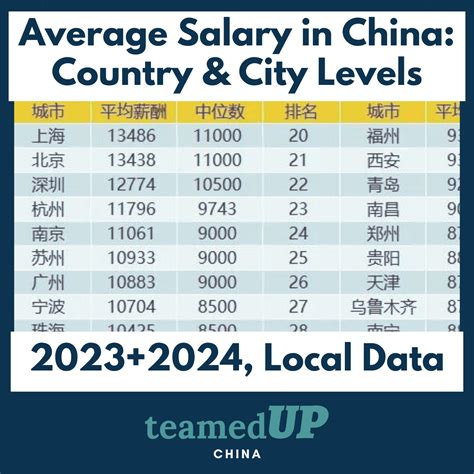
China's dynamic and rapidly evolving economy presents a world of opportunity for both local and international professionals. As one of the largest economic powerhouses, it offers unique career trajectories in cutting-edge industries. But what can you expect to earn? While the national average salary provides a baseline, a professional's earning potential in China can range from approximately ¥75,000 CNY (about $10,400 USD) for entry-level roles in smaller cities to well over ¥1,000,000 CNY (about $138,000 USD) for senior executives in high-demand sectors.
This guide will break down the complexities of salaries in China, exploring the key factors that determine your earning potential and providing a data-driven look at what to expect.
What Does the Average Salary in China Represent?
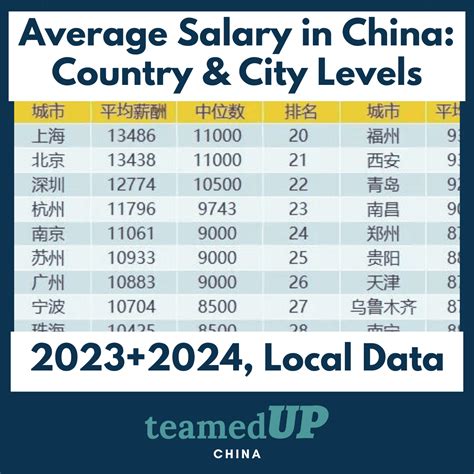
Before diving into the numbers, it's crucial to understand what the "average annual salary" figure signifies. This metric is typically a mean average calculated by national authorities, encompassing all workers across various industries, locations, and experience levels—from factory workers to tech CEOs.
Therefore, the national average serves as a broad economic indicator rather than a specific benchmark for professional, skilled roles. For ambitious professionals, especially those in major urban centers, actual salaries are often significantly higher than the national average. This figure is a starting point, and your personal earnings will be shaped by a combination of the influential factors discussed below.
The National Average Salary in China

