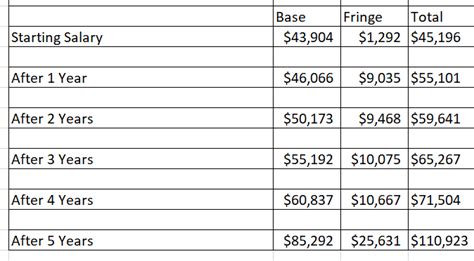
For those drawn to a career of service, courage, and critical action, the role of a Firefighter-EMT is a powerful calling. It’s a profession that combines the bravery of firefighting with the life-saving skills of an Emergency Medical Technician. But beyond the adrenaline and the sense of purpose, what is the financial reality? A career as a Fire EMT offers stable employment with a respectable salary that can grow significantly with experience, specialization, and strategic career choices.
A typical Fire EMT can expect to earn a salary ranging from approximately $40,000 for entry-level positions to over $95,000 for senior roles in high-paying metropolitan areas. This article will break down the numbers, explore the key factors that influence your pay, and provide a clear picture of what you can expect to earn in this dynamic and rewarding field.
What Does a Fire EMT Do?

A Firefighter-EMT is a dual-certified professional who responds to a wide range of emergencies. Their responsibilities are a unique blend of two critical public safety roles. On any given day, they might:
- Respond to medical emergencies: As certified EMTs, a significant portion of their calls involve medical crises like heart attacks, car accidents, injuries, and other health emergencies. They assess patients, provide immediate life-saving care (like CPR and first aid), and transport them to hospitals.
- Combat fires: They are fully trained firefighters who suppress and extinguish residential, commercial, and wildland fires. This involves operating hoses, pumps, and ladders, as well as performing search and rescue operations in hazardous environments.
- Perform technical rescues: They handle complex situations like vehicle extrications, hazardous materials (HazMat) incidents, and water or high-angle rescues.
- Engage in public education and prevention: They inspect buildings for fire code compliance and educate the community on fire safety and emergency preparedness.
This demanding job requires physical strength, mental resilience, and the ability to remain calm and decisive under extreme pressure.
Average Fire EMT Salary
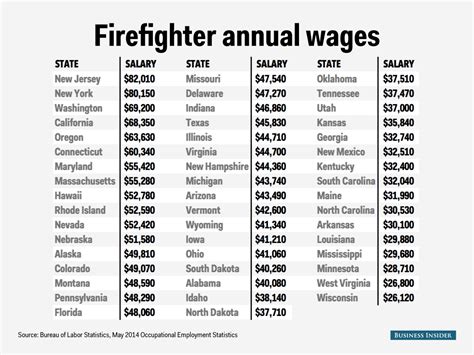
When analyzing compensation for a Fire EMT, it's essential to look at multiple authoritative sources. Because it's a dual role, salary data is often categorized under "Firefighters," with the understanding that most paid, professional firefighters are required to have at least an EMT certification.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for Firefighters was $57,690 in May 2023. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $31,540, while the highest 10 percent earned more than $94,190.
Salary aggregator websites provide a more granular look at the "Firefighter-EMT" title:
- Salary.com reports that the average salary for a Firefighter/EMT in the United States is approximately $55,593, with a common range falling between $41,695 and $69,491.
- Glassdoor estimates the total pay for a Firefighter EMT to be around $70,163 per year in the United States, which includes a base salary and additional pay like overtime and stipends.
It's crucial to note that a Fire EMT's total compensation often includes significant overtime pay due to the 24-hour shift structure, as well as allowances for uniforms, health benefits, and robust pension plans.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your base salary and overall earning potential as a Fire EMT are not static. They are influenced by a combination of your qualifications, location, and career choices.
Level of Education and Certification
While a high school diploma is the minimum educational requirement, your level of medical certification is a primary driver of salary.
- EMT-Basic (EMT-B): This is the foundational certification required by most fire departments. It qualifies you to provide basic life support, CPR, and first aid.
- Advanced EMT (AEMT): This intermediate level of certification allows for more advanced procedures, such as administering certain intravenous (IV) fluids and medications.
- Paramedic (EMT-P): This is the highest level of pre-hospital medical certification. Paramedics undergo extensive training (often an Associate's degree) and can perform advanced life support, including advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), intubation, and administering a wide range of emergency medications.
