Table of Contents

- [What Does a Learning and Development Specialist Do?](#what-does-a-learning-and-development-specialist-do)
- [Average Learning and Development Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive](#average-learning-and-development-specialist-salary-a-deep-dive)
- [Key Factors That Influence Salary](#key-factors-that-influence-salary)
- [Job Outlook and Career Growth](#job-outlook-and-career-growth)
- [How to Get Started in This Career](#how-to-get-started-in-this-career)
- [Conclusion: Is a Career in L&D Right for You?](#conclusion-is-a-career-in-ld-right-for-you)
---
Are you passionate about unlocking human potential? Do you believe that a company's greatest asset is its people? If you find yourself nodding along, a career as a Learning and Development (L&D) Specialist might be your calling. This role is far more than just "corporate training"; it's a strategic function at the heart of organizational success, responsible for cultivating talent, closing skill gaps, and building the workforce of the future.
And the rewards for this critical work are substantial. While passion fuels the desire, financial stability sustains the journey. The learning and development specialist salary reflects the growing importance of this field, with national averages comfortably sitting between $65,000 and $85,000 per year, and senior professionals or those in high-demand niches easily commanding six-figure incomes.
I remember an early project in my career where I was tasked with creating a new onboarding program. A newly hired, brilliant but shy engineer was visibly struggling to connect with his team and the company culture. After going through the redesigned, more interactive and supportive onboarding experience we built, his confidence soared. Watching him present his innovative ideas at a team meeting a month later was a profound moment; it crystallized for me that L&D isn't just about information transfer—it's about transformation. This guide is built on that understanding, combining hard data with the practical insights needed to build your own transformative career.
This comprehensive article will serve as your ultimate roadmap. We will dissect every component of a learning and development specialist salary, explore the factors that can maximize your earnings, analyze the robust job outlook, and provide a clear, step-by-step plan to launch or advance your career in this dynamic and rewarding field.
What Does a Learning and Development Specialist Do?

At its core, a Learning and Development (L&D) Specialist is an architect of employee growth. They are responsible for identifying, designing, delivering, and evaluating learning programs that enhance the skills, knowledge, and performance of an organization's workforce. They are the strategic partners who ensure that employees not only have the capabilities to perform their jobs today but are also prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.
The role is a fascinating blend of education, psychology, technology, and business strategy. L&D Specialists don't just "teach"; they create comprehensive learning ecosystems. Their work is project-based and incredibly varied, moving fluidly from one challenge to the next.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks:
- Needs Analysis: This is the crucial first step. L&D Specialists work with managers, department heads, and senior leaders to identify performance issues and skill gaps. They use surveys, interviews, and performance data to answer the question: "What does our organization need to learn to achieve its goals?"
- Instructional Design: Once a need is identified, they design the learning solution. This involves applying adult learning theories (like andragogy) to create engaging and effective content. They might develop curricula for multi-day workshops, script an interactive eLearning module, create a job aid, or design a comprehensive leadership development program.
- Content Development: This is the "creation" phase. L&D Specialists write training materials, create slide decks, record and edit training videos, and build quizzes and assessments. They often use specialized authoring tools like Articulate 360 or Adobe Captivate to create sophisticated digital learning experiences.
- Training Delivery (Facilitation): Many L&D Specialists are also skilled facilitators. They lead in-person workshops, host virtual instructor-led training (VILT) sessions on platforms like Zoom or Teams, and guide group discussions. This requires excellent public speaking, presentation, and classroom management skills.
- LMS Administration: Most modern organizations use a Learning Management System (LMS) like Cornerstone, Workday Learning, or Docebo. L&D Specialists are often responsible for uploading courses, managing user enrollments, tracking completion rates, and pulling reports from the LMS.
- Evaluation and Reporting: How do you know if the training worked? L&D Specialists use models like the Kirkpatrick Model to evaluate the effectiveness of their programs, measuring everything from initial reactions to long-term business impact. They then create dashboards and reports to demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) of their initiatives to stakeholders.
