Introduction

Have you ever dreamed of building a career in a city pulsing with innovation, culture, and opportunity? Austin, Texas, consistently ranks as one of the nation's most desirable places to live and work. But with its booming tech scene and rising cost of living, a crucial question emerges for any aspiring professional: What can you actually *earn* here? More specifically, what do City of Austin salaries look like, and is a career in public service a financially viable and rewarding path in this dynamic metropolis?
This guide is designed to be your definitive resource, whether you're a recent graduate considering your first move, a seasoned professional contemplating a career change, or simply curious about the financial landscape of public sector employment in the Texas capital. We will dissect the City of Austin's salary structures, explore the myriad of roles available, and compare public service compensation with the city's thriving private sector. For many, a public sector career is about more than just a paycheck; it's about contributing to the community you call home. I once advised a client torn between a lucrative but volatile tech startup offer and a stable, mission-driven role with a municipal government. The decision became clear only after we unpacked the entire compensation picture—benefits, pension, job security, and work-life balance—proving that the "richest" career isn't always the one with the highest base salary.
This article will provide you with the data, context, and expert analysis needed to make an informed decision about your own professional journey in Austin. We will explore everything from entry-level pay to executive compensation, the factors that can maximize your earning potential, and the long-term outlook for a career dedicated to serving the citizens of Austin.
### Table of Contents
- [Working for the City of Austin: An Overview of Roles and Responsibilities](#working-for-the-city-of-austin-an-overview-of-roles-and-responsibilities)
- [City of Austin Salary Structure: A Deep Dive](#city-of-austin-salary-structure-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Your Salary in Austin](#key-factors-that-influence-your-salary-in-austin)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth in Austin](#job-outlook-and-career-growth-in-austin)
- [How to Get a Job with the City of Austin](#how-to-get-a-job-with-the-city-of-austin)
- [Conclusion: Is a City of Austin Career Right for You?](#conclusion-is-a-city-of-austin-career-right-for-you)
Working for the City of Austin: An Overview of Roles and Responsibilities
When people think of "city jobs," they might picture a small set of administrative or bureaucratic roles. The reality of a major metropolitan employer like the City of Austin is vastly different. The City is a massive, multifaceted organization responsible for an incredible array of services that directly impact the daily lives of over 974,000 residents. It functions like a large-scale corporation, but its "product" is a safe, functional, and vibrant community.
Employment with the City of Austin means you could be working in one of over 40 departments, each with its own unique mission and set of professional roles. These aren't just desk jobs; they are hands-on, technical, creative, and leadership positions that build, maintain, and innovate the city.
Core Departments and Job Categories:
- Public Utilities (Austin Energy & Austin Water): As a publicly owned utility, Austin Energy employs hundreds of engineers (electrical, civil, mechanical), lineworkers, power plant operators, data analysts, conservation specialists, and customer service professionals. Austin Water has similar needs, employing hydrologists, water quality technicians, pipefitters, and infrastructure project managers. These are some of the most critical and often well-compensated roles within the city.
- Public Safety (Police, Fire, EMS): These uniformed, civil-service positions are the most visible city roles. Beyond Police Officers, Firefighters, and Paramedics, these departments also employ 911 dispatchers, crime scene technicians, data analysts, fleet mechanics, and administrative support staff.
- Infrastructure and Development (Public Works, Transportation, Planning): This cluster of departments is responsible for the physical shape of the city. They employ civil engineers to design roads and bridges, city planners to manage zoning and long-term growth, transportation specialists to analyze traffic flow, and skilled tradespeople to build and maintain it all.
- Community Services (Parks and Recreation, Public Library, Public Health): These departments focus on the quality of life for Austinites. Roles range from librarians and archivists to park rangers, recreation coordinators, epidemiologists, and social workers.
- Corporate and Administrative Services (IT, HR, Finance, Law, Communications): Just like any large organization, the City needs a strong internal support structure. It is a major employer of IT professionals (cybersecurity analysts, network engineers, software developers), accountants, financial analysts, attorneys, human resources specialists, and communications experts.
