Choosing a career in medicine is a monumental decision, often driven by a passion for healing and a commitment to lifelong learning. As one of the most respected and demanding professions, it also offers significant financial rewards, with physicians consistently ranking among the highest-paid professionals. A common question among aspiring doctors is whether the type of medical degree—MD (Doctor of Medicine) or DO (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine)—impacts their future earning potential.
This article provides a data-driven analysis of the salary landscape for physicians, directly addressing the query of an MD vs. DO salary difference. We will explore the nuances of physician compensation and uncover the factors that truly determine a doctor's income.
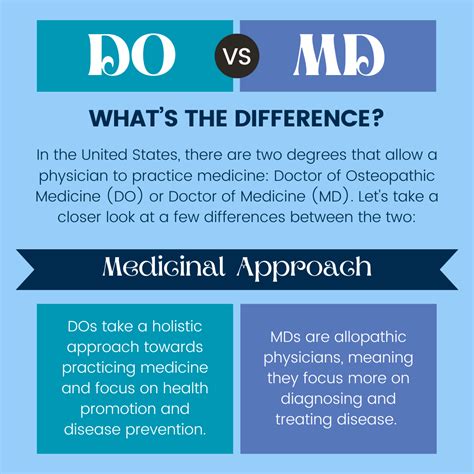
What Does a Physician (MD or DO) Do?
At their core, both MDs and DOs are fully licensed physicians who diagnose illnesses, prescribe medication, order diagnostic tests, and treat patients. They are qualified to practice in any medical specialty, perform surgery, and conduct research.
The primary distinction lies in their training philosophy. The MD path follows an allopathic approach, which focuses on diagnosing and counteracting disease through medication, surgery, and other interventions. The DO path follows an osteopathic approach, which incorporates all allopathic methods but adds a holistic perspective on patient care. DOs receive additional, specialized training in the musculoskeletal system and a hands-on technique called Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT).
Despite these philosophical differences in training, their day-to-day responsibilities, scope of practice, and licensing requirements are virtually identical in the United States.
Average Physician Salary: MD vs. DO
When examining broad national averages, a minor salary difference often appears. However, it's crucial to understand the context behind the numbers.
According to the 2023 Medscape Physician Compensation Report, one of the most comprehensive surveys in the industry:
- The average annual compensation for an MD was $357,000.
- The average annual compensation for a DO was $346,000.
At first glance, this suggests a slight edge for MDs. However, this small gap is not due to employers paying a premium for one degree over the other. Instead, it is almost entirely explained by historical trends in specialty choice. Traditionally, a higher percentage of DOs have entered primary care fields (like family medicine and pediatrics), while MDs have been more heavily represented in higher-paying surgical and procedural specialties.
When you compare an MD and a DO working in the same specialty, in the same location, with the same level of experience, their compensation is effectively identical. No reputable data suggests that an employer offers a different salary for the same role based on the letters after a physician's name.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

The "MD vs. DO" debate is a distraction from the factors that genuinely and significantly impact a physician's earnings. Let's break down the real drivers of compensation.
### Area of Specialization
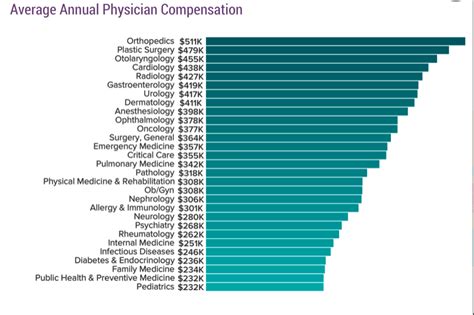
This is, by far, the most influential factor in determining a physician's salary. The gap between the highest- and lowest-paying specialties is vast—often exceeding $400,000 per year. Procedural and surgical specialties command the highest incomes due to the complexity of their work, the length of training, and reimbursement structures.
Here is a look at the average annual compensation by specialty, according to the 2023 Doximity Physician Compensation Report:
Top-Earning Specialties:
- Neurosurgery: $788,313
- Thoracic Surgery: $706,775
- Orthopedic Surgery: $624,043
- Plastic Surgery: $571,373
- Vascular Surgery: $557,632
Lower-Earning (Yet Still High-Income) Specialties:
- Family Medicine: $273,040
- Internal Medicine: $273,000
- Pediatrics: $242,834
- Endocrinology: $242,000
- Geriatrics: $236,192
As the data shows, the decision to become a neurosurgeon versus a pediatrician will have a far more profound impact on your earnings than the choice between an MD and a DO degree.
### Years of Experience
A physician's income grows significantly after completing their training.
- Residency: During residency (typically 3-7 years post-medical school), physicians earn a standardized salary, not a full attending physician's wage. According to Glassdoor, the average resident physician salary in 2024 is around $65,000 - $75,000, varying slightly by location and institution.
- Attending Physician: Upon completing residency and becoming an attending physician, salary jumps dramatically. According to Salary.com, a physician with 0-2 years of experience earns a median salary that is significantly higher than a resident's, and this continues to climb. An experienced physician with 10+ years in practice can expect to earn considerably more than an early-career counterpart in the same field.
### Geographic Location
Where you practice medicine matters. Physician salaries are driven by supply and demand. Rural and underserved areas often offer higher compensation packages to attract qualified doctors. Conversely, major metropolitan areas with a high density of physicians and academic centers (e.g., New York City, Boston) may offer slightly lower salaries, though the cost of living is much higher.
According to the Doximity 2023 report, the metropolitan areas with the highest average physician compensation include cities like Charlotte, NC, and St. Louis, MO, while those with the lowest include Washington, D.C., and Baltimore, MD.
### Practice Setting
The type of organization a physician works for also influences their pay. The Medscape report breaks this down as follows:
- Self-Employed / Private Practice Owner: This setting offers the highest earning potential, with an average compensation of $385,000. However, it also comes with the responsibilities and costs of running a business, including overhead, staffing, and malpractice insurance.
- Hospital or Health System Employee: This is the most common employment model today. It provides a stable, predictable salary (averaging around $344,000), benefits, and freedom from administrative burdens.
- Academic / Government: Physicians working in university medical centers, for the government, or in research often earn less than their counterparts in private practice. The tradeoff is often better work-life balance, research opportunities, and teaching responsibilities.
### Level of Education (Fellowships)
While both MDs and DOs hold doctorate degrees, "level of education" in a physician's career refers to post-residency training known as a fellowship. Completing a fellowship to sub-specialize almost always leads to a higher income. For example, an internal medicine physician who completes a three-year fellowship in cardiology will become a cardiologist and can expect to earn over $200,000 more per year than a general internist.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for physicians is exceptionally strong. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for physicians and surgeons will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032. This growth is driven by several factors, including the country's aging population, which requires more medical care, and a wave of retiring physicians. This sustained demand ensures that medicine will remain a stable, secure, and in-demand profession for the foreseeable future, for both MDs and DOs.
Conclusion

For any student aspiring to a career in medicine, the key takeaway is this: the salary difference between an MD and a DO is negligible and should not be a factor in your decision-making process. Both paths lead to the same destination—a rewarding and lucrative career as a fully licensed physician with the ability to practice in any specialty.
The true determinants of your future income are the choices you make *after* getting into medical school:
- Your choice of specialty is the single most significant factor.
- The geographic location and practice setting you choose will further define your compensation.
- Your income will naturally grow with experience and any sub-specialty training you pursue.
Ultimately, prospective doctors should choose the path—MD or DO—whose educational philosophy best aligns with their own values. Focus on excelling in your studies and choosing a specialty that ignites your passion. That is the true formula for a successful and fulfilling medical career.