Unveiling the Earnings: A Deep Dive into the Jewelry Designer Salary
For those who blend artistry with intricate craftsmanship, a career as a jewelry designer is a tantalizing prospect. It’s a field where creativity meets commerce, and a personal vision can be transformed into a tangible, wearable piece of art. But beyond the passion, what is the real earning potential? A jewelry designer's salary can range from modest starting figures to substantial six-figure incomes, with top-tier freelance designers earning even more.
This guide will break down the salary you can expect as a jewelry designer, exploring the critical factors that influence your income and the overall outlook for this sparkling career path.
What Does a Jewelry Designer Do?

Before we talk numbers, it's important to understand the scope of the role. A jewelry designer is much more than just a sketch artist. They are multifaceted professionals who are deeply involved in the entire lifecycle of a piece of jewelry.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Conceptualization and Design: Researching trends, finding inspiration, and sketching initial ideas by hand or using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Material Sourcing: Selecting the right precious metals (gold, platinum, silver), gemstones (diamonds, sapphires, emeralds), and other materials that fit the design and budget.
- Technical Specification: Creating detailed technical drawings and 3D models for jewelers and manufacturers to follow.
- Prototyping and Collaboration: Working with bench jewelers, model makers, and production teams to create prototypes and ensure the final piece meets quality standards.
- Market Awareness: Understanding consumer preferences, price points, and the competitive landscape to create commercially viable collections.
Average Jewelry Designer Salary
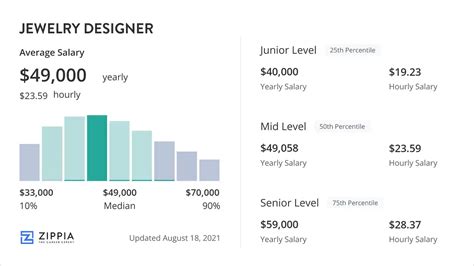
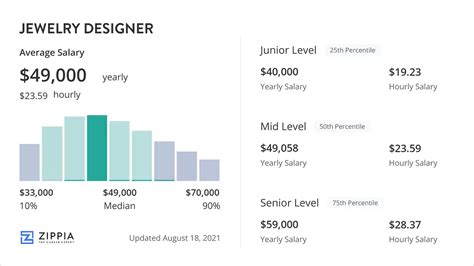
A jewelry designer's salary can vary significantly based on a number of factors, which we will explore below. However, we can establish a solid baseline by looking at data from several authoritative sources.
According to reputable salary aggregators that focus specifically on the "designer" title, the average salary for a jewelry designer in the United States typically falls between $55,000 and $65,000 per year.
- Salary.com reports a median salary for a Jewelry Designer at around $60,570 as of late 2023, with a typical range falling between $49,500 and $72,300.
- Payscale provides a similar range, breaking it down by experience, noting that entry-level designers start around $45,000 while experienced designers can earn upwards of $75,000.
For a broader government perspective, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups jewelry designers under the category "Jewelers and Precious Stone and Metal Workers." As of May 2022 (the most recent comprehensive data), the BLS reports:
- Median Annual Wage: $47,690 ($22.93 per hour)
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $30,990
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $78,950
The discrepancy between the BLS and salary aggregators often exists because the BLS category includes bench jewelers and repair technicians, while aggregators can more closely target the "designer" role, which often commands a higher salary due to its blend of creative and technical skills.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of salary potential by experience level:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): $42,000 - $52,000
- Mid-Career (3-7 years): $55,000 - $70,000
- Senior/Lead Designer (8+ years): $75,000 - $95,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary is not set in stone. It is a dynamic figure influenced by a combination of your skills, choices, and environment. Here are the most critical factors.
### Level of Education
While a formal degree is not a strict requirement to become a talented jewelry designer, it significantly impacts your hiring potential and starting salary. A degree from a respected institution demonstrates a foundation in design principles, technical skills, and art history.
- Relevant Degrees: A Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) with a concentration in Jewelry Design, Metalsmithing, or a related field is highly valuable.