### A Day in the Life of an L&D Specialist
To make this more tangible, let's walk through a typical day for "Alex," a Mid-Career L&D Specialist at a mid-sized tech company.
- 8:30 AM: Alex starts the day by checking the company's LMS dashboard. They review the completion rates for a new cybersecurity compliance module that was rolled out last week and send a targeted reminder to employees who haven't finished it yet.
- 9:00 AM: It's time for a stakeholder meeting with the Head of Sales. The sales team is struggling to articulate the value of a new product feature. Alex leads a needs analysis discussion, asking probing questions to understand the root cause of the performance gap. They agree on the next steps: Alex will observe a few sales calls and then propose a learning solution, likely a series of microlearning videos and a new role-playing workshop.
- 10:30 AM: Alex switches gears to instructional design. They open Articulate Storyline 360 and continue building an interactive eLearning module on "Giving Effective Feedback" for new managers. They spend time scripting a scenario, designing a drag-and-drop interaction, and selecting appropriate graphics.
- 12:00 PM: Lunch break. Alex listens to a popular L&D podcast to stay current on industry trends.
- 1:00 PM: Alex facilitates a 90-minute virtual workshop on "Time Management and Productivity" for a group of new hires. They use breakout rooms for small group discussions and an interactive poll to keep the energy high.
- 2:30 PM: After the workshop, Alex sends out a quick feedback survey (Level 1 of the Kirkpatrick Model) to gauge the learners' immediate reactions.
- 3:00 PM: Alex has a "train-the-trainer" session with a subject matter expert (SME) from the engineering department. They are coaching the SME on how to deliver a technical presentation in an engaging way for a non-technical audience.
- 4:00 PM: The final hour is dedicated to data. Alex pulls data from the last quarter's leadership development program and begins building a report for the Chief Human Resources Officer, highlighting pre- and post-training assessment scores and testimonials from participants.
This "day in the life" showcases the multifaceted nature of the role—a dynamic mix of strategic thinking, creative design, interpersonal facilitation, and data-driven analysis.
Average Learning and Development Specialist Salary: A Deep Dive
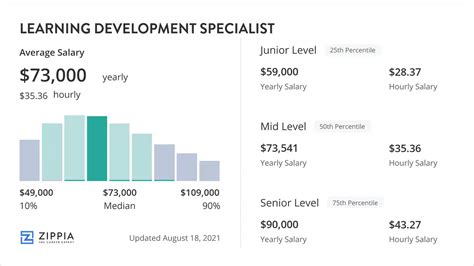
Understanding the financial landscape of the L&D profession is a critical step in your career planning. The salary for a Learning and Development Specialist is not a single, static number but a range influenced by a multitude of factors we'll explore in the next section. However, by examining data from authoritative sources, we can establish a strong baseline for what you can expect to earn.
The role's title can vary (e.g., Training Specialist, Corporate Trainer, Instructional Designer, Talent Development Specialist), but the core function is similar. For the most accurate national benchmark, we turn to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), which classifies this role under "Training and Development Specialists."
According to the most recent BLS data from May 2023, the compensation landscape is as follows:
- Median Annual Wage: $64,340
- This means that 50% of L&D specialists earned more than this amount, and 50% earned less.
- Lowest 10% Earned: Less than $40,840
- This typically represents true entry-level positions, part-time roles, or positions in non-profit organizations or low-cost-of-living areas.
- Highest 10% Earned: More than $111,040
- This figure reflects senior specialists, those with niche technical expertise, L&D managers, and individuals in high-paying industries and locations.
While the BLS provides a solid, official foundation, real-time salary aggregators, which collect user-reported data, often show a slightly higher average, reflecting current market demand and corporate compensation packages.
Here’s a look at what top salary platforms report as of late 2023/early 2024:
- Salary.com: Reports the median salary for a "Training Specialist II" (a mid-level role) in the United States to be around $73,501, with a typical range falling between $62,714 and $84,930. Their data for a Senior Specialist (III) pushes the median to over $89,000.
- Payscale.com: Lists the average base salary for a Learning and Development Specialist at approximately $68,500 per year. They also provide valuable data on how salary progresses with experience.
