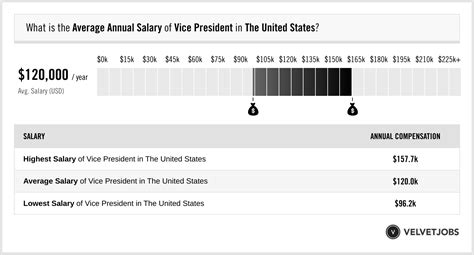
Average Vice President Salary in America
The compensation for a Vice President is multifaceted, often composed of a base salary, annual bonuses, and long-term incentives like stock options.
According to Salary.com, the median base salary for a Vice President in the United States is approximately $250,977 as of early 2024. However, the typical base salary range is broad, usually falling between $190,000 and $330,000.
It is crucial to look beyond the base salary. When including bonuses, profit sharing, and stock awards, the total compensation package is significantly higher. Data from Payscale shows that total pay can range from $120,000 to over $350,000, with bonuses alone potentially adding tens of thousands of dollars to the annual income. For VPs at large, publicly traded companies, total compensation can easily reach or exceed $500,000.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

A Vice President's salary is not a one-size-fits-all figure. It is influenced by a combination of personal qualifications and company characteristics.
### Level of Education
While a bachelor's degree is a baseline requirement, an advanced degree can significantly impact both the path to a VP role and the compensation offered. A Master of Business Administration (MBA) is particularly valuable. It equips leaders with a holistic understanding of business functions—from finance to marketing—and provides access to a powerful professional network. Employers often view an MBA from a top-tier business school as a signal of high potential, justifying a premium salary.
### Years of Experience
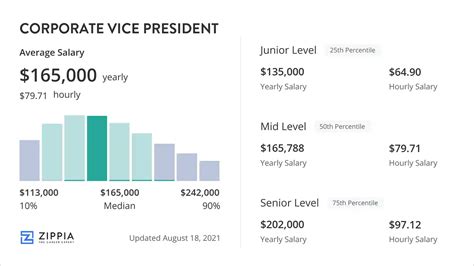
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of a VP's salary. A newly promoted Vice President with 10-15 years of professional experience will earn less than a seasoned VP with over 20 years of experience who has a proven track record of driving growth and managing complex business units. Salary platforms often show a clear progression:
- Entry-Level VP (or new to the role): Closer to the $190,000 - $220,000 base range.
- Mid-Career VP: Aligns with the median, around $250,000 base.
- Senior/Experienced VP: Can command a base salary well over $300,000, with total compensation packages being substantially higher.
### Geographic Location
Where a company is located plays a major role in salary due to variations in cost of living and the concentration of high-paying industries. VPs working in major metropolitan hubs with competitive markets command the highest salaries.
According to Salary.com data, cities like San Francisco, New York City, Boston, and Los Angeles often pay 15-30% above the national average. In contrast, VPs in smaller cities or regions with a lower cost of living may see salaries closer to the lower end of the national range.
### Company Type
The size, revenue, and industry of a company heavily influence executive pay.
- Fortune 500 vs. Startup: A VP at a large, multinational corporation (e.g., Microsoft, Johnson & Johnson) will almost certainly have a higher base salary and more structured bonus and stock plans than a VP at a mid-stage startup. However, a VP at a successful startup may have significant equity (stock options) that could result in a massive payout upon an IPO or acquisition.
- Public vs. Private: Public companies often offer more lucrative compensation packages, including Restricted Stock Units (RSUs), due to greater revenue and shareholder pressure to attract top talent.
- Industry: VPs in high-growth, high-revenue sectors like Technology, Pharmaceuticals, and Financial Services typically earn more than those in non-profit or public administration sectors.
### Area of Specialization
Not all Vice President roles are compensated equally. The specific function a VP leads has a direct impact on their market value.
- VP of Sales / Business Development: These roles are directly tied to revenue generation. Compensation is often heavily performance-based, with large bonuses tied to meeting sales targets. This makes it one of the most lucrative VP positions.
- VP of Engineering / Technology: In the tech-driven economy, technical leadership is in high demand. VPs who can lead complex engineering teams and drive innovation command premium salaries.
- VP of Marketing: Responsible for brand growth and market penetration, these VPs can also earn substantial salaries, particularly in consumer-facing industries.
- VP of Human Resources / Operations: While critical to the business, these are often seen as cost-center roles. While still highly compensated, their average salary may be slightly less than their revenue-generating counterparts.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects the employment of Top Executives to grow by 3 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
While the overall growth is stable, the BLS notes that competition for these senior positions will be intense. The number of qualified applicants will far exceed the number of available openings. Candidates with extensive managerial experience, advanced degrees, and a strong track record of success within their industry will have the best prospects.
Conclusion

Pursuing a career as a Vice President in America is a challenging but highly rewarding journey. It demands strategic vision, strong leadership skills, and years of dedicated experience. In return, it offers a position of significant influence and a compensation package that reflects that responsibility, with total earnings often reaching well into the $300,000 to $500,000+ range.
For aspiring leaders, the key takeaways are clear:
- Aim for Total Compensation: Focus on the entire package, including bonuses and equity, not just the base salary.
- Invest in Education and Experience: An MBA and a proven track record are powerful differentiators.
- Be Strategic About Industry and Location: Your choice of industry and geographic location can dramatically impact your earning potential.
Ultimately, the path to the VP office is a marathon, not a sprint. By building a strong foundation of skills and making strategic career choices, you can position yourself for a successful and financially rewarding executive career.