Embarking on a career in medicine is a monumental journey of dedication, rigorous study, and profound personal growth. For those who have successfully navigated medical school, the next critical step is residency—a multi-year, hands-on training program in a chosen specialty. While the ultimate goal is a rewarding career as an attending physician, a common and practical question on every resident's mind is: "What can I expect to earn during these demanding training years?"
While a resident physician's income—more accurately called a stipend—is modest compared to that of a fully licensed physician, it is the financial foundation for this crucial training period. The national average resident physician salary is approximately $67,400 per year, but this figure can vary significantly based on several key factors. This guide will break down the components of a resident's salary, explore what influences it, and provide a clear outlook on the profession.
What Does a Resident Physician Do?

A resident physician is a doctor who has graduated with a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree but is now training in a specialized medical field. They are not students, but rather physicians-in-training who provide direct patient care under the supervision of senior physicians (attendings).
Their responsibilities are extensive and form the backbone of many hospitals:
- Diagnosing illnesses and developing treatment plans for patients.
- Conducting physical exams and recording patient histories.
- Ordering and interpreting diagnostic tests.
- Performing medical procedures appropriate for their level of training.
- Working long hours, including nights, weekends, and holidays, often in high-stress environments.
Residency is an immersive, demanding apprenticeship where physicians hone their clinical skills, judgment, and expertise in specialties ranging from family medicine to neurosurgery.
Average Resident Physician Salary
The salary for a resident physician is not determined by market forces in the same way as other professions. Instead, it is a stipend set by the teaching hospital or institution to cover living expenses during training.
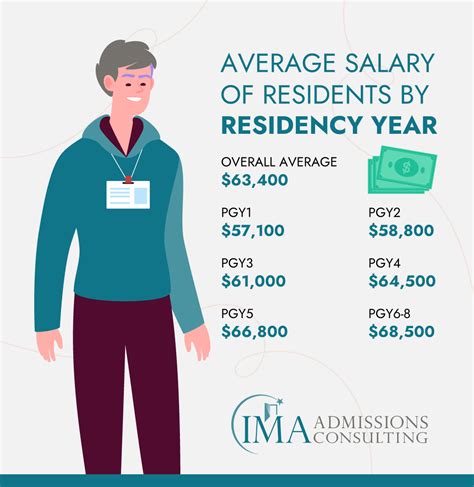
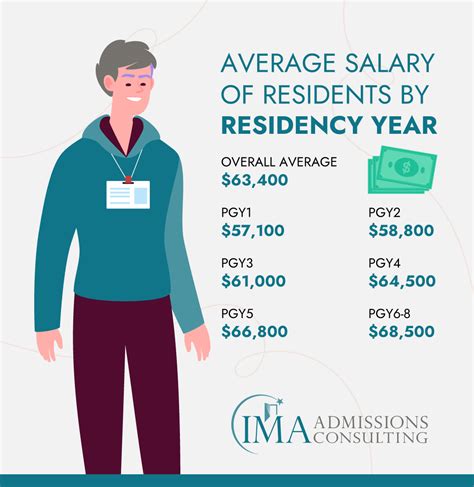
According to the 2023 Medscape Resident Salary & Debt Report, one of the most authoritative sources on this topic, the average salary for medical residents in the U.S. is $67,400.
Most residency programs provide a fairly narrow salary band that increases with each year of training. A typical range might look like this:
- First-Year Resident (Intern): $60,000 - $65,000
- Mid-Level Resident: $65,000 - $72,000
- Senior Resident/Fellow: $72,000 - $80,000+
It is crucial to view this income as a training wage. While it supports a resident through several years of intense work, it is a stepping stone to the significantly higher earning potential of a fully licensed, board-certified attending physician.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While all resident salaries fall within a relatively tight range, several factors create variation in exact compensation.
### Years of Experience
This is the single most significant factor influencing a resident's salary. "Experience" in this context refers to the Post-Graduate Year (PGY). A PGY-1 resident (also known as an intern) is in their first year of training and will earn the lowest salary in their program.
As a resident advances to PGY-2, PGY-3, and beyond, their salary increases incrementally each year. This reflects their growing expertise, responsibility, and value to the hospital. For example, a PGY-4 neurosurgery resident will earn more than a PGY-1 internal medicine resident at the same institution, not because of their specialty, but simply because they are further along in their training.
### Geographic Location
Where you complete your residency plays a major role in your stipend. Hospitals in high-cost-of-living (HCOL) areas must offer higher salaries to attract residents who need to afford housing, transportation, and daily expenses.
According to data from Salary.com, residents in metropolitan areas like New York City, San Francisco, and Boston tend to have higher-than-average stipends. Conversely, residents in states with a lower cost of living, such as in the Midwest or South, may see slightly lower figures. However, the higher salary in an HCOL city does not always translate to greater disposable income. Prospective residents should always weigh the offered salary against the local cost of living.
### Area of Specialization
This is a point of common confusion. During residency, the medical specialty has very little impact on salary. A PGY-2 psychiatry resident and a PGY-2 orthopedic surgery resident working at the same hospital will earn nearly identical salaries. The stipend is tied to the institution and PGY level, not the future earning potential of the specialty.
The dramatic income disparity between specialties like neurosurgery and family medicine only emerges *after* residency is completed and physicians begin practicing as attendings. Some institutions may offer chief residents or those in fellowships (advanced training after residency) slightly higher pay, but this is still primarily tied to their advanced PGY level.
### Company Type
The type of institution hosting the residency program can influence salary. There are generally two main types:
- University-Affiliated/Academic Medical Centers: These are large, research-focused hospitals tied to a medical school. They often set the standard for resident salaries in a region.
- Community Hospitals: These programs may be in smaller cities or suburban areas. Their salaries are often competitive with nearby academic centers to attract top candidates.
Data from salary aggregators like Glassdoor and Payscale show that while there are differences, the salary gap between these institution types is not as wide as one might expect. Factors like whether the hospital is in a major urban center or if its residents are unionized often have a more direct impact on compensation packages.
### Level of Education
For a resident physician, the level of education is standardized. The prerequisite for entering residency is an M.D. or D.O. degree from an accredited medical school. Holding additional degrees, such as an M.P.H. (Master of Public Health) or Ph.D., does not typically result in a higher residency stipend. The salary structure is built around the medical training program itself.
Job Outlook

The long-term career outlook for physicians and surgeons is excellent. The intense work and modest pay during residency are an investment in a stable, in-demand, and financially rewarding profession.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, employment for physicians and surgeons is projected to grow 3% from 2022 to 2032. This growth is driven by the needs of an aging population and increasing demand for a wide range of medical services. This sustained demand ensures that the effort and financial sacrifice made during residency will lead to strong career opportunities.
Conclusion

Becoming a resident physician is the culmination of a decade of hard work and the beginning of a specialized medical career. While the salary is not designed for wealth accumulation, it is a functional stipend that supports physicians through an essential period of intensive, hands-on learning.
Here are the key takeaways for anyone considering this path:
- Expect a Modest Stipend: The average resident earns around $67,400, a figure designed to cover living expenses during training.
- Salary Grows with Experience: Your pay will increase predictably with each Post-Graduate Year (PGY) you complete.
- Location Matters: Salaries are higher in high-cost-of-living areas, but that doesn't always mean more take-home pay.
- It's a Stepping Stone: The resident stipend is temporary. It is the gateway to a long-term career as a physician, which offers significant financial security and profound professional fulfillment.
For prospective and current medical students, understanding the financial realities of residency is a key part of career planning. It is a period of sacrifice, but one that leads to a profession that is consistently one of the most respected, essential, and rewarding in the world.