In the vast ecosystem of global e-commerce, Amazon stands as a titan. Behind every click, every package, and every query is a complex network of logistics, technology, and, most importantly, people. The frontline of this human connection is the Amazon Customer Service team. For many, a role as an Amazon Customer Service Associate (CSA) is more than just a job; it's a gateway into one of the world's most influential companies, a chance to develop critical skills, and a path toward a stable and rewarding career.
But what does that opportunity translate to in tangible terms? What can you realistically expect to earn, and what factors shape your paycheck? The query "Amazon customer service salary" is one of the most common for aspiring professionals looking to join the retail giant, and the answer is far more nuanced than a single number. It’s a figure influenced by location, experience, role specialization, and the comprehensive benefits package that Amazon offers.
I once mentored a young professional who was feeling stuck in a dead-end retail job. He was bright and empathetic but lacked a clear career direction. He took a chance on a virtual customer service role at Amazon, viewing it as a temporary measure. Within two years, he had leveraged Amazon's internal training programs to pivot into a data analyst role within the logistics team, more than doubling his initial salary. His story is a testament to the fact that an Amazon CSA role isn't just a destination; for the ambitious, it is a powerful launchpad.
This guide will provide an exhaustive breakdown of the Amazon customer service salary, offering an authoritative look at every aspect of compensation, career progression, and what it takes to get hired. We will delve into verified data, explore the hidden value of benefits, and outline a clear roadmap for success.
### Table of Contents
- [What Does an Amazon Customer Service Associate Do?](#what-do-they-do)
- [Average Amazon Customer Service Salary: A Deep Dive](#salary-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Your Amazon CSA Salary](#key-factors)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth at Amazon](#job-outlook)
- [How to Get Started in an Amazon Customer Service Career](#how-to-get-started)
- [Conclusion: Is an Amazon Customer Service Role Worth It?](#conclusion)
What Does an Amazon Customer Service Associate Do?

To understand the salary, we must first understand the role. An Amazon Customer Service Associate is far more than a call-center agent reading from a script. They are brand ambassadors, problem-solvers, and crucial navigators of Amazon's intricate web of services. They are the human voice of a company often perceived as a digital machine, tasked with upholding one of Amazon's most sacred tenets: Customer Obsession.
The core responsibility of a CSA is to resolve customer issues efficiently, accurately, and with a high degree of empathy. These issues can span the entire Amazon experience, from a simple question about an order's status to a complex technical problem with an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account or a Kindle device. The role is multifaceted and demands a blend of soft skills and technical acumen.
Breakdown of Daily Tasks and Responsibilities:
- Multi-Channel Communication: CSAs primarily interact with customers through various channels, including inbound and outbound phone calls, live chat, and email. The blend of these channels can vary depending on the team and current customer volume.
- Problem Diagnosis and Resolution: The heart of the job is active listening or reading to understand the customer's true problem. This involves asking clarifying questions, identifying the root cause, and providing a clear, actionable solution. Issues can include:
- Tracking packages and managing deliveries.
- Processing returns, refunds, and replacements.
- Assisting with account security, password resets, and payment issues.
- Troubleshooting digital products like Prime Video, Amazon Music, Kindle, and Alexa-enabled devices.
- Explaining policies and services to customers.
- Navigating Internal Tools: Amazon CSAs use a sophisticated suite of proprietary software to access customer account information, track orders, process transactions, and document every interaction. Proficiency in quickly learning and navigating these complex systems is essential.
- Documentation and Escalation: Every customer contact must be meticulously logged. For issues that are beyond the CSA's scope or require specialized knowledge, they are responsible for escalating the case to the appropriate higher-tier support team, ensuring a seamless handover.
- Adherence to Quality and Performance Metrics: Performance is measured by a variety of metrics, such as Average Handle Time (AHT), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores, and First Contact Resolution (FCR). CSAs are expected to meet these targets consistently.
