Introduction

Navigating the professional landscape of Argentina offers a unique blend of vibrant culture and dynamic economic challenges. For anyone considering a career in the country, the most pressing question is often about earning potential. Due to significant economic factors like high inflation, understanding salaries requires a nuanced approach. While a single "average salary" figure can be misleading, a deeper dive reveals significant opportunities for skilled professionals. As of early 2024, the average monthly salary in Argentina hovers around ARS $555,000 to ARS $750,000, but this figure is heavily influenced by industry, location, and experience, with tech and export-oriented sectors offering substantially higher, often dollarized, compensation.
This guide will break down the complexities of the Argentine salary landscape, providing a data-driven overview to help you understand your potential earnings and plan your career path effectively.
Understanding the 'Average Salary' in Argentina
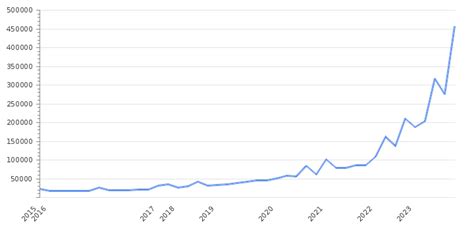
Unlike a stable economy, a single "average salary" figure in Argentina is a moving target. The country's high inflation rate means that the value of the Argentine Peso (ARS) and the nominal salaries paid in that currency change rapidly. Therefore, it's crucial to understand a few key concepts:
- Nominal vs. Real Salary: Your nominal salary is the number on your payslip (e.g., ARS $600,000). Your real salary is what that money can actually buy, which decreases as inflation rises.
- The "Blue Dollar": Argentina has multiple exchange rates. The official rate is controlled by the government, while an informal, parallel rate known as the "dólar blue" reflects a more realistic market value. Many skilled professionals, especially those working for international companies or as freelancers, aim to have their salaries pegged to or paid in US dollars to protect against peso devaluation.
- Collective Bargaining ("Paritarias"): Unions play a significant role in Argentina, regularly negotiating salary increases for their sectors to try and keep pace with inflation.
When analyzing salary data, always consider the date the data was published and the currency used.
Average Salary in Argentina: The Numbers

