For those who dream of a career that combines responsibility, travel, and a direct impact on the nation's infrastructure, becoming a railroad conductor is a compelling choice. As the face of America's passenger rail, Amtrak offers a unique and rewarding career path. But what does that path look like financially?
A career as an Amtrak conductor offers not only a dynamic work environment but also a competitive salary and robust benefits. While starting pay is solid, experienced conductors can see their annual earnings climb well into the $90,000 to $120,000+ range, making it a financially attractive long-term profession.
This article will provide a data-driven breakdown of an Amtrak conductor's salary, the factors that influence it, and the overall career outlook.
What Does an Amtrak Conductor Do?

Often described as the "captain of the train," an Amtrak conductor is the crew member in charge of the train's overall operation, safety, and service. Their responsibilities are vast and critical, extending far beyond simply collecting tickets.
Key duties include:
- Supervising the Crew: Managing the assistant conductor(s), engineers, and on-board service staff to ensure seamless operations.
- Ensuring Safety: Conducting safety briefings, inspecting equipment, and enforcing all federal and company safety regulations to protect passengers, crew, and cargo.
- Overseeing Train Operations: Coordinating the train's movement with dispatchers and engineers, managing stops, and handling any unexpected delays or operational issues.
- Passenger Service: Acting as the primary point of contact for passengers, making announcements, and ensuring a positive customer experience.
- Administrative Tasks: Completing detailed reports on train movements, passenger counts, and any incidents that occur during a trip.
It's a position that demands leadership, quick thinking, and a steadfast commitment to safety and service.
Average Amtrak Conductor Salary
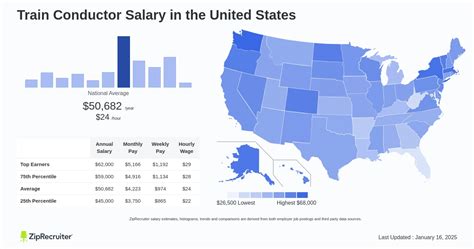
Analyzing salary for this role requires looking at data from several authoritative sources. It's important to note that pay is often structured on an hourly basis, with overtime, location-based adjustments, and other factors significantly impacting total annual compensation.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for all railroad conductors and yardmasters was $73,730 as of May 2023. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $58,350, while the top 10 percent earned more than $108,810. This data provides a strong baseline for the entire rail industry, including freight and passenger services.
However, data specific to Amtrak often shows a higher earning potential, especially for experienced professionals.
| Source | Role | Average Base Salary / Total Pay | Notes |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| U.S. BLS | Railroad Conductors (All) | $73,730 (Median) | Data for the entire industry, not just Amtrak. |
| Glassdoor | Amtrak Conductor | $91,000 - $144,000 (Estimated Total Pay) | Based on user-submitted data; reflects the impact of overtime and other compensation. |
| Salary.com | Railroad Conductor | $80,094 (Median) | Range typically falls between $70,713 and $91,378, but can go higher. |
An important takeaway is that new hires, known as Assistant Conductors or Conductor Trainees, start at a lower rate during their extensive training period. Once fully qualified, their earning potential increases substantially.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

A conductor's final paycheck is shaped by a combination of professional and geographic factors. Understanding these elements is key to mapping out your potential career earnings.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most significant factor in a conductor's salary. Amtrak, like most major railroads, operates on a seniority system governed by collective bargaining agreements.
- Entry-Level (Assistant Conductor): In the first few years, you'll work as an Assistant Conductor. Your pay will be on the lower end of the scale as you learn the routes and responsibilities.
- Qualified Conductor: After meeting the requirements to become a full Conductor (typically 1-2 years), you'll see a significant pay increase.
- Senior Conductor: With 10+ years of experience, conductors gain seniority, which grants them preference on route assignments, vacation bids, and schedules. This stability and access to more desirable (and often higher-paying) routes push their total compensation toward the top of the pay scale.
### Geographic Location
While conductors travel, their pay is tied to their "home base" or "crew base." The cost of living in these home base cities plays a major role in salary determination. Conductors based in high cost-of-living areas, particularly along the busy Northeast Corridor (e.g., Washington, D.C., Philadelphia, New York City, and Boston), often receive higher hourly rates or pay adjustments to compensate. A position based in a major metropolitan hub will almost always pay more than one in a smaller, more rural location.
### Level of Education
For a conductor role, extensive, on-the-job training is valued more than formal academic degrees. The minimum requirement is typically a high school diploma or GED. Amtrak provides a comprehensive and paid training program for all new hires, which can last several weeks or months.
While a college degree is not required to become a conductor, a bachelor's degree in logistics, transportation, or business management could provide a competitive edge for those aspiring to move into management roles like a Trainmaster or Road Foreman later in their career.
### Company Type
The type of railroad you work for heavily influences your salary and lifestyle.
- Passenger Rail (Amtrak): Working for Amtrak generally involves more regular and predictable schedules compared to freight. While top-end salaries might be slightly lower than the absolute highest in freight, the focus on customer service and more consistent home time is a major draw.
- Freight Rail (e.g., Union Pacific, BNSF): Freight conductors often have the potential for higher overall earnings due to longer trips, more overtime, and the demanding nature of being on-call 24/7. However, this comes at the cost of a less predictable schedule and more time away from home.
### Area of Specialization
Within the railroad, "specialization" is closely tied to career progression. A conductor is not an end-of-the-line position but a crucial step in a broader railroading career. Advancing to new roles is the primary way to specialize and significantly increase your salary.
Potential career advancements include:
- Yardmaster: Responsible for coordinating the complex movement of trains within a rail yard. This is a high-responsibility role with a corresponding pay increase.
- Dispatcher: Works from a central office to direct the movement of all trains across a large territory, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Road Foreman / Trainmaster: These are first-line management positions responsible for supervising crews and managing field operations. They represent a significant step up in both responsibility and compensation.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that overall employment for railroad conductors and yardmasters will show little or no change from 2022 to 2032. This is largely due to industry-wide automation and efficiency gains that allow for longer trains with the same size crews.
However, this stable outlook doesn't tell the whole story. The industry will still need to hire thousands of conductors to replace workers who retire or leave the profession. Furthermore, potential government investments in expanding passenger rail infrastructure could create new opportunities, particularly at companies like Amtrak. For a dedicated and qualified candidate, opportunities will remain available.
Conclusion

A career as an Amtrak conductor is much more than a job; it's a commitment to a unique and vital profession. While the work is demanding, the financial rewards are substantial and clear.
Key Takeaways:
- Strong Earning Potential: While the industry median is around $73,730, experienced Amtrak conductors can realistically earn over $100,000 annually with overtime and experience.
- Experience is King: Seniority is the primary driver of higher pay, better routes, and a more predictable schedule.
- Training is Provided: Amtrak invests heavily in its employees with a paid, comprehensive training program, making the career accessible to those with a high school diploma.
- A Pathway to Advancement: The conductor role is a launchpad for higher-paying management and operational positions within the railroad industry.
For individuals seeking a stable, well-compensated career that keeps America moving, the path of an Amtrak conductor is a journey worth considering.