### A Look at Different Roles: A "Day in the Life"
To make this more concrete, let's imagine a day for three different City of Austin employees:
- A "Day in the Life" of a City Planner: *Maria arrives at her office downtown and spends the morning reviewing a new mixed-use development proposal. She cross-references the plans with the city's zoning codes and the Austin Strategic Mobility Plan, noting potential conflicts with traffic flow and green space requirements. In the afternoon, she meets with a neighborhood association to present the proposed changes and gather community feedback. Her day is a blend of technical analysis, legal interpretation, and public engagement, all with the goal of shaping Austin's future growth responsibly.*
- A "Day in the Life" of an Electrical Lineworker (Austin Energy): *David's day starts with a team briefing on the day's work orders. Today, they're tasked with upgrading a transformer in a growing residential area. The work is physically demanding and requires immense focus and adherence to safety protocols, especially when working with high-voltage lines. After a storm rolls through in the evening, he's called back out to identify a fault and restore power to a grateful neighborhood, experiencing the direct and immediate impact of his work.*
- A "Day in the Life" of a Cybersecurity Analyst (Communications & Technology Management): *Samantha begins her day by reviewing threat intelligence feeds and analyzing overnight alerts from the city's security information and event management (SIEM) system. She spends a few hours conducting a vulnerability scan on a new software application before it's deployed to the Public Library system. Later, she leads a short training session for the Finance department on recognizing phishing attempts. Her work is a constant, unseen battle to protect sensitive citizen data and ensure the city's digital infrastructure remains secure and operational.*
City of Austin Salary Structure: A Deep Dive

Understanding compensation at the City of Austin requires looking beyond a single "average salary" figure. The City utilizes a structured and transparent pay system, which is a significant departure from the often-opaque compensation practices in the private sector. This system is designed to ensure equity and provide a clear path for salary progression.
As of October 1, 2023, the City of Austin has established a living wage of $20.00 per hour as the minimum for all regular, full-time city employees. This is a foundational commitment to its workforce.
The core of the City's compensation model is its Pay Plan system. Most civilian jobs are assigned a specific "Pay Grade." Each grade has a minimum, midpoint, and maximum salary. Your starting salary within that range is typically determined by your qualifications and experience.
According to the official City of Austin Fiscal Year 2024 Pay Plan, the salary ranges are publicly available. This transparency is a major benefit for potential applicants. For example, Pay Grade PI1 has a range of $20.00/hour to $25.50/hour, while a senior executive grade like EX7 has a range of $150,716.80 to $203,465.60 annually.
### Salary Brackets for Different Career Stages and Roles
Let's break down what this means in practice by looking at sample salary ranges for various positions. The data below is derived from the official FY2024 City of Austin Pay Plans and cross-referenced with data from salary aggregators like Glassdoor and Salary.com for context.
Entry-Level Positions (0-3 Years of Experience)
These roles typically require a high school diploma, an associate's degree, or a bachelor's degree with limited professional experience.
| Job Title | Pay Grade | Typical Annual Salary Range | Notes |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Administrative Specialist | OC4 | $44,782 - $55,931 | General office support and coordination. |
| Library Customer Service Aide | LI1 | $41,600 - $49,836 | Front-line staff at public library branches. |
| Engineering Associate | EN2 | $64,313 - $81,931 | Entry-level engineering support, requires B.S. |
| Public Health Technician I | HE3 | $49,150 - $62,566 | Field and lab work for the Public Health Dept. |
| Park Ranger | PR2 | $48,942 - $62,393 | Patrols parks, provides info, ensures safety. |
Mid-Career Positions (4-10 Years of Experience)
These roles usually require a degree and significant relevant experience, and often involve project management, specialized skills, or supervisory duties.
| Job Title | Pay Grade | Typical Annual Salary Range | Notes |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Senior Planner | PL3 | $77,542 - $99,236 | Manages complex zoning cases, long-range plans. |
| Financial Analyst, Senior | FN3 | $77,542 - $99,236 | Budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis. |
| IT Applications Analyst | IT3 | $81,660 - $104,540 | Supports and develops city software applications. |
| Project Manager (Public Works) | PM3 | $90,126 - $115,377 | Manages mid-sized infrastructure projects. |
| Police Officer (5 years) | *Civil Service* | ~$95,000+ (incl. stipends) | Pay set by union agreement, increases with tenure. |
Senior & Leadership Positions (10+ Years of Experience)
These positions involve managing departments, large teams, or critical city-wide functions. They require extensive experience and often advanced degrees (e.g., MPA, MBA, P.E. license).
