Pursuing a career in education in the Peach State is a decision to invest in the future of your community. It's a path defined by purpose and impact, but it's also a profession that offers a stable and competitive salary with clear avenues for financial growth. For prospective and current educators in Georgia, understanding the salary landscape is a critical part of career planning.
On average, educators in Georgia can expect to earn a salary ranging from $58,000 to $62,000 annually. However, this figure is just a starting point. With advanced degrees, years of experience, and strategic career choices, top-earning teachers and administrators can command salaries well over $85,000, making education a financially viable and rewarding long-term career.
This guide will break down everything you need to know about educator salaries in Georgia, from average earnings to the key factors that will shape your personal income potential.
What Does a Georgia Educator Do?

While "teacher" is the most common title, the term "educator" encompasses a wide range of vital roles within a school system. At its core, an educator's job is to facilitate learning and development. This goes far beyond delivering lectures.
Daily responsibilities for a classroom teacher in Georgia typically include:
- Developing and implementing engaging lesson plans that align with the Georgia Standards of Excellence.
- Assessing student progress through assignments, tests, and classroom observation.
- Adapting teaching methods to meet the needs of a diverse student body.
- Communicating effectively with students, parents, and school administrators.
- Managing classroom behavior to create a safe and productive learning environment.
- Collaborating with colleagues on curriculum development and school-wide initiatives.
Beyond the classroom, educators can also be school counselors, media specialists (librarians), instructional coaches, or administrators, each with a unique set of responsibilities aimed at supporting the educational mission of the school.
Average Georgia Educator Salary
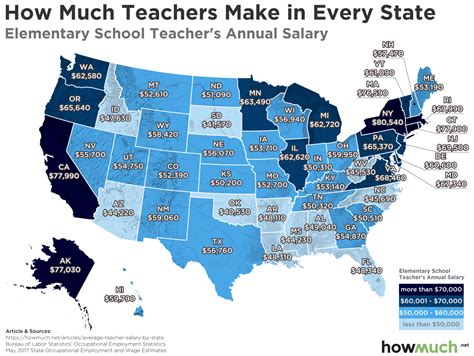
Salary data provides a snapshot of earning potential in Georgia. According to leading salary aggregators, the figures are consistent and promising.
- Salary.com reports that the median salary for a public school teacher in Georgia is $61,501 as of May 2024, with a typical range falling between $51,348 and $73,836.
- Glassdoor lists a similar average base pay of $58,629 per year based on user-submitted data.
- Payscale notes an average base salary of approximately $55,000, with income progressing significantly with experience.
The most authoritative source for public school teachers is the Georgia Department of Education (GaDOE) State Salary Schedule. It's important to understand that this schedule dictates the *minimum* salary a teacher must be paid based on their degree and experience. Most school districts, particularly in metropolitan areas, pay a "local supplement" on top of this state minimum, leading to higher actual earnings.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary as a Georgia educator is not a single, static number. It is a dynamic figure influenced by several key factors. Understanding these variables is the best way to maximize your earning potential throughout your career.
###
Level of Education
Your level of education is one of the most significant factors in determining your base pay. The GaDOE salary schedule is structured around certificate levels, which correspond to degrees. These are often referred to by their "T-level":
- T-4 Certificate: Bachelor's Degree
- T-5 Certificate: Master's Degree
- T-6 Certificate: Education Specialist (Ed.S.) Degree
- T-7 Certificate: Doctorate (Ph.D. or Ed.D.)
The salary jump between these levels is substantial. For example, according to the 2023-2024 state salary schedule, a first-year teacher with a Bachelor's degree (T-4) has a minimum salary of $41,092. A first-year teacher with a Master's degree (T-5) starts at a minimum of $47,025—a nearly $6,000 increase for the advanced degree alone. This gap widens considerably with experience.
###
Years of Experience
The state salary schedule is designed to reward commitment and experience. Teachers receive a "step" increase for each year of credible service. This creates a clear and predictable path for salary growth.
- An educator with a Master's degree (T-5) at Year 1 starts at a state minimum of $47,025.
- By Year 10, that same educator's minimum salary increases to $58,953.
- After 21+ years of service, their minimum salary reaches $64,449.
These figures represent the state base pay before any local supplements are added, highlighting the long-term financial benefits of a sustained career in education.
###
Geographic Location
Where you teach in Georgia matters immensely. Urban and suburban school districts with a higher cost of living and larger tax base typically offer significant local salary supplements to attract and retain talent.
- Metro Atlanta Districts: Districts like Gwinnett County Public Schools, Cobb County School District, and Fulton County Schools are known for offering some of the most competitive salaries in the state, often adding $5,000 to $15,000 or more to the state minimums.
- Rural Districts: Smaller, rural districts may have fewer resources and often pay closer to the state minimum salary.
When considering a position, always research the specific school district’s salary schedule, not just the state’s, to understand your true earning potential.
###
School Type
The type of school you work for also impacts your salary and benefits.
- Public Schools: These are the most common employers and follow the state salary schedule, plus any local supplements. They offer stable employment, strong retirement plans (Teachers Retirement System of Georgia), and comprehensive benefits.
- Charter Schools: As public schools, charter schools must adhere to state certification rules, but they often have more flexibility in their salary structures. Some may offer higher starting pay to attract teachers but may not follow a traditional step-increase model.
- Private Schools: Private school salaries vary dramatically. Elite, well-endowed preparatory schools may offer salaries competitive with or even exceeding top public districts. However, many smaller or religiously affiliated private schools may pay significantly less than their public school counterparts.
###
Area of Specialization
Your teaching field can unlock opportunities for additional pay. To combat shortages in critical areas, many districts offer hiring bonuses or annual stipends for educators in high-need specializations. These often include:
- STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math)
- Special Education
- Foreign Languages (e.g., Spanish, French)
Furthermore, moving into other educational roles, such as a School Counselor, Media Specialist, or Administrator (Principal, Assistant Principal), places you on a different, higher-paying salary scale.
Job Outlook

The demand for qualified educators in Georgia remains strong. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, the national outlook for teachers shows stable to modest growth through 2032.
However, Georgia's specific context is more promising. The state continues to experience population growth, which directly translates to a need for more teachers to serve a growing student body. Additionally, ongoing conversations about teacher shortages and statewide initiatives to increase teacher pay, such as the significant raises implemented in recent years, make Georgia an attractive and stable market for education professionals.
(Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Occupational Outlook Handbook, consulted May 2024)
Conclusion

A career as an educator in Georgia is a calling that comes with the promise of a secure and respectable living. While headlines may focus on a single "average" salary, your actual earnings are a product of your personal and professional choices.
The key takeaways for maximizing your salary are clear:
- Invest in Education: Pursuing a Master's degree or higher provides an immediate and lifelong boost to your income.
- Location Matters: Researching and targeting districts with strong local supplements can dramatically increase your take-home pay.
- Specialize in High-Need Fields: Choosing a specialization like STEM or Special Education can unlock additional stipends.
- Stay the Course: The salary structure is designed to reward experience, making long-term commitment financially beneficial.
For those passionate about shaping the next generation, a career in education in Georgia offers not only profound personal fulfillment but also a clear and dependable path for professional and financial growth.