- Glassdoor: Shows a total pay average (including bonuses and other compensation) of around $83,618 per year, with a likely range between $66,000 and $106,000. This higher number highlights the importance of total compensation, which we'll discuss next.
### Salary Progression by Experience Level
Your earning potential grows significantly as you accumulate experience and expertise. A career in L&D is not static; it's a ladder you can actively climb. Here is a typical salary progression, synthesized from data provided by Payscale and Salary.com:
| Career Stage | Years of Experience | Typical Salary Range (Base) | Key Responsibilities |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Entry-Level L&D Coordinator/Specialist | 0-2 years | $50,000 - $65,000 | Scheduling training, LMS administration, updating existing materials, co-facilitating sessions, logistics. |
| Mid-Career L&D Specialist | 3-8 years | $65,000 - $90,000 | Conducting needs analyses, designing and developing new programs, leading training sessions, managing L&D projects. |
| Senior L&D Specialist / Instructional Designer | 8-15 years | $85,000 - $115,000+ | Leading complex, large-scale initiatives, mentoring junior staff, specializing in a high-demand area (e.g., leadership dev, tech training), measuring business impact. |
| L&D Manager / Director | 10+ years | $110,000 - $170,000+ | Setting L&D strategy for the entire organization, managing a team of specialists, managing the L&D budget, reporting to senior leadership (CHRO/VP of HR). |
*Note: These are national averages and can be significantly higher in major metropolitan areas or certain industries.*
### Beyond the Base Salary: Understanding Total Compensation
A savvy professional looks beyond the base salary to evaluate a job offer. The total compensation package for an L&D Specialist often includes several lucrative components that can add 10-25% or more to your overall earnings.
- Annual Bonuses: This is the most common form of additional cash compensation. Based on company and individual performance, annual bonuses for L&D Specialists typically range from 5% to 15% of their base salary. In high-performing companies or in roles closely tied to revenue (like Sales Enablement), this can be even higher.
- Profit Sharing: Some companies, particularly established private firms, offer profit-sharing plans where a portion of the company's annual profits is distributed among employees. This can add a significant, albeit variable, amount to your yearly income.
- Stock Options/Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): In publicly traded companies, especially in the tech sector, equity is a major part of the compensation package. RSUs grant you company stock that vests over a period (typically 3-4 years), which can become incredibly valuable if the company's stock price performs well. For L&D roles in startups, stock options offer the potential for a high-risk, high-reward payout.
- Retirement Benefits: A strong 401(k) or 403(b) matching program is essentially free money. A company that matches 100% of your contributions up to 6% of your salary is giving you a 6% raise dedicated to your retirement.
- Health and Wellness Benefits: Comprehensive health, dental, and vision insurance is a given. However, premium packages with low deductibles and co-pays can save you thousands of dollars a year. Other perks like wellness stipends, gym memberships, and robust mental health support add significant value.
- Professional Development Budget: This is a particularly relevant and valuable benefit for an L&D professional. Many companies will provide a budget of $1,000 to $5,000+ per year for you to attend conferences (like ATD's International Conference & EXPO), get certified (like the CPTD or APTD), or take external courses. This investment in your own growth is invaluable.
- Tuition Reimbursement: For those looking to pursue a master's degree in Instructional Design, Adult Learning, or Organizational Development, a company's tuition reimbursement program can be worth tens of thousands of dollars.
When evaluating a job offer, always calculate the value of these additional components to understand your true "total compensation" and make an informed decision.
Key Factors That Influence Your Learning and Development Specialist Salary
Your salary isn't just a number pulled from a national average; it's a direct reflection of the unique value you bring to an organization. Several key factors interact to determine your specific earning potential. By strategically navigating these areas, you can significantly increase your compensation over the course of your career. This section provides an in-depth analysis of the six primary drivers of an L&D Specialist's salary.
### 1. Level of Education
Your educational background forms the foundation of your expertise and is often a primary screening tool for employers.