- Continuous Learning: The Amazon ecosystem is constantly evolving with new products, services, and policies. CSAs are required to participate in ongoing training to stay up-to-date and effective.
### A "Day in the Life" of a Virtual Amazon CSA
To make this more tangible, let's walk through a typical day for a remote (or "virtual") CSA:
- 8:45 AM: Log into the system. Check for any overnight updates from the team lead or new training modules. Review personal performance metrics from the previous day.
- 9:00 AM: The shift officially begins. The CSA sets their status to "Available" and the first customer chat pops up. It's a query about a delayed package. The CSA uses the internal tracking tool to locate the package, explains the carrier delay, and offers to issue a small promotional credit for the inconvenience.
- 10:30 AM: After handling a dozen more chats and emails, a phone call comes through. An elderly customer is having trouble setting up her new Echo Dot. The CSA patiently walks her through the Wi-Fi setup process, step-by-step, using a calm and reassuring tone. The call takes 25 minutes, but the customer is delighted.
- 12:30 PM: Lunch break. Time to step away from the screen.
- 1:30 PM: Back online. The afternoon queue is busy. The CSA encounters a complex issue where a customer was charged for a subscription they believe they canceled. This requires digging through account history, cross-referencing billing cycles, and explaining the terms of service. The issue is resolved with a refund as a one-time courtesy.
- 3:00 PM: A 30-minute block is scheduled for a mandatory training session on a new return policy for electronics.
- 3:30 PM: The CSA handles a few more straightforward issues before encountering an angry customer whose account may have been compromised. Recognizing the security implications, the CSA follows protocol to transfer the customer securely to the specialized Account Security team.
- 5:15 PM: As the shift winds down, the CSA focuses on clearing out the email queue, ensuring all pending issues are documented correctly.
- 5:30 PM: The final 15 minutes are for "wrap-up," where the CSA finalizes notes, reviews their daily stats, and logs out for the day.
This snapshot reveals a role that is structured and metric-driven but also requires immense adaptability, patience, and a genuine desire to help.
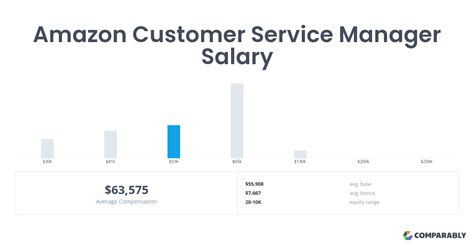
Average Amazon Customer Service Salary: A Deep Dive
Now, let's address the central question. The compensation for an Amazon Customer Service Associate is competitive for the industry, but it's crucial to look beyond a single number and understand the complete picture, which includes hourly rates, potential earnings, and the invaluable benefits package.
Unlike many professional roles, Amazon's entry-level customer service positions are typically compensated on an hourly basis. This is standard for the industry and provides clarity on earnings based on hours worked.
National Average and Typical Range
Based on an aggregation of recent data, the salary landscape for an Amazon CSA in the United States breaks down as follows:
- Average Base Hourly Rate: The typical hourly wage for an entry-level Amazon Customer Service Associate generally falls between $16.00 and $19.00 per hour.
- Starting Wage Target: Amazon has publicly stated a commitment to a minimum wage of at least $15 per hour for all its U.S. employees since 2018. In 2023, the company announced its average starting pay for front-line roles (including fulfillment and customer service) is over $20.50 per hour, with some locations offering starting wages as high as $28 per hour. The specific starting rate for a CSA role depends heavily on geographic location, which we will explore in detail later.
- Estimated Annual Salary (Full-Time): Assuming a standard 40-hour workweek for 52 weeks, the estimated annual salary for a full-time, entry-level CSA would be:
- At $17.00/hour: $35,360 per year
- At $20.50/hour: $42,640 per year
Authoritative Sources:
- According to Glassdoor, the estimated total pay for a Customer Service Associate at Amazon is approximately $43,959 per year in the United States, with an average base salary of around $37,343 per year (approximately $17.95/hour). The "total pay" figure includes additional compensation like cash bonuses or stock. *(Data as of late 2023/early 2024)*.