| Job Title | Pay Grade | Typical Annual Salary Range | Notes |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Engineering Manager | EM2 | $114,836 - $146,556 | Manages a team of engineers and large projects. |
| Division Manager (e.g., Parks) | MG2 | $104,153 - $133,370 | Oversees a major division within a department. |
| Assistant Director | EX3 | $123,073 - $157,601 | Second-in-command for a major city department. |
| Chief Information Security Officer | EX5 | $136,864 - $184,764 | Leads city-wide cybersecurity strategy and ops. |
| Assistant City Manager | *Exec Contract* | $250,000 - $300,000+ | Top-level executive overseeing multiple depts. |
*Source: City of Austin Fiscal Year 2024 Pay Plan documents. Civil Service pay for Police and Fire is determined by separate collective bargaining agreements.*
### Beyond the Base Salary: A Look at Total Compensation
A crucial mistake when evaluating any job offer is focusing solely on the salary. Public sector employment, especially with a well-funded city like Austin, often provides a robust benefits package that adds significant value.
- Health Insurance: The City of Austin offers comprehensive medical, dental, and vision plans for employees and their families, often with lower premiums than comparable private sector plans.
- Retirement (Pension): This is a key differentiator. Most permanent City of Austin employees are enrolled in the City of Austin Employees' Retirement System (COAERS), a defined-benefit pension plan. This provides a guaranteed lifetime income after retirement based on your salary and years of service. This is an increasingly rare benefit, especially in the tech-dominated private sector where 401(k)s are the norm.
- Paid Time Off: The City offers generous vacation leave, sick leave, and paid holidays. Employees accrue leave based on their years of service, often reaching 4-5 weeks of vacation per year in senior roles, in addition to separate sick time.
- Other Benefits: Additional perks often include tuition reimbursement programs, employee assistance programs (EAP) for mental health and wellness, life insurance, disability insurance, and access to wellness programs.
When you factor in the value of the pension and lower healthcare costs, the "total compensation" for a city job can often be more competitive with the private sector than the base salary alone might suggest.
Key Factors That Influence Your Salary in Austin

Whether you're aiming for a job with the City of Austin or in the broader Austin market, your earning potential isn't fixed. Several key factors will significantly influence your salary. Understanding and strategically navigating these factors is essential to maximizing your compensation.
###
Level of Education
Your educational background serves as the foundation of your career and is a primary determinant of your starting salary and long-term earning potential.
- Base Qualifications: For many City of Austin roles, a high school diploma or GED is the minimum requirement, particularly for skilled trades, administrative support, and some entry-level operational jobs. A bachelor's degree, however, is the typical entry point for most professional-track careers in fields like planning, finance, IT, and management. It immediately opens the door to higher pay grades. For example, an Engineering Associate (requiring a B.S. in Engineering) starts at a pay grade with a minimum over $64,000, significantly higher than administrative roles.
- Advanced Degrees (Master's/PhD): An advanced degree can provide a substantial salary boost and is often a prerequisite for senior leadership positions. A Master of Public Administration (MPA) or Master of Business Administration (MBA) is highly valued for management and director-level roles. A Master of Science in Engineering or Information Technology can push a technical expert's salary into the upper echelons of the city pay scale. In the private sector, particularly in R&D or specialized finance roles, a PhD can command a premium salary. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), on a national level, individuals with a master's degree earn a median of nearly 18% more than those with only a bachelor's degree.
- Professional Certifications: In many fields, specific certifications are as valuable, if not more so, than a graduate degree. They signal proven expertise in a specific domain. For city jobs, a Professional Engineer (P.E.) license is critical for civil engineers seeking senior project management roles and can add tens of thousands to an annual salary. A Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is highly sought after for project managers in IT and Public Works. In cybersecurity, certifications like CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) or CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) are industry standards that command top dollar both in government and private industry.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is perhaps the single most powerful driver of salary growth throughout your career. Employers pay for proven track records and the wisdom that comes from navigating real-world challenges.
