Decoding Your Worth: An In-Depth Guide to Automation Engineer Salaries in 2024

In a world driven by efficiency and digital transformation, the role of an Automation Engineer has become more critical—and more lucrative—than ever. These architects of automated systems are the engines behind scalable software, streamlined manufacturing, and robust digital infrastructure. If you're considering this dynamic career path, one of your primary questions is likely about compensation.
The great news is that this is a highly rewarding field. An automation engineer salary in the United States typically falls between $92,000 and $147,000 annually, with the national average hovering around $115,000. This guide will break down what an Automation Engineer does, explore the salary landscape in detail, and analyze the key factors that determine your earning potential.
What Does an Automation Engineer Do?

At its core, an Automation Engineer designs, builds, and maintains the automated systems that allow businesses to operate faster, more reliably, and at a greater scale. Instead of performing repetitive tasks manually, they write scripts and create frameworks to execute those tasks automatically.
While the role is common in software quality assurance (QA), it spans many industries. Key responsibilities often include:
- Designing and developing automated testing scripts to ensure software quality.
- Creating and managing automation frameworks (like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright) that other engineers can use.
- Integrating automation into CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines to accelerate development cycles.
- Automating infrastructure provisioning and management in a DevOps environment using tools like Ansible or Terraform.
- Developing robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline business operations in fields like finance and logistics.
In short, they are expert problem-solvers who leverage technology to eliminate manual effort and minimize human error.
Average Automation Engineer Salary
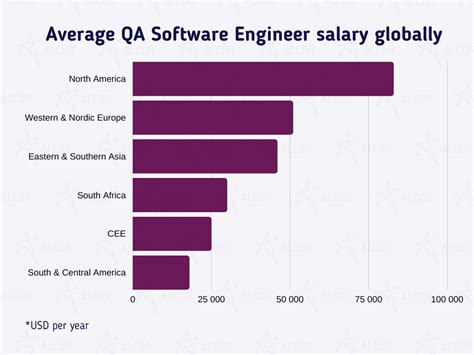
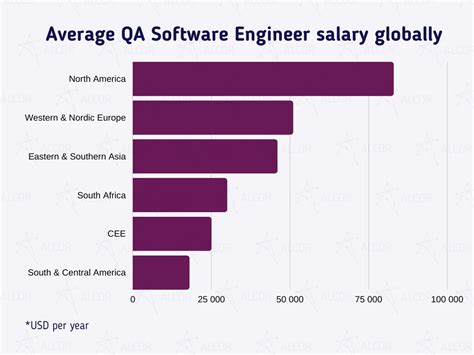
The compensation for an Automation Engineer is competitive, reflecting the high-demand nature of their skills. While salary figures can vary, data from leading sources provides a clear picture of the current landscape.
- Salary.com reports the median salary for an Automation Engineer in the United States is $115,117 as of early 2024, with a typical range between $103,428 and $126,672.
- Glassdoor states the average total pay is $123,576 per year, which includes an average base salary of $104,774 plus additional compensation like cash bonuses and stock options.
- Payscale places the average base salary at $96,654, with a reported range from $73,000 for entry-level positions to $134,000 for experienced professionals.
The slight variation in these numbers highlights that an "average" salary is a composite of several influencing factors. Your specific earnings will depend on a combination of your experience, location, education, and specialization.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