- Bachelor's Degree (The Standard): A bachelor's degree is the standard entry requirement for most L&D Specialist roles. Relevant majors include Human Resources, Education, Communications, Business Administration, and Psychology. A bachelor's degree will qualify you for entry-level and mid-career roles and place you within the standard salary bands (e.g., $60k - $85k).
- Master's Degree (The Accelerator): Pursuing a master's degree is one of the most effective ways to accelerate your career and salary. A Master of Science (M.S.) in Instructional Design and Technology (IDT), Organizational Development (OD), or Adult Learning and Education (ALE) is highly prized. This advanced degree signals deep theoretical knowledge and practical expertise. Employers are often willing to pay a premium of 10% to 20% for candidates with a relevant master's degree. It can be the key that unlocks senior specialist roles, instructional design leadership positions, and salaries exceeding $100,000 much earlier in your career.
- Certifications (The Enhancer): Professional certifications demonstrate a commitment to the field and validate specific skill sets. They can give you a competitive edge and a salary bump. The most recognized certifications in the L&D world are offered by the Association for Talent Development (ATD):
- Associate Professional in Talent Development (APTD): Aimed at early-career professionals, this certification validates foundational knowledge and is an excellent way to stand out when you have 1-3 years of experience.
- Certified Professional in Talent Development (CPTD): This is the gold standard for experienced L&D professionals. It signifies a comprehensive understanding of the entire talent development capability model. Holding a CPTD can directly lead to higher-level roles and is a common requirement for L&D Manager positions.
- Other valuable certifications include those related to specific tools (e.g., Articulate Storyline), methodologies (e.g., project management like PMP), or coaching (e.g., from the International Coaching Federation - ICF).
### 2. Years and Quality of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most significant factor in salary determination. However, it’s not just about the number of years, but the *quality* and *type* of experience you gain.
- 0-2 Years (Coordinator/Entry-Level Specialist): At this stage, you're learning the ropes. Your focus is on execution and support. Salaries typically range from $50,000 to $65,000. To grow, focus on mastering the fundamentals: LMS administration, basic content updates, and flawless event coordination.
- 3-8 Years (Mid-Career Specialist): You are now an independent contributor, trusted to manage projects from start to finish. You conduct needs analyses, design programs, and facilitate with confidence. Your salary will see a significant jump into the $65,000 to $90,000 range. This is the time to start specializing and building a portfolio of successful projects.
- 8-15 Years (Senior/Lead Specialist): You are now a strategic advisor. You handle the most complex and high-impact projects, such as designing a global leadership curriculum or implementing a new learning technology. You mentor others and have deep expertise in a specific area. Salaries here routinely cross the six-figure mark, from $85,000 to $115,000+.
- 15+ Years (Principal Specialist/Manager/Director): With over 15 years of experience, you are likely in a leadership role, managing teams and setting organizational L&D strategy. Your focus shifts from "doing" to "enabling." Your work directly impacts business outcomes, and your compensation reflects this, with salaries ranging from $110,000 to $170,000+, often with significant bonus potential.
### 3. Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Cost of living and demand for talent create significant salary disparities across the United States. A salary that feels modest in a major tech hub could provide an excellent quality of life in a smaller city.
High-Paying Metropolitan Areas:
These locations combine a high cost of living with a dense concentration of large corporations and tech companies, driving salaries upward. Expect salaries here to be 15% to 35% above the national average.
- San Jose / San Francisco Bay Area, CA: Average L&D salaries often range from $95,000 to $125,000+.
- New York City, NY: A major hub for finance and media, with average salaries from $90,000 to $120,000.
- Boston, MA: Driven by biotech, finance, and tech, expect averages around $85,000 to $115,000.
- Seattle, WA: Home to tech giants, with averages in the $85,000 to $110,000 range.
- Washington, D.C.: A mix of government contracting and corporate headquarters leads to salaries from $80,000 to $105,000.
Mid-Tier & Lower-Cost-of-Living Areas:
In these cities, salaries may be closer to or slightly below the national average, but the lower cost of living means your purchasing power can be just as high, if not higher.
