Pursuing a career as a community college professor is a path rich with purpose, offering the unique opportunity to shape the futures of a diverse student body. But beyond the immense personal satisfaction, what is the financial reality of this profession? For those considering this rewarding career, understanding the earning potential is a crucial step.
A career as a full-time community college professor offers a stable and competitive salary, with most professionals earning a median salary between $80,000 and $95,000 per year. However, this figure is just the starting point. Your ultimate earnings will be shaped by a variety of factors, from your educational background and field of expertise to your geographic location. This guide will break down everything you need to know about a community college professor's salary.
What Does a Community College Professor Do?

A community college professor, often referred to as an instructor or postsecondary teacher, is an educator who works at a two-year institution. These colleges offer associate degrees, vocational training, and affordable transfer pathways to four-year universities.
Unlike professors at large research universities, the primary focus of a community college professor is teaching. Their core responsibilities include:
- Instruction: Designing and delivering engaging lectures, labs, and classroom activities.
- Curriculum Development: Creating syllabi, selecting textbooks, and developing course materials.
- Student Support: Holding office hours, advising students on academic paths, and providing mentorship.
- Assessment: Grading assignments, creating exams, and evaluating student progress.
- Committee Work: Participating in departmental and college-wide committees to help guide the institution's academic and administrative policies.
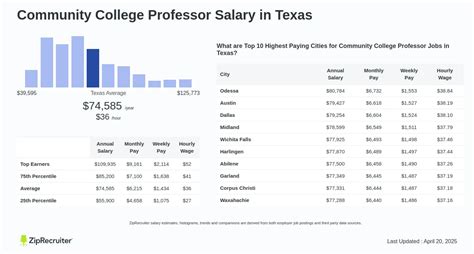
Average Community College Professor Salary
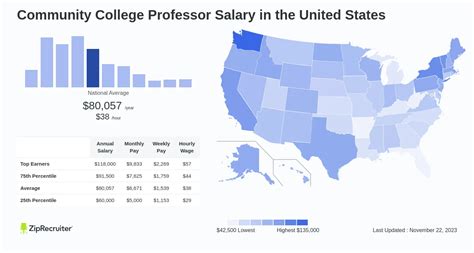
While salaries can vary significantly, we can establish a clear baseline by examining data from authoritative sources. It's important to distinguish between full-time, tenure-track faculty and part-time (adjunct) instructors, whose pay structures are vastly different.
For full-time community college professors, the data presents a strong financial picture.
- Salary.com reports the median annual salary for a Community College Professor in the United States is $91,968, with a typical range falling between $81,591 and $103,989 (2024).
- Glassdoor lists a national average base pay of $79,850 per year, based on user-submitted data (2024).
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups all "Postsecondary Teachers" together, reporting a median annual wage of $80,840 in May 2022. While this category is broader than just community colleges, it confirms a similar earning potential.
It is crucial to note that adjunct instructors are typically paid on a per-course basis. This rate can range from $2,500 to over $5,000 per course, depending on the institution and discipline. This model provides flexibility but often lacks the benefits and salary stability of a full-time position.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a community college professor isn't set in stone. Several key factors will directly influence your earning potential throughout your career.
###
Level of Education
Your academic credentials are the foundation of your career. For most community college teaching positions, a Master's degree in your subject area is the minimum requirement. However, holding a Doctorate (Ph.D. or Ed.D.) can provide a significant advantage. While not always required, a terminal degree often places you at a higher starting salary step and may be necessary for promotion to the highest academic ranks, such as a full professorship.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth in academia. Community colleges typically have a clear rank structure, with salary increasing at each level:
- Instructor (Entry-Level): This is the starting point for professors, usually with a Master's degree and less than five years of teaching experience.
- Assistant Professor: After a few years of successful teaching and service, an instructor may be promoted to this rank, which comes with a pay increase.
- Associate Professor: Typically achieved after five to seven years, this rank (often tied to tenure) represents a significant milestone with a corresponding salary bump.
- Full Professor: The highest academic rank, reserved for veteran educators with a long track record of excellence in teaching and service to the college. This position commands the highest salaries.
According to Payscale, a professor with less than one year of experience may start around $58,000, while a late-career professor with 20+ years of experience can earn upwards of $95,000 on average.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters immensely. Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the regional cost of living. States with major metropolitan areas and higher living costs tend to offer higher pay.
For example, community college professors in states like California, New York, Washington, and Massachusetts often report salaries that are 15-25% higher than the national average. Conversely, salaries in many rural states in the South and Midwest may fall below the national median. When evaluating a job offer, always consider it in the context of the local cost of living.
###
Institution Type
The specific college where you teach also plays a role. Large, well-funded community college districts in major urban centers typically have higher salary schedules than smaller, rural colleges. Publicly funded community colleges, which make up the vast majority of two-year institutions, often have transparent, union-negotiated salary scales that are publicly available. This allows prospective faculty to see exactly how salary progresses with experience and education.
###
Area of Specialization
Market demand directly impacts salaries. Professors in high-demand, high-wage fields can command significantly higher pay. Disciplines that have lucrative private-sector counterparts must offer competitive salaries to attract qualified experts.
- High-Paying Fields: Nursing, Computer Science, Engineering, Information Technology, and Business Administration.
- Lower-Paying Fields: Humanities, Social Sciences, and Fine Arts.
While the passion for one's subject is paramount, understanding the market value of your discipline can help set realistic salary expectations.
Job Outlook

The future for community college professors is bright. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for all postsecondary teachers is projected to grow 8 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by rising student enrollment. As four-year tuition costs continue to climb, more students are turning to community colleges as a cost-effective pathway to higher education and valuable vocational skills. This sustained demand will create a steady need for qualified and dedicated professors across the country.
Conclusion

A career as a community college professor offers a unique blend of intellectual engagement, community impact, and financial stability. While the path to a six-figure salary requires experience, strategic choices, and dedication, the profession provides a competitive income and a robust benefits package for full-time faculty.
Key Takeaways:
- Solid Earning Potential: Expect a median salary between $80,000 and $95,000 for full-time positions.
- Your Value is Key: Higher education, years of experience, and a high-demand specialization will significantly increase your earnings.
- Location Matters: Salaries are highest in states with a higher cost of living.
- Strong Future Demand: With a projected job growth of 8%, this is a stable and expanding career field.
For those passionate about education and looking for a meaningful career that also provides a comfortable living, becoming a community college professor is an excellent and achievable goal.