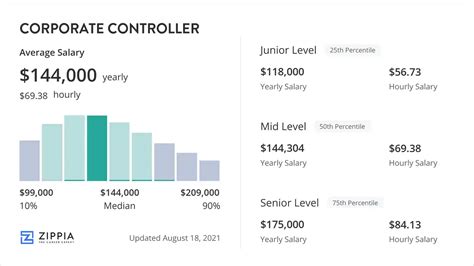
The role of a Corporate Controller is a cornerstone of a company's financial leadership—a demanding and prestigious position for any accounting and finance professional. For those with the ambition to climb the corporate ladder, this career path offers not only significant influence over a company's financial health but also substantial earning potential. A six-figure salary is the standard, with top-tier professionals in major markets often earning well over $250,000 annually.
But what exactly drives this impressive compensation? This guide will break down the corporate controller salary, exploring the national averages, the key responsibilities of the role, and the critical factors that will determine your ultimate earning power.
What Does a Corporate Controller Do?

Often described as the company's chief accountant, the corporate controller is responsible for the integrity and accuracy of all accounting operations. While the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) focuses on broad financial strategy and investor relations, the controller is hands-on, managing the day-to-day tactical functions of the finance department.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Financial Reporting: Preparing and presenting accurate monthly, quarterly, and annual financial statements in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Team Management: Overseeing the entire accounting team, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, and general ledger accountants.
- Internal Controls: Designing and implementing robust internal controls to safeguard company assets and ensure compliance with regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX).
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Assisting in the preparation of budgets and financial forecasts to guide business planning.
- Audits and Compliance: Serving as the primary point of contact for external auditors and ensuring compliance with all local, state, and federal tax laws.
In essence, the controller ensures the financial engine of the company runs smoothly, accurately, and efficiently.
Average Corporate Controller Salary
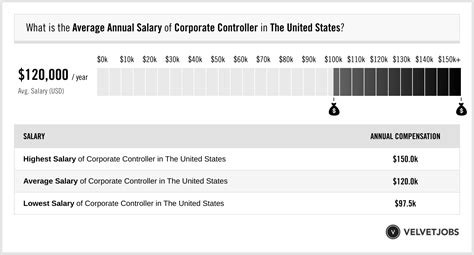
Due to the high level of responsibility, corporate controller salaries are highly competitive. While figures vary based on numerous factors, we can establish a strong baseline by looking at data from leading salary aggregators.
According to Salary.com, the median corporate controller salary in the United States is approximately $167,760 as of early 2024. The typical salary range for this role falls between $142,570 and $195,960.
Other authoritative sources provide a similar picture:
- Payscale reports a wide range, from $91,000 to $182,000, with a median of around $129,500, reflecting a broad spectrum of company sizes and experience levels.
- Glassdoor lists a national average base pay of $145,188 per year based on user-submitted data.
It's important to remember that these figures represent base salaries. Many controllers, especially in larger or public companies, receive significant additional compensation in the form of annual bonuses, profit-sharing, or stock options, which can add tens of thousands of dollars to their total earnings.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a corporate controller will be determined by a combination of your qualifications, the nature of your employer, and your location. Let's explore the most influential factors.
### Level of Education
A bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a related field is the minimum requirement for a controller position. However, advanced credentials are what truly unlock higher earning potential.
- Master's Degree: An MBA or a Master of Accountancy (MAcc) can provide a significant salary advantage. These programs equip professionals with advanced leadership, strategic thinking, and complex financial analysis skills that are highly valued in a controller.
- CPA License: The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation is the gold standard in the accounting industry. For many companies, particularly larger or publicly traded ones, a CPA is a non-negotiable requirement for a controller. Holding a CPA license not only validates your expertise but also directly correlates with a higher salary, often commanding a premium of 5-15% over non-certified peers.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of a controller's salary. The path to this role is not a direct one; it requires years of progressive experience in accounting.
- Junior/Assistant Controller (5-8 years of experience): Professionals at this stage have typically advanced from senior accountant or accounting manager roles. They may handle controller duties in a smaller organization or work under a senior controller in a larger one. Salaries are at the lower end of the national range.
- Corporate Controller (8-15 years of experience): This is the sweet spot for the role. These professionals have extensive experience managing accounting cycles, leading teams, and handling complex financial reporting. Their salaries align with the national median figures.
- Senior/Group Controller (15+ years of experience): In large, multinational corporations, senior-level controllers may oversee the accounting for an entire division or region. Their expertise in complex issues like international consolidation and SEC reporting puts their salaries in the highest percentiles, often exceeding $200,000 - $250,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters immensely. Salaries are adjusted based on the local cost of living and the demand for top-tier financial talent in that market. Major metropolitan areas with a high concentration of corporate headquarters naturally offer the highest pay.
Top-paying metropolitan areas include:
- San Francisco, CA
- San Jose, CA
- New York, NY
- Boston, MA
- Washington, D.C.
Conversely, salaries will be lower in smaller cities and rural areas, though the reduced cost of living can often offset the difference.
### Company Type
The size and type of your employer have a profound impact on compensation. The 2024 Robert Half Salary Guide provides excellent data on how salaries vary by company revenue:
- Small Company (up to $50M in revenue): $115,000 - $177,250
- Medium Company ($50M - $500M in revenue): $149,000 - $241,250
- Large Company (over $500M in revenue): $191,750 - $318,750
Furthermore, industry plays a key role. Fast-growing industries like technology, biotechnology, and financial services tend to offer more competitive salaries and lucrative equity packages compared to non-profit, government, or some manufacturing sectors. Publicly traded companies also pay a premium due to the added complexity and risk of SEC reporting requirements.
### Area of Specialization
Within the controller function, certain specialized skills are in high demand and can command higher pay. Expertise in areas such as:
- Technical Accounting: Deep knowledge of complex accounting standards like revenue recognition (ASC 606) or leases (ASC 842).
- SEC Reporting: Experience preparing and filing forms 10-K and 10-Q for public companies.
- Systems Implementation: Proven ability to lead the implementation of new Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems like NetSuite, SAP, or Oracle.
Job Outlook

The future is bright for aspiring corporate controllers. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for Financial Managers—the category that includes controllers—will grow by 16% from 2022 to 2032. This is much faster than the average for all occupations.
The BLS attributes this strong growth to the increasing complexity of the global economy, the need for stringent financial oversight to ensure regulatory compliance, and the growing importance of data analysis in corporate decision-making. This indicates a stable and expanding demand for skilled financial leaders for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

The path to becoming a corporate controller is a challenging journey that requires a strong educational foundation, years of dedicated experience, and a commitment to continuous learning. However, the rewards are substantial. With salaries frequently reaching the mid-to-high six-figure range—especially for those with a CPA, advanced experience, and a role in a large company or major market—it stands as one of the most lucrative and influential careers in the world of finance.
For ambitious accounting professionals looking for a rewarding long-term goal, the role of corporate controller offers a clear and financially compelling destination.