For those with a passion for sound, a career as an audio engineer is a thrilling blend of technical skill and creative artistry. But beyond the mixing consoles and recording studios, a critical question arises: what is the earning potential for this dynamic profession? While the answer is complex, the career path offers significant financial rewards for dedicated professionals. An audio engineer's salary can range from a modest starting wage of around $40,000 to well over $120,000 for seasoned experts in high-demand fields.
This guide will break down the salary you can expect as an audio engineer, explore the key factors that dictate your income, and provide a clear outlook for the profession.
What Does an Audio Engineer Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's important to understand the scope of the role. An audio engineer is a highly skilled technician responsible for the technical and creative aspects of sound. They don't just push buttons; they shape the auditory experience for audiences everywhere.
Key responsibilities often include:
- Recording: Capturing sound from musicians, actors, or other sources using microphones and recording equipment.
- Mixing: Balancing, treating, and combining multiple tracks of audio into a cohesive final product.
- Mastering: The final stage of audio post-production, preparing the mixed track for distribution by ensuring quality and loudness standards.
- Live Sound: Managing sound reinforcement for concerts, theater productions, corporate events, and broadcasts.
- Equipment Setup and Maintenance: Ensuring all audio equipment, from microphones to digital audio workstations (DAWs), is functioning correctly.
Average Audio Engineer Salary
Salary data for audio engineers can vary based on the source and the specific job title included in the data set. By synthesizing information from several authoritative sources, we can build a comprehensive picture.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the most relevant category is "Broadcast, Sound, and Video Technicians." As of May 2023, the BLS reports the following:
- Median Annual Wage: $60,480 (or $29.08 per hour)
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $35,500
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $108,130
This data provides a reliable baseline, showing that while entry-level positions may be modest, there is a clear path to a six-figure income.
Reputable salary aggregators, which collect real-time, user-submitted data, offer further insight:
- Salary.com reports the median salary for an Audio Engineer in the United States is around $68,819, with a typical range falling between $58,958 and $79,933.
- Glassdoor places the average total pay (including base salary and additional compensation like bonuses) for an Audio Engineer at approximately $71,500 per year.
- Payscale notes that the average base salary is around $60,000, closely aligning with the BLS median figure.
In summary: A realistic salary range for an audio engineer spans from $45,000 to $85,000, with the median hovering right around the $60,000 to $70,000 mark. However, this is just the average; your personal earnings will be heavily influenced by the factors below.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as an audio engineer is not a fixed number. It's a dynamic figure determined by a combination of your qualifications, choices, and environment.
### Level of Education
While the audio engineering field has traditionally valued hands-on experience over formal degrees, a relevant education can give you a significant competitive edge and a higher starting salary. An Associate's or Bachelor's degree in Audio Production, Sound Engineering, or Music Technology provides a structured foundation in acoustics, signal flow, and digital audio theory. More importantly, it provides access to professional-grade studios and networking opportunities.
Certifications in industry-standard software like Pro Tools, Logic Pro X, or Ableton Live are also highly valuable and can directly boost your hiring prospects and earning potential.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most critical factor in determining an audio engineer's salary. As you build your portfolio, reputation, and technical skills, your value to employers and clients increases exponentially.
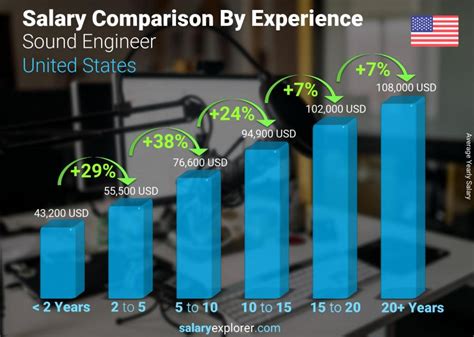
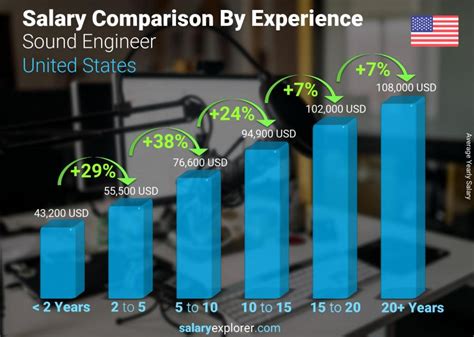
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Engineers at this stage are often in assistant roles, focusing on setup, session prep, and learning from senior engineers. Salaries typically range from $38,000 to $50,000.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With a solid portfolio and proven skills, these engineers take on lead roles in recording or mixing sessions. According to Payscale, their average earnings climb into the $60,000 to $75,000 range.