Impact on Salary: A Firefighter-Paramedic will almost always earn significantly more than a Firefighter-EMT. This "paramedic premium" can be a pay differential of $10,000 to $20,000 or more annually, as departments place high value on these advanced life-saving skills.
Years of Experience
Like most professions, experience is directly correlated with pay. Fire departments have structured pay scales and promotional tracks.
- Entry-Level (0-3 years): A rookie or probationary firefighter will start at the bottom of the department's pay scale, often earning in the $40,000s to low $50,000s.
- Mid-Career (4-10 years): With several years of experience, firefighters receive scheduled pay increases and may be promoted to roles like Driver-Engineer, increasing their salary into the $60,000s and $70,000s.
- Senior/Leadership (10+ years): Experienced firefighters can be promoted to leadership positions like Lieutenant, Captain, or Battalion Chief. These roles come with significant supervisory responsibility and command salaries often exceeding $80,000 and even reaching six figures in many departments.
Geographic Location
Where you work is one of the most significant factors determining your paycheck. Salaries vary widely by state and even by municipality to account for competition and cost of living.
According to the BLS, the top-paying states for firefighters in May 2023 were:
1. California: $87,660 (Annual Mean Wage)
2. New Jersey: $85,270
3. Washington: $83,790
4. New York: $83,430
5. Oregon: $79,270
Conversely, states in the Southeast and parts of the Midwest tend to offer lower salaries, though this is often offset by a lower cost of living. Large metropolitan fire departments (e.g., in Los Angeles, Seattle, New York City) typically offer the highest salaries to attract top talent and compensate for the high cost of living.
Company Type (Department/Employer)
The type and size of the employing department play a key role in compensation.
- Municipal/City Departments: Large, urban fire departments are often the highest-paying employers due to larger tax bases and higher call volumes.
- County Fire Departments: These departments often serve suburban and unincorporated areas and offer competitive, though sometimes slightly lower, salaries than their major city counterparts.
- Federal Government: Firefighters working for federal agencies like the Department of Defense or the U.S. Forest Service (as wildland firefighters) are paid on the General Schedule (GS) scale, which offers a different but often competitive pay and benefits structure.
- Private Industry: Some large industrial facilities (e.g., oil refineries, airports) employ their own private fire brigades, which can offer highly competitive salaries.
Area of Specialization
Developing specialized skills can open doors to promotions and additional pay in the form of stipends. Beyond the paramedic certification, valuable specializations include:
- Hazardous Materials (HazMat) Technician: Responding to chemical spills and other hazardous incidents.
- Technical Rescue Specialist: Expertise in disciplines like swift water rescue, trench rescue, high-angle rope rescue, or structural collapse.
- Fire Inspector/Investigator: Certifications in fire cause and origin investigation can lead to specialized, higher-paying roles.
- Aircraft Rescue and Firefighting (ARFF): A specialized certification for firefighters working at airports.
These specializations not only make you a more valuable asset to your department but also directly increase your earning potential.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for Fire EMTs is stable and positive. The BLS projects that employment for firefighters will grow by 3 percent from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by the need to replace firefighters who retire or leave the profession. While overall growth is steady, competition for paid positions can be intense, especially in desirable metropolitan departments. Candidates with paramedic certification, specialized skills, and a strong physical and academic record will have the best job prospects.
Conclusion

A career as a Firefighter-EMT is a commitment to public service that offers a solid, middle-class living with excellent benefits and opportunities for advancement. While the national median salary provides a useful benchmark, your personal earning potential is in your hands.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring Fire EMTs:
- Aim for Paramedic: The single most effective way to maximize your salary is to achieve Paramedic certification.
- Specialize Your Skills: Pursue certifications in high-demand areas like HazMat or technical rescue to earn stipends and become eligible for promotion.
- Be Strategic About Location: Research the pay scales of different departments and regions, balancing salary with cost of living.
- Focus on the Long-Term: Your salary will grow steadily with experience and promotion. Look beyond the starting salary to the long-term earning potential and excellent retirement benefits.
For those with the dedication and drive, a career as a Fire EMT is more than just a job—it's a path to a stable, prosperous, and profoundly meaningful life.