- Payscale.com reports a similar average hourly rate for an Amazon.com Customer Service Associate, placing it at $17.18 per hour. The reported range spans from $13.59 to $23.16, showcasing the significant variance based on factors like location and experience. *(Data as of early 2024)*.
### Salary Progression by Experience Level
While many CSA roles are entry-level, Amazon provides a structure for advancement. As an employee gains experience, takes on more responsibilities, or moves into specialized or leadership roles, their compensation increases accordingly.
| Career Stage / Role | Typical Hourly Rate | Estimated Annual Salary (Full-Time) | Key Responsibilities |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level (Tier 1) CSA | $16 - $21 / hour | $33,280 - $43,680 | Core customer issue resolution, meeting standard performance metrics. |
| Experienced/Specialist CSA | $18 - $23 / hour | $37,440 - $47,840 | Handling more complex issues (e.g., technical, digital devices), may have bilingual skills. |
| Tier 3 / Team Lead / Mentor | $20 - $26 / hour | $41,600 - $54,080 | Assisting with escalations, mentoring new hires, handling supervisory tasks, quality assurance. |
| L4 Area Manager / Supervisor | Salaried Position | $55,000 - $75,000+ | Managing a team of associates, performance management, operational planning. |
*(Note: These are estimates based on aggregated data and can vary significantly. Salaried positions often include much larger stock grants.)*
### Beyond the Paycheck: A Breakdown of Total Compensation
A critical error when evaluating an Amazon customer service salary is focusing only on the hourly rate. Amazon's total compensation package is a significant part of the overall value proposition.
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): This is a major differentiator. Many full-time Amazon employees, including hourly CSAs, are eligible for RSU grants. These are shares of Amazon stock ($AMZN) that are granted to an employee and vest (i.e., become fully owned by the employee) over a period of time. Given Amazon's stock performance over the long term, this can add thousands of dollars to an employee's net worth annually. The vesting schedule is typically back-loaded (e.g., 5% after year 1, 15% after year 2, and 40% after years 3 and 4) to encourage retention.
- Sign-On Bonuses: In competitive markets or during peak hiring seasons (like the holidays), Amazon often offers sign-on bonuses for new hires. These can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, paid out over the initial months of employment.
- Comprehensive Health Benefits: Full-time (and many part-time) employees are eligible for comprehensive health, vision, and dental insurance from day one. This is a significant financial benefit that can be worth thousands of dollars per year compared to roles without such coverage.
- 401(k) Retirement Plan: Amazon offers a 401(k) plan with a company match. For example, they might match 50% of an employee's contributions up to 4% of their pay, effectively providing "free money" for retirement savings.
- Paid Time Off (PTO): Employees accrue vacation time, paid sick leave, and paid holidays, providing financial stability when taking time away from work.
- The "Career Choice" Program: Perhaps one of the most valuable benefits, Amazon's Career Choice program prepays up to 95% of tuition for courses in high-demand fields—even if those fields are not related to a future career at Amazon. They will pay for certificates, associate's degrees, and bachelor's degrees in areas like nursing, commercial truck driving, IT, and mechanical trades. For an employee looking to build a long-term career, this benefit is potentially worth tens of thousands of dollars.
- Employee Discount: Employees receive a 10% discount on products sold and shipped by Amazon.com, up to an annual limit.
When you combine the hourly wage with the potential value of RSUs, health benefits, retirement matching, and the groundbreaking Career Choice program, the "total compensation" for an Amazon CSA is often substantially higher than the base pay suggests.
Key Factors That Influence Your Amazon CSA Salary

The salary ranges provided above are not arbitrary. They are the result of a complex calculation influenced by several key variables. If you're aiming for the higher end of the pay scale, understanding these factors is paramount. This section, the most detailed in our guide, breaks down precisely what determines your specific hourly rate and overall earning potential.
