A career as an infectious disease (ID) doctor is more than a job; it's a commitment to solving some of medicine's most complex puzzles. These specialists stand on the front lines of public health, from managing global pandemics to treating complex, individual infections. For those considering this challenging yet highly rewarding path, a key question arises: what is the financial outlook?
While passion for the field is paramount, understanding the compensation landscape is a crucial part of career planning. The simple answer is that a career as an infectious disease doctor is financially robust, with average salaries comfortably exceeding $250,000 annually. However, this figure is just the starting point. Your ultimate earning potential is shaped by a variety of critical factors, which we will explore in detail.
What Does an Infectious Disease Doctor Do?

Infectious disease specialists are the detectives of the medical world. They are expert diagnosticians who focus on identifying and treating illnesses caused by microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Their work is incredibly diverse and critically important.
Key responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing and treating complex infections, such as HIV/AIDS, hepatitis, tuberculosis, meningitis, and severe hospital-acquired infections.
- Managing infection control and prevention programs within hospitals to protect patients.
- Leading antibiotic stewardship programs to combat the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
- Consulting with other physicians on difficult cases involving a potential infectious component.
- Working in public health with organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to track, investigate, and control outbreaks.
They work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, private clinics, academic medical centers, and public health agencies.
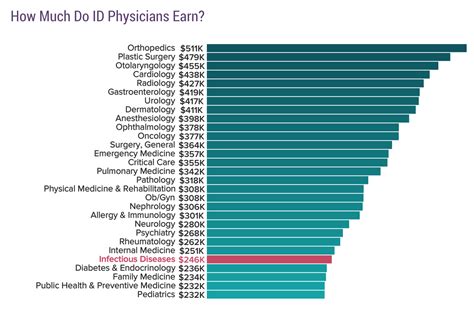
Average Infectious Disease Doctor Salary
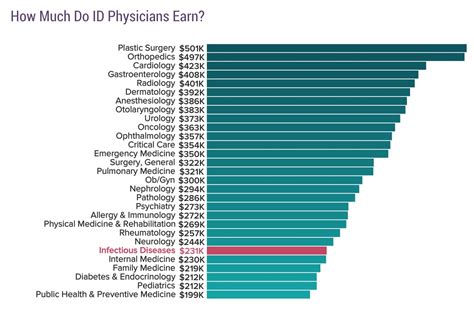
The compensation for an infectious disease doctor is substantial, reflecting the extensive education, training, and expertise required. While specific figures vary between data aggregators, they paint a consistent picture of a high-earning profession.
According to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023, one of the most respected industry benchmarks, the average annual salary for an infectious disease specialist is $262,000.
Other authoritative sources provide a similar range:
- Salary.com reports a median salary of $261,630 as of late 2023, with a typical range falling between $225,570 and $303,160.
- Doximity's 2023 Physician Compensation Report places the average compensation for infectious disease specialists at $277,155.
It's important to note that while this is an excellent income, infectious disease is often cited as one of the lower-paid physician specialties. This is typically attributed to the cognitive, consult-heavy nature of the work, which involves fewer lucrative, high-volume procedures compared to fields like cardiology or orthopedic surgery.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary is not a single, static number. It is a dynamic figure influenced by a combination of your personal background and professional choices. Here are the most significant factors.
### Level of Education
To become an infectious disease doctor, the educational path is fixed and rigorous, directly contributing to the high baseline salary. This journey includes:
1. A four-year bachelor's degree.
2. A four-year medical degree (M.D. or D.O.).
3. A three-year residency in Internal Medicine.
4. A two-to-three-year fellowship specifically in Infectious Disease.
This totals over a decade of post-secondary education and training. While all board-certified ID physicians have this background, holding additional degrees, such as a Master of Public Health (MPH), can open doors to higher-paying administrative or public health leadership roles.
### Years of Experience
Experience is a primary driver of salary growth in medicine. Compensation generally increases as a physician builds a reputation, gains expertise, and takes on more complex or senior-level responsibilities.
- Entry-Level (0-5 years): A physician just completing their fellowship can expect a salary on the lower end of the typical range, likely starting around $210,000 to $230,000.
- Mid-Career (6-20 years): With significant experience, physicians can command salaries at or above the national average, often reaching the $260,000 to $290,000 bracket. They may also take on leadership roles, such as a department head or medical director.
- Senior-Level (20+ years): Highly experienced doctors, particularly those in private practice or senior administrative positions, can earn well over $300,000.
### Geographic Location
Where you practice has a powerful impact on your paycheck. This is driven by local market demand and cost of living. Some states and metropolitan areas offer significantly higher compensation to attract and retain top medical talent.
For example, Medscape data has historically shown that physicians in regions like the South Central (e.g., Alabama, Tennessee) and North Central (e.g., Wisconsin, North Dakota) United States tend to have higher average salaries than those in the Northeast, where the supply of physicians is greater.
However, rural and underserved areas may offer higher starting salaries and significant financial incentives, such as loan forgiveness programs, to attract physicians. When evaluating an offer, it is essential to balance the salary against the local cost of living to understand your true purchasing power.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for is one of the biggest differentiators in an ID doctor's salary.
- Private Practice (Self-Employed or Partnership): This setting often offers the highest earning potential. According to Medscape, self-employed physicians across all specialties earn significantly more than their employed counterparts. However, this comes with the added responsibilities of running a business, including managing staff, billing, and overhead.
- Hospital-Employed: Working directly for a hospital or a multi-specialty healthcare system provides a stable, predictable salary and often includes a strong benefits package and performance bonuses. This is an increasingly common and lucrative employment model.
- Academic Medical Center: Salaries in academia are typically lower than in private practice or hospital systems. The trade-off is often a better work-life balance, opportunities to teach and conduct research, and robust institutional benefits.
- Government/Public Health: Working for an entity like the CDC or a state department of health usually results in a lower salary. The compensation is a rewarding mission, excellent job security, and strong government benefits.
### Area of Specialization
Within the broader field of infectious disease, certain niche roles can influence compensation. For instance, an ID doctor who also serves as the Hospital Epidemiologist or Director of Infection Prevention and Control may receive an additional administrative stipend, boosting their overall income. Specialists focusing on lucrative areas like treating Hepatitis C or providing care at infusion centers may also see higher revenue and, consequently, higher earnings.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for physicians and surgeons, in general, is positive. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for this group is projected to grow 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
For infectious disease specialists, the demand is expected to remain strong and may even exceed this average. The COVID-19 pandemic starkly illuminated the essential role these experts play in national and global health security. Ongoing challenges such as antibiotic resistance, the threat of emerging pathogens, and the medical needs of an aging population ensure that the expertise of ID physicians will be in high demand for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as an infectious disease doctor is a path for the intellectually curious and deeply committed. The journey requires immense dedication, but the rewards are multifaceted. Beyond the profound satisfaction of protecting public health and saving lives, the profession offers excellent financial stability.
Key Takeaways:
- Strong Compensation: You can expect an average salary in the range of $260,000 to $280,000, with the potential to earn well over $300,000.
- Growth is Key: Your earnings will grow significantly with experience.
- Choices Matter: Your choice of practice setting (private vs. hospital vs. academic) and geographic location will be the most significant factors in determining your specific salary.
For prospective students and medical professionals, the field of infectious disease represents a financially secure and immensely fulfilling career at the very heart of modern medicine.