Pursuing a career as an infectious disease (ID) specialist is a calling for those fascinated by the intricate world of pathogens, epidemiology, and public health. These medical detectives are on the front lines of everything from managing complex hospital infections to responding to global pandemics. But beyond the profound impact, what is the financial outlook for this critical specialty?
While it's one of the lower-compensated physician specialties, a career as an infectious disease doctor still promises a substantial six-figure salary, with the potential for significant growth. The national average salary for an ID specialist typically falls between $245,000 and $275,000 per year, but this figure is just the beginning of the story.
This article will break down the salary you can expect as an infectious disease doctor and explore the key variables that will shape your ultimate earning potential.
What Does an Infectious Disease Doctor Do?

An infectious disease doctor is a specialist, typically with a background in internal medicine or pediatrics, who has completed additional fellowship training in the diagnosis and treatment of complex infections. Their expertise is sought when an infection is difficult to diagnose, is accompanied by a high fever, or fails to respond to conventional treatments.
Key responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Managing care for patients with chronic infections, such as HIV/AIDS or Hepatitis C.
- Leading antimicrobial stewardship programs in hospitals to combat antibiotic resistance.
- Serving as hospital epidemiologists to control and prevent the spread of infections within healthcare facilities.
- Consulting with other physicians on complex cases and providing expert guidance.
- Working in public health to track and manage outbreaks and develop vaccination strategies.
Average Infectious Disease Doctor Salary
Salary data for physicians can vary based on the source, the methodology, and the demographics of those surveyed. However, top-tier industry reports provide a reliable snapshot of the landscape.
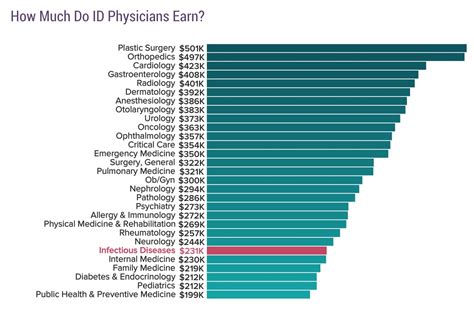
According to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023, infectious disease specialists earn an average annual salary of $262,000. This places them on the lower end of the physician compensation spectrum, alongside specialties like pediatrics and family medicine.
Other authoritative sources provide similar figures:
- Doximity's 2023 Physician Compensation Report cites a slightly higher average of $277,395.
- Salary.com reports a median salary of $248,301, with a typical range falling between $214,195 and $289,307 as of late 2023. This range highlights the significant variation based on factors we'll explore below.
While not reaching the heights of surgical or cardiology specialties, this salary is still well above the national average for all occupations and reflects a highly rewarding and stable career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

The national average is a useful benchmark, but your individual salary as an ID doctor will be determined by a combination of critical factors. Understanding these variables is key to maximizing your earning potential.
Level of Education
For any physician, the educational path is long and standardized. It includes an undergraduate degree, a medical degree (M.D. or D.O.), a three-year residency in internal medicine, and a subsequent two-to-three-year fellowship in infectious diseases. While the *level* of education is non-negotiable, board certification from the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) in both Internal Medicine and Infectious Disease is the industry standard. This certification is essential for securing top positions and maximizing salary, as it signals the highest level of expertise and competence to employers and insurance providers.
Years of Experience
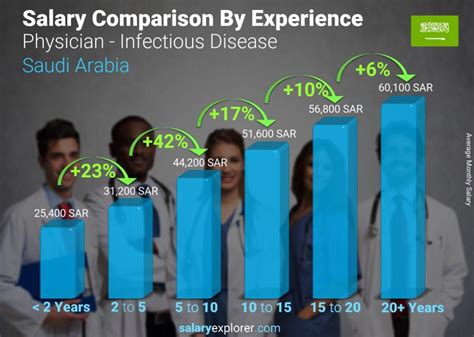
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth. An ID physician just finishing their fellowship is considered entry-level and will likely earn a salary at the lower end of the spectrum, closer to the $215,000 mark.
- Early Career (0-5 years): Focus is on building clinical skills and reputation. Salary growth is steady.
- Mid-Career (6-15 years): Physicians often take on leadership roles (e.g., Director of Antimicrobial Stewardship, Hospital Epidemiologist) or build a robust patient panel in private practice, leading to significant salary increases.
- Senior/Late Career (16+ years): With extensive experience, senior ID specialists are highly valued for their expertise. They may command top salaries as department heads, senior partners in a practice, or sought-after consultants, pushing their earnings toward the $300,000+ range.
Geographic Location
Where you practice has a massive impact on your salary. Compensation varies significantly by state and even between urban and rural areas, often due to differences in cost of living and local demand for specialists.
According to industry data, physicians often earn more in the Southeast and Midwest compared to the Northeast and West Coast. For example, states like Alabama, Kentucky, and Oklahoma often report higher average physician salaries than New York or Massachusetts. This is typically driven by a greater need to attract and retain specialized talent in those regions. A physician considering a move should always weigh the higher salary against the local cost of living to understand their true earning power.
Company Type
The setting in which you work is arguably one of the most significant factors in determining your salary and overall compensation package.
- Private Practice: This setting has historically offered the highest earning potential. ID physicians who are partners in a multi-specialty or single-specialty group can earn significantly more, as they benefit directly from the practice's revenue. However, this comes with the added responsibilities of business management and overhead costs.
- Hospital or Health System Employment: This is an increasingly common model offering a stable, predictable salary and comprehensive benefits package. While the base salary may be slightly lower than in a top-earning private practice, it removes the volatility and administrative burden of running a business.
- Academic Medical Centers: ID physicians in academia typically earn less than their counterparts in private or hospital-based practice. This "pay cut" is often balanced by non-monetary benefits, such as opportunities for research, teaching medical students and residents, intellectual stimulation, and the prestige of an academic appointment.
- Government and Public Health: Roles at institutions like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are driven more by mission than by salary. These positions are often the lowest paying but offer excellent benefits, work-life balance, and the opportunity to shape public health policy on a national or global scale.
Area of Specialization
Within the broader field of infectious diseases, further sub-specialization can enhance your value and salary. ID physicians who develop expertise in a high-demand niche can command higher compensation, especially in leadership roles. Key areas include:
- HIV/AIDS Medicine: A core component of many ID practices.
- Transplant Infectious Disease: A highly specialized field focused on managing infections in immunocompromised organ transplant recipients.
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Directing hospital-wide programs to optimize antibiotic use is a valuable and increasingly compensated leadership role.
- Hospital Epidemiology: Preventing and controlling healthcare-associated infections is a critical function that carries significant responsibility and corresponding compensation.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for physicians and surgeons, in general, is positive. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, employment for physicians and surgeons is projected to grow 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
For infectious disease specialists, the demand is particularly robust. Several factors contribute to this strong outlook:
- The ever-present threat of emerging infectious diseases, as highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The growing challenge of antibiotic-resistant organisms.
- An aging population that is more susceptible to complex infections.
- The increasing use of immunosuppressive therapies for cancer and autoimmune diseases.
These factors ensure that the expertise of ID specialists will remain in high demand across all healthcare settings.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as an infectious disease doctor is a commitment to a lifetime of learning and a passion for solving medicine's most complex puzzles. While it may not be the most lucrative medical specialty, it offers a secure, professionally rewarding, and financially comfortable career path with an average salary well into the six figures.
Prospective specialists should understand that the national average is merely a baseline. By carefully considering factors like geographic location, practice setting, and developing niche expertise, you can strategically navigate your career to maximize your earnings while making an invaluable contribution to patient care and public health.