- Entry-Level (0-3 years): At this stage, you're primarily paid for your potential and academic qualifications. Your starting salary will likely be near the minimum of the assigned pay grade for a City of Austin job. In the private sector, negotiation might offer a little more flexibility. The focus here is on learning and building a foundation.
- Mid-Career (4-10 years): This is where significant salary growth occurs. You've demonstrated competence and can now manage projects, mentor junior staff, and operate with greater autonomy. For City employees, this means progressing through the "steps" within your pay grade and qualifying for promotions to higher grades. A Planner I might be promoted to a Planner II and then a Senior Planner, each jump coming with a substantial pay increase. For instance, moving from an IT Analyst (Grade IT2, max ~$92k) to an IT Analyst Senior (Grade IT3, max ~$104k) represents a significant career step.
- Senior/Expert Level (10+ years): At this stage, you are valued for your deep expertise, strategic insight, and leadership. Your salary reflects your ability to manage large teams, control significant budgets, and solve the most complex problems. For the City of Austin, these are the Division Manager, Department Director, and Executive-level roles. A Senior Engineer with 15 years of experience and a P.E. license could be managing multi-million dollar infrastructure projects and earning well over $130,000. In the private sector, this is the level of a Principal Engineer, a Director of Marketing, or a Senior Finance Manager, where salaries in Austin's tech and finance sectors can easily exceed $180,000 - $200,000.
###
Geographic Location (Cost of Living Context)
While this article focuses on Austin, it's critical to understand how Austin's salaries stack up in the context of its cost of living and in comparison to other cities.
- Austin's Cost of Living: Austin is an expensive city. According to data from the Council for Community and Economic Research's Cost of Living Index (Q3 2023), Austin's overall cost of living is approximately 9.5% higher than the national average. The primary driver is housing, which is nearly 26% higher than the national average. This means that a $90,000 salary in Austin does not have the same purchasing power as a $90,000 salary in a city like San Antonio or Houston, where the cost of living is at or below the national average.
- Comparison to Other Texas Cities: Salaries in Austin, for both public and private sector jobs, are generally higher than in Dallas, Houston, or San Antonio to compensate for the higher cost of living. For example, according to Salary.com, the median salary for a Software Engineer in Austin is about 5-7% higher than in Dallas or Houston. City of Austin salaries are also competitive and often higher than their municipal counterparts in other Texas cities.
- Comparison to Other Tech Hubs: When compared to major tech hubs like San Francisco or New York, Austin is significantly more affordable. While salaries for a tech role in the Bay Area might be 30-50% higher, the cost of living there is over 80% higher than the national average. This "salary-to-cost-of-living" ratio is a major reason why Austin remains an attractive destination for professionals. Your paycheck goes further here than in coastal tech hubs.
###
Public vs. Private Sector in Austin
The choice between a public sector career with the City of Austin and a private sector role is one of the most significant decisions a professional in Austin can make.
- Salary: On average, the private sector—especially in tech and finance—offers higher base salaries. A Senior Software Engineer at a major tech company like Oracle or a well-funded startup in Austin can earn a base salary of $150,000 - $200,000+, which is higher than most non-executive city IT roles. However, the City's structured pay scales provide more predictable salary growth.
- Bonuses & Equity: This is a major private sector advantage. Tech and sales professionals often receive substantial annual bonuses, stock options, or RSUs (Restricted Stock Units) that can add 20-50% or more to their total compensation. This type of variable, high-upside pay is absent in government work.
- Job Security & Stability: The public sector is the clear winner here. City of Austin jobs, particularly after a probationary period and for those in civil service roles, offer exceptional job security. Layoffs are rare compared to the volatile tech industry, which often sees cycles of boom and bust.
- Benefits & Retirement: As discussed earlier, the City's pension plan (COAERS) and often more affordable health insurance provide immense long-term financial security that is difficult to quantify but extremely valuable, especially when planning for retirement.
- Work-Life Balance: While not universal, government jobs are well-known for offering a better work-life balance. A standard 40-hour work week is more common, and there's often a stronger emphasis on using paid time off. Tech startups, in contrast, are notorious for demanding long hours.
###
Area of Specialization
Within both the City of Austin and the broader job market, your chosen field of specialization has a massive impact on your earnings.