To truly understand your earning potential, you must look beyond the national average. Here are the most significant factors that will shape your salary as an Automation Engineer.
###
Level of Education
A strong educational foundation is typically the first step into this career.
- Bachelor’s Degree: The vast majority of Automation Engineers hold a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or a related engineering field (like Electrical or Mechanical). This is considered the standard entry requirement.
- Master’s Degree: A master's degree can provide a competitive edge, particularly for highly specialized or research-intensive roles in areas like AI-driven automation or robotics. It may lead to a higher starting salary and open doors to senior or architectural positions more quickly.
- Certifications: While not a substitute for a degree, professional certifications demonstrate up-to-date expertise. Certifications like ISTQB Advanced Level Test Automation Engineer, AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, or vendor-specific credentials for RPA tools (e.g., UiPath Certified Professional) can directly boost your desirability and earning potential.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most important factor in determining your salary. As you gain expertise, your ability to design complex systems and mentor others grows, making you significantly more valuable.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Engineers just starting their careers can expect to earn in the $80,000 to $95,000 range. In this phase, you are learning established frameworks and executing predefined automation tasks.
- Mid-Level (3-7 years): With several years of experience, you are now building new automation solutions, maintaining frameworks, and working more independently. Salaries typically climb to the $100,000 to $125,000 range.
- Senior/Lead (8+ years): Senior engineers are responsible for architectural decisions, setting the automation strategy for entire teams or departments, and mentoring junior engineers. Their compensation reflects this leadership, often reaching $130,000 to $160,000+, with lead and principal roles commanding even higher figures.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters immensely. Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the local cost of living and the concentration of demand for tech talent.
- Top-Tier Markets: Major tech hubs offer the highest salaries. Cities and regions like San Francisco, CA; San Jose, CA; Seattle, WA; New York, NY; and Austin, TX consistently pay a premium to attract top talent. Salaries in these areas can be 20-30% higher than the national average.
- Mid-Tier Markets: Other strong markets include cities like Denver, CO; Chicago, IL; and Atlanta, GA, where salaries are competitive and often above the national average.
- Remote Work: The rise of remote work has complicated geographic-based pay. Some companies now offer location-agnostic salaries, while others adjust pay based on where the employee resides. This has created new opportunities for engineers in lower cost-of-living areas to access high-paying jobs.
###
Company Type
The type and size of your employer have a direct impact on your compensation package.
- Big Tech (FAANG & similar): Companies like Google, Meta, Apple, and Microsoft offer top-of-the-market compensation packages that include high base salaries and substantial stock options (RSUs), pushing total compensation well above industry averages.
- Established Enterprises: Large, non-tech corporations (in finance, healthcare, or retail) offer stable, competitive salaries and strong benefits but may not match the total compensation of Big Tech.
- Startups: Startups often offer a lower base salary but compensate with significant equity (stock options). This is a high-risk, high-reward proposition where a successful company exit could lead to a massive financial windfall.
- Consulting Firms: Working for a consulting or contracting agency can lead to higher hourly rates but may come with fewer benefits like paid time off and retirement matching.
###
Area of Specialization
"Automation" is a broad term. Your specific niche can significantly affect your salary.
- QA / Software Test Automation: This is the most common specialization, focused on ensuring software quality. Expertise in tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright is essential.
- DevOps / Infrastructure Automation: This is one of the highest-paying areas. These engineers automate the deployment and management of cloud infrastructure using tools like Terraform, Ansible, Kubernetes, and Docker. Their skills are critical for modern cloud-native companies.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): This field focuses on automating repetitive business and administrative tasks. Professionals skilled in platforms like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere are in high demand in industries like finance, insurance, and logistics.
- Industrial Automation: This specialization involves automating manufacturing processes using PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), robotics, and SCADA systems. It requires a blend of mechanical, electrical, and software engineering skills.
Job Outlook

The future for Automation Engineers is exceptionally bright. As companies of all sizes continue to embrace digital transformation, the need for skilled automation professionals is only growing.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides strong evidence for this trend. While the BLS doesn't have a dedicated category for "Automation Engineer," the closely related role of "Software Developers, Quality Assurance Analysts, and Testers" is projected to grow by 25 percent from 2022 to 2032. This is much faster than the average for all occupations. The BLS attributes this rapid growth to the increasing demand for new software and the need to ensure its quality and reliability through automated testing.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as an Automation Engineer is a sound investment in your future. It offers a challenging and intellectually stimulating work environment combined with a robust and rewarding salary structure.
Key takeaways for anyone considering this career path:
- High Earning Potential: With a national average well over $100,000, this is a financially secure profession.
- Growth is Key: Your salary is not static. It will grow significantly with experience, especially as you move into senior and lead roles.
- Location and Specialization Matter: To maximize your earnings, target high-demand tech hubs and consider specializing in high-growth areas like DevOps or RPA.
- The Future is Bright: With projected job growth far outpacing the national average, you can be confident in your long-term career stability and prospects.
For those with a passion for problem-solving, a talent for coding, and a desire to build the efficient systems of tomorrow, a career in automation engineering is not just a job—it's a path to becoming an indispensable part of the modern digital economy.