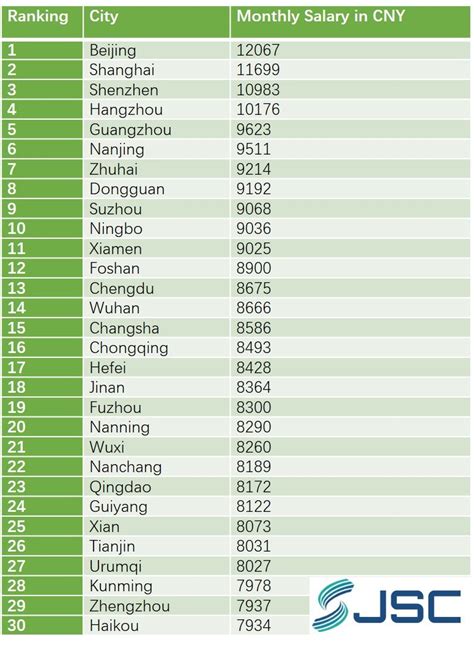
What is the Average Salary in China? A Deep Dive for 2024
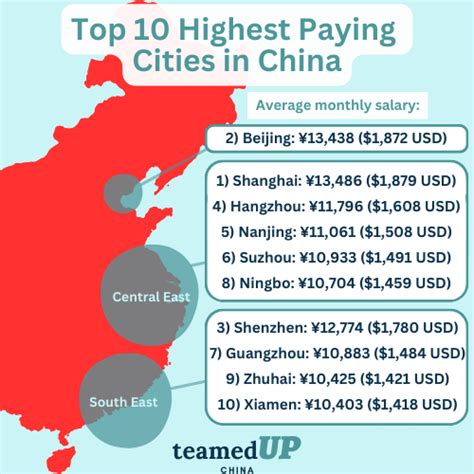
China's economy is a global powerhouse, offering a dynamic and rapidly evolving job market. For professionals considering a career in the country or simply seeking to understand its economic landscape, one of the most pressing questions is: "What can I expect to earn?" While a single "average salary" figure can be misleading, understanding the data reveals a landscape of immense opportunity, with earning potential in major cities rivaling that of many Western nations.
This article will provide a data-driven look at the average salary in China, breaking down the key factors that determine your real-world earning potential.
Understanding the 'Average Salary' in China
Unlike a specific job title, the "average Chinese salary" is a broad economic indicator, not a role one performs. It represents a statistical measure of the typical earnings across a vast and diverse workforce of hundreds of millions.
Official figures are typically released by China's National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). It's crucial to understand that these figures often focus on *urban* employees and are usually divided into two main categories:
1. Urban Non-Private Sector: Includes state-owned enterprises (SOEs), government agencies, and collective-owned units. These salaries are often higher due to greater stability and benefits.
2. Urban Private Sector: Includes privately-owned domestic companies and multinational corporations (MNCs).
This article will analyze both official data and figures from salary aggregators to provide a holistic view of the compensation landscape in China.
The National Average Salary in China

According to the latest data from China's National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), the average annual salary for urban employees continues to show steady growth.
- Official 2023 Data (Urban Non-Private Sector): The average annual salary was 120,698 Chinese Yuan (CNY). This translates to approximately $16,650 USD per year, or 10,058 CNY per month.
- Official 2023 Data (Urban Private Sector): The average annual salary was 65,237 CNY. This is approximately $9,000 USD per year, or 5,436 CNY per month.
*(Note: USD conversions are based on an approximate exchange rate of 1 USD = 7.25 CNY and are for illustrative purposes. Exchange rates fluctuate.)*
Why the large gap? The official "private sector" data includes millions of workers in lower-paying manufacturing and service jobs, pulling the average down. In contrast, professionals in high-demand fields within the private sector often earn significantly more than the non-private sector average.
For a more practical perspective, salary aggregators provide insight into professional roles. For instance, Payscale reports an average base salary in China of 291,000 CNY (approx. $40,100 USD), reflecting the higher earnings of white-collar professionals who are more likely to self-report their data on such platforms.
This highlights a key reality: the national average is just a starting point. Your actual salary will be determined by a combination of powerful factors.
Key Factors That Influence Salary in China
Your background, location, and career choices are the most significant determinants of your earning potential in China. Let's explore the most impactful factors.
### Level of Education
Education level creates a distinct salary premium in China's competitive job market. While a bachelor's degree is often the minimum requirement for professional roles, advanced degrees open doors to higher-paying, specialized positions.
- Bachelor's Degree: The standard for entry-level professional and administrative roles.
