The field of infectious diseases (ID) has never been more visible, highlighting the critical role these medical detectives play in public health and individual patient care. For aspiring medical professionals and students, a career as an infectious disease specialist is not only intellectually stimulating and impactful but also financially rewarding. This article provides a data-driven look into the salary you can expect, the factors that influence it, and the promising future of this vital profession.
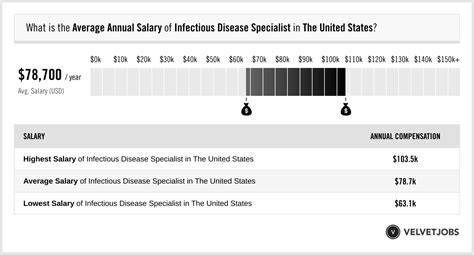
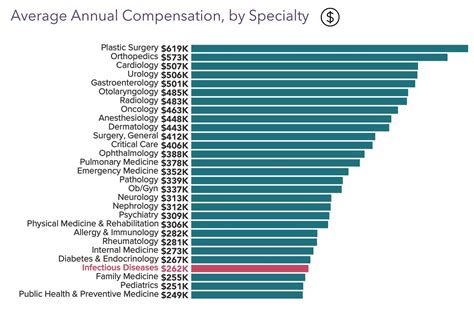
While salaries can vary significantly, most infectious disease specialists in the United States can expect to earn an average annual salary between $245,000 and $265,000, with top earners in private practice or specialized roles commanding well over $300,000.
What Does an Infectious Disease Specialist Do?

An infectious disease specialist is a board-certified physician who has completed extensive training in diagnosing and treating complex conditions caused by microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They often consult on the most challenging cases in a hospital, from mysterious fevers and tropical diseases to severe post-operative infections.
Their responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing complex infectious diseases, such as HIV/AIDS, hepatitis, meningitis, and tuberculosis.
- Managing care for patients with antibiotic-resistant infections.
- Leading hospital infection control programs (hospital epidemiology).
- Advising on public health policies and outbreak responses.
- Conducting research on new pathogens and treatments.
Think of them as the ultimate medical investigators, piecing together clues to identify and defeat microscopic adversaries.
Average Infectious Disease Specialist Salary

Salary data from multiple authoritative sources provides a clear picture of earning potential in this field. It's important to look at both the average and the typical range to understand the full spectrum of compensation.
According to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023, infectious disease specialists earn an average annual salary of $260,000.
Salary aggregators provide a similar outlook. As of early 2024, Salary.com reports that the median salary for an infectious disease physician is $252,190. The site notes a typical salary range that reflects the career trajectory:
- 10th Percentile (Entry-Level): $217,160
- 50th Percentile (Median): $252,190
- 90th Percentile (Senior-Level): $314,350
This wide range highlights that while the starting salary is substantial, there is significant room for financial growth throughout one's career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary


Averages provide a great benchmark, but an individual's specific salary is determined by a combination of critical factors. Understanding these variables is key to maximizing your earning potential.
Level of Education
The path to becoming an infectious disease specialist is long and rigorous, which is a primary reason for the high compensation. It involves:
1. A four-year bachelor's degree.
2. A four-year medical degree (M.D. or D.O.).
3. A three-year residency in Internal Medicine.
4. A two-to-three-year fellowship specifically in Infectious Diseases.
This decade-plus of higher education and training represents a significant investment. While the M.D./D.O. is the standard, obtaining further degrees like a Master of Public Health (MPH) can open doors to higher-paying leadership roles in public health organizations or hospital administration, further boosting earning potential.
Years of Experience
As with most professions, experience is a major driver of salary growth. Seasoned specialists who have managed a wide variety of complex cases are more valuable to employers and can command higher compensation.
- Entry-Level (0-3 Years): Physicians fresh out of fellowship can expect to earn a salary on the lower end of the scale, typically in the $215,000 to $235,000 range.
- Mid-Career (5-10 Years): With a solid track record, specialists will see their salaries climb toward the national average, earning between $250,000 and $280,000.
- Senior-Level (15+ Years): Highly experienced specialists, particularly those who take on leadership roles (e.g., Chief of Infectious Diseases) or become partners in a private practice, can easily surpass $300,000 annually.
Geographic Location
Where you practice has a significant impact on your paycheck. This is driven by local market demand, the cost of living, and the number of competing specialists.
- High Cost-of-Living Areas: Major metropolitan centers like New York City, San Francisco, and Boston often offer higher nominal salaries to offset the high cost of living.
- Rural or Underserved Areas: To attract top talent, states and regions with a physician shortage may offer highly competitive salaries, student loan forgiveness programs, and significant signing bonuses. States like North Dakota, Wyoming, and Alaska frequently appear on lists of top-paying states for physicians for this reason.
- Metropolitan vs. Non-Metropolitan: According to Medscape, physicians in the South Central region of the U.S. (including Texas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas) reported some of the highest average compensation.
Company Type
The setting where an infectious disease specialist works is another key determinant of their salary and overall compensation package.
- Private Practice: This setting typically offers the highest earning potential. Specialists who are partners in a physician-owned group benefit directly from the practice's profits. However, this comes with the added responsibilities of running a business.
- Hospital or Healthcare System: This is the most common employment model. Salaries are competitive and often come with robust benefits packages and bonuses tied to quality metrics or productivity. A specialist who also serves as the hospital's epidemiologist or director of infection control often receives an additional stipend, increasing their overall income.
- Academic Medical Centers: Salaries here may be slightly lower than in private practice. However, this is often offset by excellent benefits, opportunities for research, teaching responsibilities, and the prestige of working at a leading institution.
- Government and Public Health: Roles at agencies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the National Institutes of Health (NIH) generally offer lower base salaries than clinical practice. The trade-off is often better work-life balance, federal benefits, and the opportunity to shape national health policy.
Area of Specialization
Within the broader field of infectious diseases, certain sub-specialties can lead to higher compensation due to their complexity and demand.
- Hospital Epidemiology/Infection Control: As hospitals face immense pressure to reduce healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), physicians with expertise in this area are highly sought after and well-compensated.
- Transplant Infectious Disease: This niche focuses on managing infections in highly immunocompromised organ transplant recipients and commands a premium.
- HIV Medicine: While a core part of ID training, specialists who build a large practice focused on long-term HIV care can have a stable and lucrative patient base.
Job Outlook


The career outlook for physicians, in general, is positive, and the need for infectious disease specialists is particularly acute. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for physicians and surgeons will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032, which is as fast as the average for all occupations.
However, several factors suggest the demand for ID specialists will remain robust:
- The ongoing threat of global pandemics and emerging infectious diseases.
- The growing crisis of antimicrobial resistance.
- An aging population with more complex, chronic health conditions.
- The critical need for infection prevention and control within all healthcare facilities.
This steady demand ensures a high degree of job security for those entering the field.
Conclusion


Choosing a career as an infectious disease specialist is a commitment to lifelong learning and a passion for solving medicine's most complex puzzles. The journey is demanding, but the rewards are substantial.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Substantial Earnings: The average salary for an ID specialist is strong, typically ranging from $245,000 to $265,000, with significant potential for growth.
- Key Drivers of Income: Your earning potential is heavily influenced by your years of experience, geographic location, practice setting, and any specialized expertise you develop.
- Secure Future: With a stable job outlook driven by persistent and emerging health threats, ID specialists will remain an indispensable part of the healthcare landscape.
For those drawn to a field that combines intellectual challenge, profound societal impact, and excellent financial compensation, the career of an infectious disease specialist is an outstanding choice.