### `
`Geographic Location`
`Location is arguably the single most significant factor impacting the base hourly rate for an Amazon CSA. The company adjusts its pay scales based on the local cost of labor and cost of living. A role in a major metropolitan area with high living expenses will almost always pay more than the exact same role in a rural area.
Amazon has both physical customer service centers and a massive network of Virtual Customer Service (VCS) or work-from-home employees. For on-site roles, the pay is tied directly to that site's designated pay scale. For virtual roles, the pay is often determined by the employee's state of residence.
Examples of Geographic Pay Variation:
- High-Cost Areas: In cities like Seattle, WA (Amazon's HQ1), or in regions like Northern Virginia (HQ2) and the San Francisco Bay Area, starting wages for front-line employees can push well above the national average, potentially starting at $22/hour or more to remain competitive.
- Mid-Cost Areas: In many suburban or mid-sized metropolitan areas across the country, the starting rate will likely hew closer to the national average, in the $17-$20/hour range.
- Low-Cost Areas: In more rural states or regions with a lower cost of living, the starting wage might be closer to the company-wide minimum, around $16-$17/hour.
How to Leverage This: When searching on the Amazon.jobs portal, pay close attention to the specific pay rate listed in the job description. If a role is listed as "Virtual - Washington," it will likely have a different (and higher) pay rate than a role listed as "Virtual - Tennessee." While moving for a CSA role is unlikely, being aware of the pay bands in your specific state is crucial for setting realistic expectations.
### `
`Level, Tier, and Role Specialization`
`While "years of experience" is a common salary driver in many professions, within Amazon's customer service structure, it's more about the specific level, tier, and specialization of your role. Amazon has a well-defined internal hierarchy.
- Tier 1 (T1) Associate: This is the standard, entry-level CSA position that all new hires start in. They handle the bulk of incoming customer contacts. Their pay is at the base rate for their location.
- Tier 3 (T3) Associate / Process Assistant (PA): After demonstrating high performance, expertise, and leadership potential, a T1 associate can apply for a T3 role. These are hourly, non-supervisory leadership positions. T3s often act as Subject Matter Experts (SMEs), mentors for new hires, quality auditors, or handle the most complex customer escalations. A promotion to T3 typically comes with a significant hourly pay increase of $2-$5 per hour or more.
- Level 4 (L4) Area Manager: This is the first level of salaried management. An Area Manager is a supervisor who leads a team of T1 and T3 associates. This is a major career step that involves a shift from hourly pay to an annual salary, often accompanied by a much larger RSU grant. Salaries for L4 managers in customer service can start in the $55,000-$75,000 range, again, highly dependent on location.
Specialization also plays a critical role:
- Technical Support: CSAs who specialize in troubleshooting complex technical products, such as AWS, Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP), or advanced Alexa-device issues, may command a higher pay rate due to the additional skills required.
- Bilingual Skills: A CSA who is fluent in a high-demand second language (like Spanish, Mandarin, or French) can earn a "language differential." This is typically an additional $1-$2 per hour on top of their base rate.
- Executive Customer Relations (ECR): This is a highly specialized team that handles issues escalated to senior Amazon executives (e.g., the "jeff@amazon.com" email). These roles are not entry-level and are filled by the most experienced, skilled, and diplomatic CSAs. The compensation for these positions is significantly higher.
### `
`Employment Type and Schedule`
`The nature of your employment contract directly affects your earnings and benefits.
- Full-Time: A full-time role (typically 40 hours per week) provides the most stable income and the most comprehensive benefits package, including health insurance from day one and eligibility for the full Career Choice program and RSU grants.
- Part-Time: Part-time roles (typically 20-29 hours per week) offer more flexibility. Employees in these roles often receive a pro-rated benefits package, and some benefits like RSU grants may be smaller or unavailable. The hourly rate is usually the same as for full-time employees.