- Master's Degree / MBA: Highly valued in fields like finance, technology, and management. Graduates can often command a starting salary 30-50% higher than those with only a bachelor's degree.
- Ph.D.: Essential for R&D, university-level instruction, and senior scientific roles, particularly in sectors like pharmaceuticals, AI, and engineering, where they command the highest salaries.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most powerful driver of salary growth. Chinese employers place a high value on proven skills and a track record of success.
- Entry-Level (0-3 Years): Typically earn at or slightly below the city's average for their role. The focus is on learning and development.
- Mid-Career (3-8 Years): Professionals with proven experience see significant salary jumps. This is often the period of fastest career and salary progression.
- Senior/Managerial (8+ Years): Senior experts and managers are highly compensated. Earnings at this level, especially in Tier 1 cities and high-demand industries, can easily exceed 600,000 CNY ($82,750 USD) or much more.
### Geographic Location
Location is a critical factor, with a massive disparity in both salaries and cost of living between different tiers of cities.
| City Tier | Major Cities | Typical Salary Range (Professional Roles) | Key Characteristics |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Tier 1 | Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou | 250,000 - 700,000+ CNY | Highest salaries, greatest number of MNCs and tech giants, highest cost of living. |
| New Tier 1 / Tier 2| Hangzhou, Nanjing, Chengdu, Suzhou | 150,000 - 450,000 CNY | Strong economies, growing tech and finance hubs, more manageable cost of living. |
| Tier 3 & Below | Various provincial capitals and smaller cities | 80,000 - 200,000 CNY | Lower salaries, dominated by traditional industries and SOEs, significantly lower cost of living. |
*Source: Analysis based on data from Michael Page's 2024 China Salary Guide and Glassdoor salary reports.*
### Company Type
The type of company you work for directly impacts your compensation structure and overall package.
- Multinational Corporations (MNCs): Generally offer the highest base salaries and most comprehensive benefits packages (e.g., health insurance, housing allowance). They seek international talent and offer a more Western-style corporate culture.
- Private Tech Giants (e.g., Tencent, Alibaba, ByteDance): Known for very competitive salaries, stock options, and performance-based bonuses. The work culture can be demanding, often associated with the "996" model (9 am to 9 pm, 6 days a week).
- State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): Offer moderate salaries but provide unparalleled job security, excellent social benefits, and a better work-life balance. They are the backbone of industries like banking, energy, and telecommunications.
### Area of Specialization / Industry
As in any major economy, your industry dictates your value. Sectors at the forefront of China's economic strategy offer the highest compensation.
Top-Paying Industries:
1. Technology & AI: Software engineers, data scientists, and AI/machine learning specialists in cities like Shenzhen and Hangzhou are among the highest-paid professionals in the country.
2. Financial Services: Roles in investment banking, private equity, and venture capital in financial hubs like Shanghai and Beijing offer exceptionally high salaries and bonuses.
3. Life Sciences & Healthcare: With a growing and aging population, R&D and senior commercial roles in pharmaceuticals and medical devices are highly lucrative.
4. Professional Services: Management consultants and senior legal professionals at top-tier firms are very well-compensated.
Economic and Job Market Outlook in China
While facing global economic headwinds, China's job market continues to evolve. The government is heavily invested in transitioning the economy from traditional manufacturing to a high-value, technology-driven model.
According to a 2024 report from the World Bank, long-term growth will depend on structural reforms that boost productivity and rebalance the economy towards consumption and services. This points to sustained demand in sectors like:
- The Digital Economy: E-commerce, FinTech, and enterprise software.
- Green Technology: Renewable energy, electric vehicles, and environmental engineering.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Robotics, aerospace, and semiconductors.
For job seekers, this means that aligning skills with these strategic growth areas will ensure strong career prospects and salary potential for years to come.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways

Navigating the salary landscape in China requires looking beyond a single national average. For any prospective student or professional considering a career there, here are the key takeaways:
- The "Average" is Just a Benchmark: The official average salary is a useful economic indicator but has little bearing on the earning potential for skilled professionals in major urban centers.
- Location is Everything: Your salary can more than double by moving from a Tier 3 to a Tier 1 city, though cost of living will rise accordingly.
- Specialize in High-Growth Fields: Technology, finance, and advanced healthcare are where the highest salaries and most robust opportunities are found.
- Experience Pays: Demonstrating expertise and leadership is the surest path to significant salary increases throughout your career.
China's job market is complex, competitive, and full of opportunity. By strategically choosing your industry, location, and company, you can build a highly rewarding and financially prosperous career in one of the world's most dynamic economies.