Japan, the world's fourth-largest economy, offers a unique blend of rich cultural heritage and cutting-edge technological innovation. For professionals considering a move or starting their careers here, understanding the earning potential is a critical first step. While the average salary provides a useful benchmark, your actual income can vary significantly. This guide will break down the average salary in Japan and explore the key factors that will shape your compensation.
Understanding the Japanese Salary Landscape
Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the structure of compensation in Japan. Unlike the straightforward monthly or bi-weekly salaries common in many Western countries, Japanese compensation is often composed of a base salary plus significant bonuses.
These bonuses are typically paid twice a year (summer and winter) and can equal several months' worth of salary. Therefore, when discussing annual income, it's crucial to consider the total package. Furthermore, the traditional concept of _nenkō joretsu_ (年功序列), or seniority-based wages, still influences many traditional companies, meaning salary often increases steadily with tenure at a single company. However, this is changing, with more companies, especially foreign firms, adopting a merit-based pay system.
Average Salary in Japan
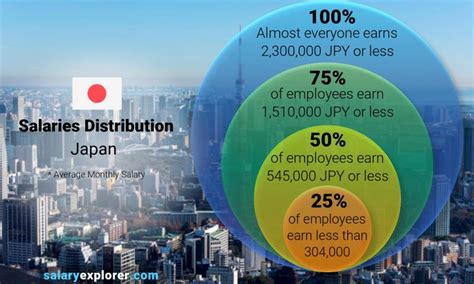
So, what can you expect to earn? According to the latest data from Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) in its "Basic Survey on Wage Structure," the average monthly salary is approximately ¥318,300. When factoring in bonuses, the average annual salary for a full-time worker is approximately ¥5 to ¥5.5 million.
Converting this to US dollars can be illustrative, but it's important to remember that exchange rates fluctuate and the cost of living differs. As of mid-2024, this translates to roughly $32,000 to $35,500 USD per year.
However, this is a national average across all industries, ages, and roles. Salary aggregators provide a slightly different, often higher, picture which may better reflect the white-collar professional roles they survey:
- Payscale reports an average base salary of ¥4.98 million per year.
- Glassdoor shows a national average salary of ¥5.3 million per year.
A realistic salary range for a professional in Japan might look like this:
- Entry-Level (0-3 years experience): ¥3.0 million - ¥4.5 million
- Mid-Career (5-10 years experience): ¥5.0 million - ¥8.0 million
- Senior/Managerial Level (10+ years): ¥8.0 million - ¥15+ million
Key Factors That Influence Salary in Japan

Your personal earnings will depend on a combination of factors. This section breaks down the most significant influencers on your potential salary in Japan.
###
Level of Education
Education plays a foundational role in determining starting salaries. Japanese companies place a high value on university degrees, especially from prestigious institutions. A candidate with a bachelor's degree from a well-regarded university will typically receive a higher starting salary than one without. Furthermore, professionals with a Master's degree, MBA, or Ph.D., particularly in technical or specialized fields, can command significantly higher compensation packages.
###
Years of Experience
As mentioned, the seniority-based wage system (_nenkō joretsu_) means experience is arguably one of the most powerful drivers of salary growth in Japan. New graduates (_shinsotsu_) all tend to start at a similar, relatively modest salary. However, with each year of loyal service, employees can expect steady, predictable raises. Professionals who switch jobs mid-career may be able to negotiate a higher salary based on their proven skills, but the culture still heavily rewards tenure and accumulated experience within a specific company or industry.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work in Japan has a massive impact on your salary and your cost of living. The Kanto region, which includes Tokyo, is the country's economic powerhouse and offers the highest salaries by a significant margin.
| City | Average Annual Salary (Approx.) | Notes |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Tokyo | ¥6.2 million | Highest salaries, but also the highest cost of living in Japan. |
| Osaka | ¥5.5 million | Japan's second-largest metropolitan area, offering competitive salaries. |
| Nagoya | ¥5.3 million | A major industrial and automotive hub with strong earning potential. |
| Fukuoka | ¥4.8 million | A rapidly growing tech hub with lower living costs than Tokyo. |
Professionals in Tokyo can expect to earn 20-30% more than their counterparts in smaller cities or rural prefectures, a premium that helps offset the city's high rent and living expenses.
###
Company Type & Size
The type and size of your employer are critical.
- Foreign Companies (_Gaishikei_): These firms often pay the highest salaries to attract top-tier, often bilingual, talent. They tend to follow a more performance-based compensation structure and may offer more competitive benefits packages compared to their Japanese counterparts.
- Large Japanese Corporations: Major domestic companies (_keiretsu_ like Mitsubishi, Sumitomo, etc.) offer excellent job security, comprehensive benefits, and predictable salary growth, though starting salaries may be lower than at foreign firms.
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs make up the backbone of Japan's economy. Salaries here can vary widely but are generally lower than at large corporations or foreign companies.
###
Area of Specialization / Industry
Your profession is a primary determinant of your salary. In-demand industries with a shortage of skilled labor naturally offer higher pay.
High-Paying Industries:
- IT & Technology: Software Engineers, Data Scientists, and Cybersecurity experts are in extremely high demand. Senior engineers can easily earn over ¥10 million.
- Finance & Investment Banking: Roles in banking, asset management, and financial analysis are consistently among the highest-paid in Japan.
- Medical & Pharmaceutical: Doctors, specialists, and researchers in the life sciences command very high salaries.
- Management Consulting: Consultants at top-tier firms are highly compensated for their expertise.
Average to Lower-Paying Industries:
- Education: While stable, roles like English teaching (e.g., Assistant Language Teacher) are on the lower end of the professional salary scale.
- Hospitality & Tourism: Service-oriented roles generally offer more modest salaries.
- Administrative Support: These essential roles typically fall within the lower-to-mid range of the national average.
Job Outlook in Japan

The job outlook in Japan, particularly for skilled foreign professionals, is highly encouraging. Japan is facing a significant demographic challenge with an aging population and a shrinking workforce. In response, the government and private sector are actively seeking to attract foreign talent to fill critical skills gaps.
Unlike the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), Japan's statistics focus on labor shortages. Reports from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare consistently highlight severe shortages in sectors like IT, engineering, healthcare, and advanced manufacturing. This demand creates significant opportunities and gives skilled professionals strong negotiating power for higher salaries and better benefits. The "Specified Skilled Worker" visa program is a clear indicator of the country's commitment to bringing in foreign workers to fill these gaps.
Conclusion

The "average salary in Japan" is a useful but broad metric. Your true earning potential is a reflection of your unique qualifications, industry, and strategic career choices.
Key Takeaways:
- The average annual salary is around ¥5.0 - ¥5.5 million, but this is just a starting point.
- Experience is highly rewarded, with seniority playing a key role in salary growth at many traditional firms.
- Location and industry are critical. A software engineer in Tokyo will earn vastly more than an administrative assistant in a rural area.
- Consider foreign-owned companies (_gaishikei_) for potentially higher, merit-based pay.
- The job market is strong for skilled professionals, especially in tech and healthcare, due to demographic shifts creating a labor shortage.
For anyone considering building a career in Japan, the opportunities are abundant. By understanding these salary dynamics, you can better position yourself for a financially rewarding and professionally fulfilling experience in the Land of the Rising Sun.