- Dallas, TX: Averages range from $70,000 to $90,000.
- Chicago, IL: Averages range from $75,000 to $95,000.
- Atlanta, GA: Averages range from $70,000 to $90,000.
- Kansas City, MO: Averages range from $60,000 to $80,000.
The Rise of Remote Work: The pandemic has changed the calculus. While some companies now pay a single "national rate" regardless of location, many still adjust salaries based on a geographic tier system. However, remote work gives you the power to live in a lower-cost area while potentially earning a salary from a company based in a high-cost hub, creating a powerful financial advantage.
### 4. Company Type & Size
The type of organization you work for has a profound impact on your salary, work culture, and the nature of your projects.
- Large Corporations (Fortune 500): These companies typically offer the highest base salaries and most robust benefits packages. They have large, well-funded L&D departments with clear career paths. The work is often more structured, specialized, and focused on large-scale program deployment.
- Tech Companies & Startups: This sector is known for competitive salaries and, crucially, significant equity potential (stock options/RSUs). A mid-level specialist at a pre-IPO startup might have a base of $90,000 but hold equity that could be worth much more upon a successful exit. The pace is fast, the work is innovative, and you'll often be expected to be a "jack-of-all-trades."
- Consulting Firms: Working for a consulting firm like Deloitte, PwC, or a boutique L&D consultancy can be highly lucrative. You'll work on diverse projects for various clients, but it often requires longer hours and frequent travel. Salaries for L&D consultants are often 20-40% higher than in-house corporate roles at a similar level of experience.
- Non-Profit Organizations: These roles are driven by mission, not profit. As a result, salaries are typically 10% to 25% lower than in the corporate sector. However, they offer immense personal fulfillment and often a better work-life balance.
- Government & Higher Education: These positions offer job security, excellent benefits (pensions, healthcare), and work-life balance, but salaries are generally lower than in the private sector and have less room for negotiation. Salary bands are often rigid and publicly defined.
### 5. Area of Specialization
As you advance in your L&D career, specializing can make you a highly sought-after (and highly-paid) expert. Generalists are valuable, but specialists solve specific, expensive problems for businesses.
- Leadership and Management Development: This is a perennially in-demand and high-value specialization. Designing programs that cultivate strong leaders directly impacts retention, engagement, and business success. Specialists in this area often command top-tier salaries.
- Sales Enablement / Sales Training: This is one of the most lucrative L&D paths. Because your work is directly tied to the company's revenue generation, your value is easy to measure. A great Sales Enablement Specialist who can demonstrably increase sales performance can command a salary of $100,000 - $150,000+, often with a significant performance bonus.
- Technical Training: Specialists who can train employees on complex software, proprietary systems, or technical processes are invaluable, especially in the tech, engineering, and manufacturing industries. If you can translate dense technical information into effective learning, you will be well-compensated.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DE&I): In recent years, DE&I has become a critical business function. L&D specialists who can design and facilitate meaningful and impactful training on topics like unconscious bias, inclusive leadership, and allyship are in extremely high demand.
- Instructional Design & eLearning Development: While many L&D specialists are generalists, those who become true masters of instructional design theory and eLearning authoring tools (Articulate 360, Vyond, Camtasia) are highly sought after for creating the scalable, digital learning experiences that modern companies rely on.
### 6. In-Demand Skills
Beyond your formal title, the specific skills you possess are what employers are paying for. Cultivating these high-value skills will directly impact your salary negotiations and career trajectory.
High-Value Hard Skills:
- eLearning Authoring Tools: Deep proficiency in the Articulate 360 suite (especially Storyline and Rise) is the number one technical skill for modern L&D professionals. Experience with Adobe Captivate, Camtasia, and Vyond is also highly valuable.
- Learning Management System (LMS) Administration: Experience managing and configuring enterprise-level LMS platforms like Cornerstone OnDemand, Workday Learning, Docebo, or SuccessFactors is a critical operational skill.
- Data Analysis & Reporting: The ability to go beyond completion rates and measure the business impact of training is a key differentiator. Skills in **Excel,