According to the most recent official data, China's National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) reported that the average annual salary for urban non-private employees in 2022 was ¥114,029 CNY (approximately $15,800 USD). For employees in the private sector, the average was lower at ¥65,237 CNY (approximately $9,000 USD).
*(Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China. USD conversion based on an exchange rate of ~7.2 CNY to 1 USD; rates fluctuate.)*
However, these figures can be misleading for professionals considering roles in major cities. Data from salary aggregators and professional recruitment firms paints a more relevant picture for skilled workers. For example, reports from international HR firms often show average salaries for professional positions in major cities starting from ¥120,000 to ¥300,000 CNY ($16,600 to $41,600 USD) and rising steeply with experience.
A typical salary progression might look like this:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): ¥75,000 - ¥150,000 CNY ($10,400 - $20,800 USD)
- Mid-Career (3-7 years): ¥180,000 - ¥400,000 CNY ($25,000 - $55,500 USD)
- Senior/Managerial (8+ years): ¥450,000 - ¥800,000+ CNY ($62,500 - $111,000+ USD)
*(Source: Synthesized data from Payscale, Michael Page China Salary Guide, and industry reports.)*
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your individual salary in China is determined by a powerful combination of factors. Understanding these drivers is essential for negotiating compensation and planning your career path.
### Geographic Location: Tier 1 vs. Lower-Tier Cities
This is arguably the most significant factor. China's cities are often unofficially categorized into tiers based on economic size, development, and cost of living.
- Tier 1 Cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou): These megacities are the country's economic engines. They host the headquarters of most multinational corporations and domestic tech giants, offering the highest salaries to attract top talent. However, they also have the highest cost of living.
- "New" Tier 1 & Tier 2 Cities (Hangzhou, Nanjing, Chengdu, Suzhou): These rapidly developing cities are becoming major economic hubs in their own right, particularly in tech and advanced manufacturing. Salaries are competitive and often provide a better quality of life due to a lower cost of living compared to Tier 1.
- Tier 3 & 4 Cities: These smaller cities offer significantly lower salaries, as the economy is typically focused on traditional manufacturing, agriculture, or local services.
For example, a marketing manager in Shanghai might earn ¥400,000 CNY, while the same role in a Tier 3 city like Lanzhou might command ¥150,000 CNY.
### Industry and Specialization
Your industry has a massive impact on your earnings. High-growth, high-value sectors consistently offer top-tier compensation.
- High-Paying Industries: Technology (AI, Big Data, SaaS), Finance (Investment Banking, Venture Capital, Fintech), Biopharmaceuticals & Health, and Advanced Manufacturing (EVs, robotics) are currently the most lucrative fields.
- Mid-Range Industries: Consumer goods, professional services, education, and logistics offer solid, competitive salaries.
- Lower-Paying Industries: Traditional manufacturing, hospitality, and administrative support roles typically fall on the lower end of the professional salary scale.
Within an industry, specialization is key. An AI engineer will earn substantially more than a generalist IT support specialist.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for plays a crucial role in compensation structure and benefits.
- Foreign-Invested Enterprises (FIEs) / Multinational Corporations (MNCs): These companies, particularly from North America and Europe, have historically offered the highest base salaries and most comprehensive benefits packages to attract talent familiar with Western business practices.
- Domestic Private Companies (e.g., Tencent, Alibaba, Huawei): China's tech giants are highly competitive and often offer lucrative packages that include high base salaries, significant performance-based bonuses, and valuable stock options, especially for tech and R&D roles.
- State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): While their base salaries may be more modest compared to MNCs or tech giants, SOEs offer unparalleled job security, excellent social benefits (housing funds, healthcare, pensions), and a better work-life balance, which constitutes a significant part of the total compensation package.
### Years of Experience
As with any global market, experience is directly correlated with salary. China's fast-paced environment, however, can lead to rapid career progression. Professionals who demonstrate strong performance and adaptability can often move into managerial roles faster than in more mature Western markets. An employee with 10 years of experience, particularly with leadership responsibilities, can expect to earn several multiples of an entry-level salary.
### Level of Education
A strong educational background is highly valued. A bachelor's degree is typically the minimum requirement for professional roles. However, candidates with master's degrees, PhDs, or MBAs from prestigious domestic or international universities can command significantly higher starting salaries and are often fast-tracked for leadership positions. Specialized certifications in fields like finance (CFA) or project management (PMP) also boost earning potential.
Job Outlook

While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not provide outlooks for China, economic trends from sources like the World Bank and reports from major recruitment firms provide strong indicators. The Chinese government's strategic focus on technological self-sufficiency, green energy, and advanced manufacturing ("Made in China 2025" initiative) is fueling massive demand for skilled professionals in these areas.
- High-Growth Fields: AI Specialists, Data Scientists, R&D Engineers, Biopharma Scientists, and experts in carbon neutrality are in extremely high demand.
- Steady Growth: Roles in digital marketing, e-commerce, wealth management, and healthcare administration continue to see robust growth as China's middle class expands.
While China's economy faces some headwinds, the long-term outlook for skilled, adaptable professionals in strategic sectors remains highly positive.
Conclusion

Navigating the job market in China offers a rewarding and dynamic career path. While the national "average salary" provides a basic economic snapshot, it doesn't tell the whole story. Your true earning potential is a reflection of a nuanced interplay between location, industry, company type, experience, and education.
For anyone considering a career in China, the key takeaways are:
- Aim for Tier 1 or strong Tier 2 cities for the highest earning potential.
- Target high-growth industries like technology, finance, and advanced manufacturing.
- Leverage your experience and education to negotiate a competitive salary.
- Understand the trade-offs between different company types—high-risk, high-reward tech firms versus the stability of SOEs and MNCs.
By strategically positioning yourself within China's evolving economic landscape, you can unlock significant professional growth and financial success.