You’ve navigated the interviews, impressed the hiring manager, and received a fantastic job offer. The annual salary meets your expectations, and the benefits look great. But as you scan the details, you see a small but crucial phrase: "pay frequency: bi-weekly." What exactly does that mean for your bank account and your budget?
Understanding how and when you get paid is just as important as knowing your total annual compensation. A bi-weekly pay schedule is the most common in the United States, but it's often confused with other pay frequencies, leading to financial surprises. This guide will break down everything you need to know about a bi-weekly salary, how it's calculated, and how it compares to other models, empowering you to manage your finances with confidence.
What Does "Bi-Weekly Salary" Mean?
In the simplest terms, a bi-weekly salary means you are paid once every two weeks. These paydays typically fall on the same day of the week, such as every other Friday.
Because there are 52 weeks in a year, a bi-weekly pay schedule results in 26 paychecks per year.
This is the most critical detail. The 26-paycheck model has a unique effect on monthly budgeting. Most months, you will receive two paychecks. However, twice a year, you will have a month with three paychecks. For professionals who budget carefully, these "extra" paychecks can provide a significant financial boost, perfect for paying down debt, boosting savings, or covering a large expense.
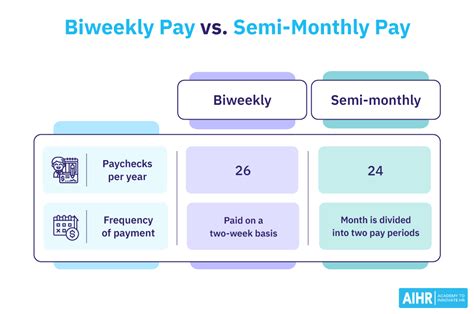
The Critical Difference: Bi-Weekly vs. Semi-Monthly

The most common point of confusion is the difference between being paid bi-weekly and semi-monthly. While they sound similar, they are fundamentally different and impact your cash flow.
| Feature | Bi-Weekly Pay | Semi-Monthly Pay |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Paychecks per Year | 26 | 24 |
| Payment Schedule | Every two weeks (e.g., every other Friday) | Twice per month (e.g., the 15th and 30th) |
| Payday Consistency| Payday is always on the same day of the week. | Payday dates are consistent, but the day of the week changes. If a payday falls on a weekend, it's usually paid the Friday before. |
| Gross Paycheck Amount| Slightly smaller per check (Annual Salary / 26) | Slightly larger per check (Annual Salary / 24) |
| "Bonus" Paychecks | Two months of the year will have three paychecks. | Every month has exactly two paychecks. No "bonus" checks. |
How to Calculate Your Bi-Weekly Gross Pay
Calculating your gross pay (your earnings before any taxes or deductions) on a bi-weekly schedule is straightforward.
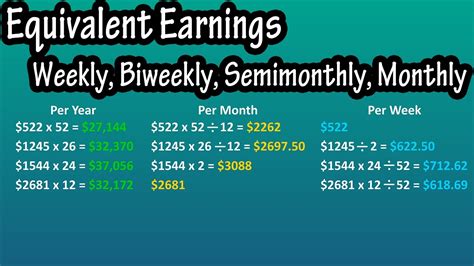
Formula: `Annual Salary / 26 = Gross Bi-Weekly Pay`
Let's use a real-world example. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median usual weekly earnings for full-time wage and salary workers was $1,145 in the fourth quarter of 2023. This equates to an approximate annual salary of $59,540.
Calculation Example:
- Annual Salary: $59,540
- Calculation: $59,540 / 26
- Gross Bi-Weekly Pay: $2,290
This $2,290 is your gross pay. Your net pay, or take-home pay, will be lower after federal and state taxes, Social Security, Medicare, 401(k) contributions, and health insurance premiums are deducted.
Key Factors That Influence Your Salary

While "bi-weekly" describes *how* you're paid, your actual annual salary—the number used in the calculation—is determined by several key factors. Understanding these can help you maximize your earning potential.
###
Level of Education
Generally, higher educational attainment correlates with higher earnings. According to BLS data from 2022, individuals with a bachelor's degree had median weekly earnings of $1,432, while those with only a high school diploma earned a median of $853. Advanced degrees, like a master's or doctorate, push these earnings even higher.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary. An entry-level employee will earn considerably less than a senior-level professional with a decade of proven results. Salary aggregators reflect this clearly. For example, a role like "Software Engineer" on Salary.com shows a typical range from around $70,000 for an entry-level position to over $130,000 for a senior-level one, based on experience.
###
Geographic Location
Where you live and work dramatically impacts your salary due to variations in cost of living and local demand for skills. A marketing manager in San Francisco or New York City will command a much higher salary than one in Omaha, Nebraska, to compensate for the higher housing, tax, and living expenses.
###
Company Type & Industry
The size, type, and industry of your employer are major factors. A large tech company or a major financial firm will typically offer higher salaries than a small non-profit or a local retail business for the same role. High-margin industries like technology, pharmaceuticals, and finance often have a greater capacity for higher compensation.
###
Area of Specialization
Within any given profession, certain specializations are more in-demand and thus pay more. A general practice physician earns less than a specialized surgeon. In IT, a cybersecurity analyst with expertise in cloud security will likely earn more than a general IT support specialist. Keeping your skills current and aligned with high-demand specializations is key to increasing your value.
How Common is Bi-Weekly Pay?
A bi-weekly pay schedule is not just a random choice; it's the dominant method of payment in the United States.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics' National Compensation Survey (March 2023), bi-weekly pay is the most common pay frequency. The data shows:
- 45.8% of U.S. workers are paid bi-weekly.
- 34.3% are paid weekly.
- 17.9% are paid semi-monthly.
This prevalence is largely due to the ease of payroll administration. Since overtime for non-exempt employees is calculated based on a 7-day workweek, a bi-weekly (two-week) pay period simplifies these calculations compared to a semi-monthly schedule.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Your Career

Understanding the term "bi-weekly salary" is a fundamental piece of financial literacy for any professional. It's more than just jargon on an offer letter—it dictates the rhythm of your financial life.
Here are the essential takeaways:
- Bi-Weekly Means 26 Paychecks: You get paid every two weeks, resulting in 26 pay periods per year.
- It Is Not Semi-Monthly: Don't confuse it with a semi-monthly (24 paychecks) schedule, as your individual paycheck amount will be different.
- Budget for the "Extra" Paychecks: Twice a year, you'll receive three paychecks in a month. Plan ahead to use this "bonus" income wisely to achieve your financial goals.
- Always Clarify: When you receive a job offer, never hesitate to ask an HR representative to confirm the pay frequency and the date of the first payday.
By understanding the mechanics of your pay, you can build a more stable and predictable budget, enabling you to focus on what truly matters: growing your career and achieving your long-term goals.