- High-Demand Fields (City of Austin):
- Engineering: With Austin's constant growth, Civil, Electrical, and Water Resource Engineers are in perpetual demand to manage infrastructure and utility projects. These are consistently among the highest-paid professional tracks in the city government.
- Information Technology: Cybersecurity, cloud infrastructure management, and data analytics are critical needs. The City must compete with the private sector for this talent, driving up salaries for specialized IT roles.
- Skilled Trades: Licensed Electricians, Water/Wastewater Plant Operators, and heavy equipment mechanics are difficult to recruit and retain, making them some of the best-compensated non-degree roles.
- High-Demand Fields (Austin Private Sector):
- Software Engineering: Austin is a major hub for software development. Expertise in areas like AI/Machine Learning, full-stack development, and DevOps can command salaries well over $200,000 at senior levels.
- Finance & Sales: Corporate finance roles at large companies (Dell, Oracle) and high-commission sales roles in the tech sector are also among the city's highest-paying jobs.
###
In-Demand Skills
Beyond your job title, possessing specific, high-value skills can increase your leverage in salary negotiations and make you a more competitive candidate.
- Data Analysis: The ability to work with data is a valuable skill in any department. Proficiency in tools like SQL, Python (with libraries like Pandas), and data visualization software like Tableau or Power BI is highly sought after for roles in finance, transportation, public health, and city planning.
- Bilingualism (Spanish): Given Austin's demographics, fluency in Spanish is a significant asset, particularly for customer-facing and community engagement roles in the Library, Parks department, Public Health, and for first responders. The City of Austin often offers a pay stipend for certified bilingual employees.
- Project Management: Formal project management skills, especially with a PMP certification, are transferable across nearly every department and are essential for anyone looking to move into management.
- Cybersecurity: With the increasing threat of cyberattacks on public infrastructure, skills in network security, ethical hacking, and risk assessment are at a premium in the City's IT department.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): Expertise in GIS software like ArcGIS is critical for roles in city planning, public works, Austin Water, and emergency management to analyze spatial data and make informed decisions.
Job Outlook and Career Growth in Austin
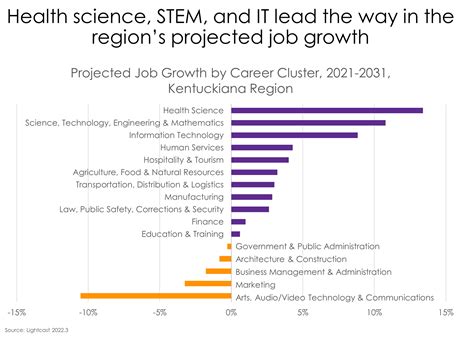
Austin is not just a city; it's an economic phenomenon. Its rapid growth provides a powerful engine for job creation in both the private and public sectors, creating a promising long-term outlook for professionals.
### The Austin Economic Engine
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides a clear picture of Austin's dynamic economy. The Austin-Round Rock Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) has consistently been one of the fastest-growing job markets in the country. Key data points highlight this trend:
- Overall Job Growth: Over the past decade, job growth in the Austin MSA has far outpaced the national average. Even with national economic fluctuations, Austin has shown remarkable resilience. The BLS projects continued strong growth in professional and business services, education and health services, and leisure and hospitality.
- Tech Sector Dominance: The BLS identifies "Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services" as a cornerstone of the Austin economy. This sector, which includes software developers, computer systems analysts, and engineers, is projected to see robust growth over the next ten years. Nationally, the BLS projects employment for software developers to grow by 25% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is amplified in a tech-centric market like Austin.
- Public Sector Growth: The city's population boom directly fuels the need for more public services. A growing population requires more infrastructure (roads, water, power), more public safety officers, more schools, more parks, and more administrative staff to manage it all. Therefore, the job outlook for the City of Austin is intrinsically linked to the city's own growth. As Austin continues to expand, so will the need for a larger municipal workforce.
### Emerging Trends and Future Challenges
While the outlook is overwhelmingly positive, professionals in Austin must be aware of emerging trends that will shape the future of work.
- The Rise of AI and Automation: Artificial intelligence will impact jobs across all sectors. For the City of Austin, this could mean automating certain data entry and administrative tasks, but it also creates a massive need for professionals skilled in AI implementation, data science, and ethics. The challenge will be to upskill the existing workforce to
