Ever wondered who researches the issues, drafts the language, and briefs the elected officials behind the laws that shape our country? The answer is often a dedicated and sharp-minded Legislative Assistant (LA). This career offers a front-row seat to the democratic process and a unique opportunity to make a tangible impact on public policy.
But beyond the passion for public service, a career as a legislative assistant can be financially rewarding. While salaries can vary significantly, the average legislative assistant in the United States can expect to earn a competitive salary, typically ranging from $48,000 to over $85,000 per year, with senior roles commanding well over six figures.
This guide will break down what you can expect to earn as a legislative assistant and, more importantly, the key factors that will influence your salary throughout your career.
What Does a Legislative Assistant Do?

A Legislative Assistant is a professional staff member who works for a legislator at the federal, state, or local level. They are the policy specialists of a legislative office. Far from being just an "assistant," they are trusted advisors responsible for a specific portfolio of policy issues, such as healthcare, defense, technology, or agriculture.
Key responsibilities include:
- Researching and analyzing legislation: They track bills as they move through the legislative process and provide in-depth analysis on their potential impacts.
- Writing and Drafting: They draft policy memos, talking points, speeches, and even sections of proposed legislation.
- Constituent Communication: They meet with constituents, lobbyists, and advocacy groups to understand different perspectives on key issues.
- Briefing the Legislator: They prepare their boss for committee hearings, votes, and public appearances, ensuring they are well-informed on their assigned policy areas.
- Building Coalitions: They work with staff in other legislative offices to build support for their legislator’s priorities.
Average Legislative Assistant Salary
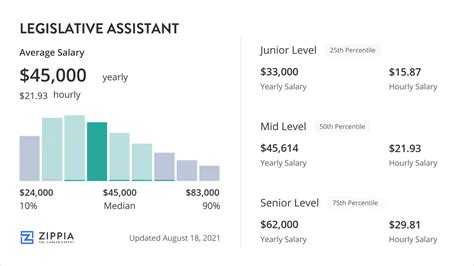
Salary data for legislative assistants shows a wide but promising range, reflecting the clear career progression available in this field. It's important to look at multiple sources to get a complete picture.
According to Salary.com, as of early 2024, the median salary for a Legislative Assistant in the United States is $66,901. The typical salary range falls between $54,772 and $80,958. This range often represents mid-career professionals.
Other data sources provide a similar perspective:
- Payscale reports an average base salary of around $54,000 per year, highlighting that entry-level positions like Legislative Correspondent (a common stepping stone to an LA role) start lower, while senior positions earn significantly more.
- Glassdoor places the average total pay at approximately $65,000 per year, combining base salary and any potential additional compensation.
The path often looks like this:
- Entry-Level (e.g., Staff Assistant, Legislative Correspondent): $40,000 - $55,000
- Mid-Career (Legislative Assistant): $55,000 - $80,000
- Senior-Level (e.g., Senior LA, Legislative Director): $85,000 - $150,000+
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a legislative assistant is not a single number but a figure influenced by several critical factors. Understanding these will help you maximize your earning potential.
###
Level of Education
While a bachelor’s degree is typically the minimum requirement for an LA position, advanced degrees can significantly boost your starting salary and career ceiling. Common undergraduate degrees include Political Science, Public Policy, Economics, and Communications. However, a graduate degree like a Juris Doctor (J.D.), a Master of Public Policy (MPP), or a Master of Public Administration (MPA) can make you a more competitive candidate for specialized, higher-paying roles, especially for positions leading to Legislative Director or Chief Counsel.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant driver of salary growth in this field. A clear career ladder exists within most legislative offices, and compensation rises with each step.
- 0-2 Years: Professionals often start as a Staff Assistant or Legislative Correspondent, handling administrative tasks and constituent mail. This experience is crucial for learning the legislative process and office dynamics.
- 2-5 Years: After proving their skills, an individual is often promoted to Legislative Assistant, taking on their own policy portfolio. This is where salaries begin to align with the national averages.
- 5+ Years: With substantial experience, an LA can become a Senior Legislative Assistant, handling the most complex issues, or be promoted to Legislative Director. The Legislative Director oversees the entire policy team and acts as the legislator's primary policy advisor, with salaries often exceeding $120,000, particularly at the federal level.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work has a massive impact on your salary.
- Federal (Washington, D.C.): Working for the U.S. Congress generally offers the highest salaries to compensate for the high cost of living in Washington, D.C., and the national scope of the work. According to salary data compiled by LegiStorm, House Legislative Assistants typically earn between $60,000 and $90,000, while Senate salaries are often slightly higher due to larger state constituencies and office budgets.
- State Legislatures: Salaries at the state level vary dramatically. An LA working for a full-time legislature in a large state like California or New York will earn substantially more than one in a state with a part-time legislature, such as New Hampshire or Wyoming.
- Local Government (City/County): Pay at the municipal level depends entirely on the size and budget of the city or county government.
###
Employer Type
The type of organization you work for is a crucial determinant of salary. While the title might be "Legislative Assistant" in a government office, the skills are transferable to the private sector, where compensation is often higher.
- Public Sector (U.S. Congress, State Legislatures): Salaries are funded by public budgets and are therefore often transparent but can be more modest than private sector equivalents.
- Private Sector (Lobbying Firms, Corporations, Trade Associations): The same skill set is used in roles like "Government Affairs Specialist" or "Policy Analyst." These positions are focused on influencing legislation from the outside. Due to private funding, these roles frequently offer significantly higher salaries, often starting at or above the senior-level pay in the public sector.
###
Area of Specialization
The policy portfolio you manage can also affect your earnings. LAs who specialize in highly complex, technical, or economically sensitive areas are in high demand and can command higher salaries. In-demand specializations include:
- Finance, Tax, and Appropriations: Expertise in these areas is critical for work on powerful committees.
- Healthcare: A perennially complex and high-stakes policy area.
- Technology and Cybersecurity: A rapidly growing field with a high need for specialized knowledge.
- Energy and Environment: Policies with massive economic and regulatory implications.
Job Outlook

While the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not maintain a separate category for "Legislative Assistant," we can look at related professions to gauge career prospects. For Paralegals and Legal Assistants, a role with similar research and analytical duties, the BLS projects job growth of 4% from 2022 to 2032. For Political Scientists, the projection is a 7% growth rate over the same period, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
The demand for skilled legislative staff remains steady. While the number of legislators is fixed, turnover from elections consistently creates job openings. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of policy issues ensures a continued need for bright, analytical, and dedicated professionals to support the legislative process.
Conclusion

A career as a legislative assistant is a unique blend of public service and intellectual challenge. While it is a passion-driven field, it offers a viable and rewarding career path with a clear ladder for advancement and salary growth.
Key Takeaways:
- Competitive Pay: Expect a salary that is competitive with other professional roles, with significant growth potential.
- Experience is King: Your earnings will grow substantially as you move from entry-level to senior roles like Legislative Director.
- Location and Employer Matter: Working in Washington, D.C., or for a private sector government affairs firm will typically yield the highest salaries.
- Specialization Pays: Developing expertise in a complex policy area can make you an invaluable and higher-paid asset.
For those looking to influence policy and be at the center of decision-making, the role of a legislative assistant offers not just a job, but a deeply impactful career with solid financial prospects.