To provide a clear picture, we must look at data from multiple authoritative sources. It's important to note that the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not track foreign salary data. We will rely on Argentina's official statistics and reputable global aggregators.
- Official Government Data: According to Argentina's National Institute of Statistics and Census (INDEC), the average monthly salary for a registered private-sector worker (RIPTE) was ARS $555,269 as of December 2023. The minimum wage (Salario Mínimo, Vital y Móvil) was set at ARS $202,800 for March 2024.
- Salary Aggregator Data: Websites that collect user-reported data provide a broader perspective.
- Salary Explorer reports an average monthly salary of ARS $741,000. Their data suggests a range from a low average of ARS $187,000 to a high average of ARS $3,310,000 for highly specialized roles.
- Payscale notes that for Buenos Aires, the average salary is approximately ARS $3 million per year, which translates to ARS $250,000 per month, though this figure may not fully capture the higher end of the professional market.
A realistic salary range for a professional in Argentina can be summarized as follows:
- Entry-Level/Junior Roles: ARS $250,000 - ARS $450,000 per month
- Mid-Career Professionals: ARS $500,000 - ARS $1,200,000 per month
- Senior/Management/Specialist Roles (especially in Tech/Finance): ARS $1,500,000 - ARS $4,000,000+ per month (or a USD equivalent).
*Note: All ARS figures are subject to rapid change due to inflation. When possible, negotiating a salary benchmarked to the US dollar is highly advantageous.*
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your individual earning potential will vary significantly based on several critical factors.
### Level of Education
Education remains a strong determinant of salary in Argentina. A university degree is often a prerequisite for professional roles and commands a higher salary than a technical or secondary school diploma. Professionals with postgraduate degrees (Master's, PhD) in specialized fields like data science, finance, or engineering can access the highest salary brackets, particularly within multinational corporations.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most critical factor. The leap in salary from an entry-level position to a senior role is substantial.
- 0-2 Years: Professionals are in a learning phase, with salaries often near the lower end of the professional spectrum.
- 2-5 Years: With proven skills and experience, individuals can expect significant salary increases and more responsibilities.
- 10+ Years (Senior/Lead): Senior professionals with deep expertise and leadership skills are highly valued. They command top-tier salaries and are often the most likely to receive compensation pegged to the US dollar.
### Geographic Location
Where you work in Argentina has a major impact on your salary.
- Buenos Aires (CABA): The Autonomous City of Buenos Aires is the country's economic and corporate hub. It offers the highest concentration of jobs and the highest average salaries.
- Major Provincial Capitals (Córdoba, Rosario, Mendoza): These cities have robust economies and offer competitive salaries, though typically 10-20% lower than in CABA.
- Patagonia (e.g., Neuquén): This region can offer surprisingly high salaries, driven by the lucrative oil and gas industry (Vaca Muerta shale formation).
- Northern Provinces: These regions generally have lower economic activity and, consequently, lower average salaries.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for is a crucial differentiator.
- Multinational Corporations (MNCs): These companies typically offer the highest salaries, often benchmarked against or paid in US dollars. They also tend to provide better benefits packages and more structured career growth.
- Local Argentine Companies ("Empresas Nacionales"): Large national companies can be competitive, but salaries are almost always in ARS and may struggle to keep pace with inflation as effectively as MNCs.
- Startups: Tech startups can be a mixed bag. Early-stage startups may offer lower base salaries but compensate with equity. Well-funded, successful startups, especially in the FinTech and SaaS sectors, often compete directly with MNCs for top talent.
- Public Sector: Government jobs offer stability and good benefits but generally pay less than the private sector for comparable professional roles.
### Industry and Specialization
Your area of expertise is paramount. Certain industries are booming and pay a significant premium for skilled talent.
- Information Technology: This is the highest-paying sector by a large margin. Software developers, data scientists, cybersecurity experts, and DevOps engineers are in extremely high demand. Many work remotely for foreign companies, earning international salaries directly in USD.
- Agribusiness & Export: As a pillar of the Argentine economy, professionals in logistics, export management, and agricultural science can earn very competitive salaries tied to a dollar-based industry.
- Energy (Oil & Gas): Engineers, geologists, and project managers working in the energy sector, particularly in Vaca Muerta, command some of the highest salaries in the country.
- Financial Services & FinTech: Professionals in banking, investment, and the booming FinTech scene also have high earning potential.
- Traditional Sectors (Retail, Manufacturing): While essential to the economy, these sectors generally offer more modest salaries that are more exposed to local economic volatility.
Job Outlook

Despite its economic challenges, Argentina has a resilient and innovative workforce. The job outlook is highly positive for specific, high-demand sectors. According to reports from the World Bank and various market analyses, the key growth areas are:
- Knowledge-Based Services: Argentina is a leading global exporter of IT services. The demand for tech talent is expected to continue growing robustly.
- Energy and Mining: The development of the Vaca Muerta shale play and the country's vast lithium reserves (for batteries) are creating thousands of high-paying jobs.
- Agribusiness: As a global food production powerhouse, this sector will remain a stable source of employment and career growth.
The primary challenge for the overall job market remains economic instability. However, professionals who align their skills with these high-growth, export-oriented industries will find themselves in a strong and secure position.
Conclusion

Determining the "average salary" in Argentina is a complex task that goes far beyond a single number. The economic climate demands that professionals be strategic and informed.
Key takeaways:
- Look Beyond the Average: The national average salary is heavily skewed by lower-paying jobs and the public sector. Focus on industry-specific data.
- Aim for Dollar-Pegged Income: In a high-inflation environment, the most valuable compensation is tied to a stable foreign currency like the US dollar. This is most common in IT, some MNCs, and freelance roles for foreign clients.
- Specialize in High-Demand Fields: Technology, Energy, and Agribusiness are the clear leaders for high earning potential and job security.
- Location Matters: Buenos Aires remains the primary market for top-tier salaries, but specific industries may create high-paying hubs elsewhere.
For ambitious professionals, Argentina offers a wealth of opportunity. By understanding these key economic factors and strategically positioning yourself in a growth industry, you can build a successful and financially rewarding career.