- Seasonal: Amazon hires a large number of seasonal CSAs to handle peak volume during the holiday season (typically from October to January). These roles are temporary and often do not include benefits like health insurance or paid time off, though they are eligible for the $15/hour minimum wage and may receive a completion bonus. A seasonal role can be an excellent way to get a foot in the door for a permanent position.
Furthermore, some roles may offer a shift differential—a small pay premium for working undesirable hours, such as overnight shifts or weekends.
### `
`Level of Education and Certifications`
`For a Tier 1 entry-level CSA role, the educational requirement is typically a high school diploma or equivalent. A college degree is not required and will not usually result in a higher starting hourly rate for this specific role.
However, education becomes a significant factor for career advancement.
- Internal Advancement: A bachelor's degree (especially in fields like business, communications, or management) can make an internal candidate much more competitive for a promotion to a salaried L4 Area Manager position.
- Leveraging the Career Choice Program: The true value of education lies in using Amazon's benefits. An employee can use the Career Choice program to earn a degree or certification in a field like IT Support, Project Management, or Data Analytics. Upon completion, they can apply for a higher-paying internal role in a different department. For example, a CSA who gets an AWS Cloud Practitioner certification could transition to a role within the AWS support division, which has a much higher salary ceiling.
While a degree doesn't boost your *initial* CSA pay, it's a powerful tool for moving *beyond* the CSA role within Amazon.
### `
`In-Demand Skills That Boost Your Value`
`While base pay is often standardized, possessing and demonstrating specific skills can fast-track you for promotions to higher-paying T3 and L4 roles. These are the skills to cultivate from day one:
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Go beyond the script. Show an ability to analyze complex situations, identify the unstated needs of the customer, and devise effective, logical solutions.
- Ownership and Bias for Action: These are two of Amazon's core Leadership Principles. Demonstrate that you take full responsibility for your customers' issues from start to finish and that you act with a sense of urgency to resolve them. Documenting instances where you "took ownership" is crucial for performance reviews and promotion applications.
- Technical Proficiency: Become an expert in Amazon's internal tools. The faster and more accurately you can navigate the system, the more efficient you are. Volunteer to learn about new tools or processes.
- Communication and De-escalation: The ability to remain calm, empathetic, and professional with a frustrated or angry customer is invaluable. Mastering de-escalation techniques can get you noticed for roles on specialized teams.
- Data Literacy: Learn to understand your own performance metrics (AHT, CSAT, FCR). Show an interest in team-level data and ask thoughtful questions about what the numbers mean. This analytical mindset is a key differentiator for leadership roles.
- Mentorship and Teamwork: Proactively help new hires. Be a positive voice in team chats and meetings. Demonstrating that you can elevate the performance of those around you is a clear sign of leadership potential.
By focusing on these six areas, you are not just performing your job; you are actively building a case for your own promotion and, consequently, a higher salary.
Job Outlook and Career Growth at Amazon

When considering a career, salary is only one part of the equation. Job security and the potential for advancement are equally, if not more, important for long-term financial health and professional satisfaction. Here, the outlook for a role within Amazon diverges significantly from the general industry trend.
The Broader Industry Outlook for Customer Service Representatives
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the overall employment of customer service representatives is projected to show a decline of 4 percent from 2022 to 2032. This projected decline is largely attributed to:
- Automation and AI: The increasing sophistication of chatbots, AI-powered voice response systems (IVRs), and self-service online portals is allowing companies to automate the handling of simple, repetitive customer inquiries.
- Offshoring: Some companies continue to move contact center operations overseas to reduce labor costs.
However, the BLS also notes that the need for actual human representatives will remain. As automation handles the basic queries, the role of the human agent is shifting to become more specialized, focusing on complex, sensitive, or high-value customer interactions that require empathy, critical thinking, and advanced problem-solving skills—precisely the