For professionals with a knack for numbers and a passion for strategic planning, a career as a budget analyst offers a stable and rewarding path. These financial stewards are essential to the health of every organization, from government agencies to global corporations. But what does this critical responsibility translate to in terms of compensation?
While a six-figure salary is well within reach, your earning potential is shaped by a variety of factors. In this in-depth guide, we will break down the typical budget analyst salary and explore the key variables—from your education and location to your area of specialization—that can significantly boost your income.
What Does a Budget Analyst Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it’s important to understand the role. A budget analyst is a financial professional responsible for developing, analyzing, and executing budgets. They are the gatekeepers of an organization's financial resources, ensuring money is spent efficiently and effectively.
Key responsibilities include:
- Preparing budget reports and presenting them to senior management.
- Monitoring spending to ensure it stays within budget limits.
- Analyzing financial data to identify trends and make future spending recommendations.
- Advising program managers and department heads on the financial implications of their decisions.
- Justifying budget proposals and funding requests.
In essence, they provide the critical analysis that allows an organization to achieve its strategic goals without overspending.
Average Budget Analyst Salary
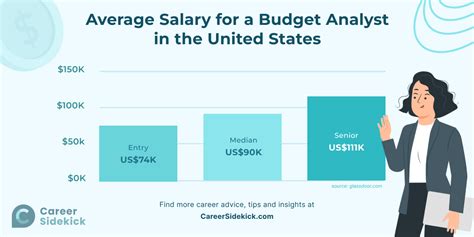
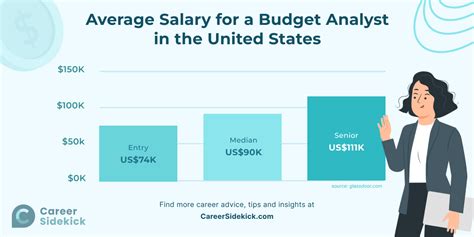
So, what can you expect to earn? The most authoritative data provides a strong baseline for understanding compensation in this field.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for budget analysts was $84,940 in May 2023. This figure represents the midpoint—half of all budget analysts earned more than this, and half earned less.
However, the full salary spectrum reveals the significant potential for growth:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $59,710 (typical for entry-level positions).
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $134,730 (typical for senior, experienced analysts in high-paying sectors).
Data from reputable salary aggregators, which compile real-time, user-reported data, aligns with these findings. For example, Salary.com places the median budget analyst salary around $88,140 as of early 2024, with a common range falling between $77,880 and $99,440. Glassdoor reports a similar average base pay of approximately $85,000, with total pay often increasing with bonuses and profit-sharing.
This data paints a clear picture: while a starting salary is solid, strategic career moves can propel you toward a six-figure income.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary is not a static number. It's a dynamic figure influenced by your unique qualifications, experience, and career choices. Here are the most impactful factors.
###
Level of Education
A bachelor’s degree in finance, accounting, economics, or a related field is the standard entry point for a budget analyst career. However, advanced education and certifications are a direct pathway to higher earnings.
- Master's Degree: Pursuing a Master of Business Administration (MBA) or a specialized master's degree in finance or public administration can significantly increase your earning potential. It signals advanced analytical and strategic thinking skills, making you a prime candidate for senior and leadership roles.
- Professional Certifications: Earning a respected certification demonstrates a high level of expertise and commitment to the field. Key certifications that boost a budget analyst's salary include:
- Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM): Essential for those in the public sector.
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA): Highly valued everywhere for its rigorous standards in accounting and finance.
- Certified Management Accountant (CMA): Focuses on corporate finance and accounting, ideal for private sector analysts.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth. As you gain more experience, you take on more complex tasks, manage larger budgets, and assume greater strategic responsibility.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Analysts typically focus on data gathering, preparing basic reports, and monitoring departmental budgets. Salaries generally align with the lower end of the national range, from $60,000 to $75,000.
- Mid-Career (3-8 years): With proven experience, analysts develop complete budgets, conduct more complex forecasting, and begin advising department heads. Their salaries move toward the national median and beyond, often in the $75,000 to $95,000 range.
- Senior/Lead Analyst (9+ years): Senior analysts often oversee an organization's entire budget process, present to C-suite executives, and play a key role in long-term strategic planning. They command top-tier salaries, frequently exceeding $100,000 and reaching the $130,000+ mark reported by the BLS.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for budget analysts vary significantly by state and metropolitan area due to differences in cost of living and demand for financial professionals.
According to BLS data, the top-paying states for budget analysts include:
- District of Columbia
- California
- Maryland
- Washington
- New York
Metropolitan areas like Washington D.C., San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA, and New York-Newark-Jersey City, NY-NJ-PA consistently offer the highest average salaries, often well over $100,000. Conversely, salaries in rural areas and states with a lower cost of living will typically be closer to the lower end of the national range.
###
Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a major impact on your compensation. The BLS identifies a clear hierarchy in median pay by industry.
- Private Sector (Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services): This is often the highest-paying sector. Companies in tech, consulting, and financial services rely on sharp budget analysis to maximize profit and often pay a premium for top talent.
- Federal Government: As one of the largest employers of budget analysts, the federal government offers competitive salaries, excellent benefits, and a structured pay scale (the General Schedule or GS system). The work is stable and provides opportunities for advancement.
- State and Local Government: These roles also offer job security and strong benefits packages. While salaries may be slightly lower than in the federal government or top private firms, they remain competitive.
- Educational Services and Non-Profits: While compensation in these sectors is generally lower, the work often provides a strong sense of mission and purpose.
###
Area of Specialization
Within the field, specializing in a high-stakes area can lead to higher pay. An analyst managing a multi-billion dollar capital expenditure budget for a tech firm will likely earn more than one managing a smaller operational budget.
Potential specializations include:
- Capital Budgeting: Analyzing large-scale, long-term investments like new facilities or technology infrastructure.
- Operational Budgeting: Focusing on the day-to-day financial needs of departments.
- Program/Project Budgeting: Allocating and monitoring funds for specific, time-bound initiatives.
- Public Sector Budgeting: Navigating the complex regulations and funding cycles of government finance.
Job Outlook

The future for budget analysts is stable. The BLS projects job growth of 2 percent for budget analysts from 2022 to 2032. While this is slower than the average for all occupations, it reflects the role's fundamental importance.
Organizations across all sectors will always need skilled professionals to manage their finances effectively. This ensures a steady, ongoing demand for budget analysts, making it a secure career choice for those entering the field.
Conclusion

A career as a budget analyst is an excellent choice for detail-oriented individuals who enjoy making a tangible impact on an organization's success. With a median salary of nearly $85,000 and a clear path to earning over $130,000, the financial rewards are substantial.
Your ultimate earning potential is in your hands. By investing in advanced education and certifications, gaining diverse experience, and strategically choosing your location and industry, you can build a highly successful and lucrative career as a financial guardian. For those ready to turn numbers into strategy, the opportunities are waiting.