- Senior/Experienced (10+ years): Top-tier engineers with extensive credits, a strong client list, or specialized skills can command premium rates. It is at this level that salaries frequently surpass $90,000 and can easily exceed $120,000, especially for freelance or in-demand specialists.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Major media and entertainment hubs not only have more job opportunities but also offer higher salaries to compensate for a higher cost of living. The top-paying metropolitan areas for audio engineers include:
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Nashville, TN
- Atlanta, GA
- Austin, TX
Working in one of these hubs can result in a salary that is 15-30% higher than the national average. Conversely, working in a smaller market will likely yield a salary closer to the lower end of the national range.
### Company Type / Industry
The term "audio engineer" is broad and spans numerous industries, each with different budget scales and pay structures.
- Film & Television: Post-production audio engineers (dialogue editors, sound designers, re-recording mixers) often earn high salaries due to large studio budgets.
- Video Games: Game audio is a rapidly growing and lucrative field. Sound designers and audio implementation specialists at major game studios are among the highest earners.
- Music Production: Salaries in recording studios can vary wildly. Working for a world-renowned studio or a major record label will pay far more than a small, independent studio. Freelance mixing and mastering engineers' incomes depend entirely on their client base and reputation.
- Live Events & Touring: A Front of House (FOH) or Monitor Engineer for a major international touring artist can earn a substantial income, often on a per-show or weekly contract basis.
- Corporate: Many large corporations employ A/V technicians and audio engineers to manage sound for town halls, webcasts, and large-scale company events. These roles often offer stable hours and competitive salaries with benefits.
### Area of Specialization
Developing a deep expertise in a specific niche is one of the fastest ways to increase your value. Specialized roles often command higher salaries due to the specific skill set required.
- Mastering Engineer: This is a highly specialized, "final check" role. Top mastering engineers are in high demand and are among the highest-paid professionals in the music industry.
- Sound Designer: Creating custom sound effects for film, television, or video games requires a unique blend of creativity and technical ability, making it a well-compensated specialty.
- Acoustic Consultant: These engineers specialize in designing the acoustic properties of spaces like concert halls, theaters, and recording studios. This scientific and technical role is a high-earning niche.
- Forensic Audio Analyst: A less common path, these experts work with law enforcement to clarify and analyze audio evidence, a role that requires precision and commands a professional salary.
Job Outlook

The future for audio professionals is bright. The BLS projects that employment for broadcast, sound, and video technicians will grow 6% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is fueled by the explosion of digital content. The ever-increasing demand for professionally produced audio for podcasts, video games, streaming services (Netflix, Disney+), online videos (YouTube, TikTok), and corporate webcasting means more opportunities for skilled engineers. While competition for top jobs in music and film remains intense, the overall demand for audio expertise is expanding.
Conclusion

A career as an audio engineer offers a path that is both creatively fulfilling and financially rewarding. While the median salary hovers around $60,000 to $70,000, this figure is merely a starting point. Your ultimate earning potential is not predetermined; it is shaped by your dedication to continuous learning, the experience you accumulate, the network you build, and the specialty you choose to master.
For those aspiring to enter the field, the key takeaways are clear: pursue education, gain hands-on experience at every opportunity, develop a deep understanding of the technology, and specialize in a high-demand area. By doing so, you can turn your passion for sound into a prosperous and long-lasting career.