- Certifications: Professional certifications can provide a substantial salary boost. A credential from the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), such as the Graduate Gemologist (G.G.) or Accredited Jewelry Professional (A.J.P.), is the industry gold standard and can make you a far more valuable asset, especially in fine jewelry.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant factor in determining your salary. As you progress in your career, you build a portfolio, refine your skills, and prove your commercial value.
- Entry-Level: Designers focus on assisting senior designers, learning CAD software, and understanding production processes.
- Mid-Career: Professionals take on more responsibility, leading small projects, developing parts of a collection, and having more client-facing interaction.
- Senior Level: Senior designers often set the creative direction for a brand, manage design teams, work on high-value bespoke pieces, and have a direct impact on the company's bottom line.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Major metropolitan areas that serve as fashion, luxury, and commerce hubs offer higher salaries to compensate for a higher cost of living and a greater concentration of high-end companies.
According to BLS data, the top-paying states for this profession include:
1. Rhode Island: A historic hub for jewelry manufacturing.
2. New York: The heart of the U.S. fashion and luxury market.
3. Connecticut: Proximity to New York City and a wealthy client base.
4. California: Particularly in Los Angeles, which has a strong design and fashion scene.
Working in a major city like New York or Los Angeles will almost certainly yield a higher salary than working in a smaller, more rural market.
### Company Type
The type of company you work for will dramatically affect your earning potential and day-to-day work.
- High-End Luxury Brands (e.g., Tiffany & Co., Harry Winston): These companies offer the highest salaries, excellent benefits, and immense prestige. However, competition is fierce, and the creative environment can be highly structured.
- Mass-Market Retailers (e.g., Signet Jewelers - Kay, Zales): These large corporations offer stable employment and competitive salaries. The focus is on creating commercially successful, trend-driven designs for a broad audience.
- Independent Boutiques/Studios: Working for a smaller, independent designer can offer more creative freedom and a hands-on experience. The salary might be lower initially, but there could be opportunities for profit-sharing or rapid growth.
- Freelance / Self-Employed: This path offers unlimited earning potential but comes with the greatest risk. Your income is directly tied to your ability to build a brand, market your designs, and manage a business. Successful independent designers can earn well into the six figures, but income can be inconsistent.
### Area of Specialization
Developing a niche skill set can make you a highly sought-after, and better-paid, professional.
- CAD/3D Modeling: Proficiency in software like Rhinoceros 3D, Matrix, and ZBrush is no longer a bonus—it's a core requirement for most modern design jobs. Experts in CAD can command top dollar.
- Fine Jewelry vs. Fashion Jewelry: Designers specializing in fine jewelry (using precious metals and genuine gemstones) typically earn significantly more than those focused on fashion or costume jewelry (using plated metals and non-precious materials).
- Bridal and Engagement: This is a perennially lucrative and stable sector of the market. Specialists in engagement rings and bridal collections are always in demand.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that overall employment for "Jewelers and Precious Stone and Metal Workers" will see a slight decline of 2% from 2022 to 2032.
However, this number requires context. Much of this projected decline is attributed to automation impacting traditional bench jeweler and manufacturing roles. The outlook for skilled designers remains more optimistic. Demand will be strongest for professionals who possess a powerful combination of creative vision, technical CAD skills, and a keen understanding of market trends. The rise of e-commerce and social media has also created new opportunities for independent designers to build a brand and reach a global audience directly.
Conclusion

A career as a jewelry designer offers a unique opportunity to build a profession around creativity and beauty. While the median salary provides a solid starting point, it's clear that your earning potential is largely in your own hands.
To maximize your salary, focus on these key takeaways:
- Build a Strong Foundation: Pursue formal education and industry-recognized certifications like those from the GIA.
- Embrace Technology: Become an expert in CAD and 3D modeling software.
- Gain Diverse Experience: Build a compelling portfolio across different types of companies or projects.
- Consider Your Location: Be willing to relocate to a major industry hub for the best opportunities.
- Never Stop Learning: Stay on top of market trends and consumer desires.
For the passionate and strategic individual, a career in jewelry design is not just creatively fulfilling—it can be a financially rewarding and brilliant path to follow.
