Are you charting your career path and wondering how your potential salary will translate into real-world living standards? One of the most critical, yet often overlooked, metrics for professional success is the rent-to-salary ratio. Understanding this concept is not just about budgeting; it's about making strategic career decisions—from negotiating your salary to choosing where you work—that support your long-term financial well-being. This guide will break down what the ratio is, how your career choices impact it, and how you can leverage this knowledge to build a more secure future.
What is the Rent-to-Salary Ratio?

The rent-to-salary ratio is a simple yet powerful personal finance metric that calculates what percentage of your income is spent on rent. It's a fundamental measure of housing affordability and a key indicator of your overall financial health.
Financial advisors and property managers have long relied on a common benchmark known as the 30% rule. This guideline suggests that you should spend no more than 30% of your *gross* monthly income (your salary before taxes and other deductions) on rent. Exceeding this threshold can put a significant strain on your budget, leaving little room for other essential expenses, savings, and discretionary spending. For a professional, this ratio serves as a reality check, connecting the salary you earn to the lifestyle you can afford.
How to Calculate Your Rent-to-Salary Ratio
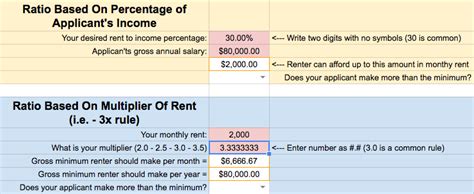
Calculating your ratio is straightforward. You can do it using either your gross income (most common for landlords) or your net income (more realistic for personal budgeting).
Formula: (Monthly Rent / Monthly Income) x 100 = Rent-to-Salary Ratio %
Example:
Let's assume you've been offered a job with a $75,000 annual salary.
1. Calculate Your Gross Monthly Income:
$75,000 / 12 months = $6,250 per month
2. Find a Potential Apartment:
You find an apartment you like that costs $1,800 per month.
3. Calculate the Ratio:
($1,800 / $6,250) x 100 = 28.8%
In this scenario, your rent-to-salary ratio is 28.8%, which falls comfortably within the recommended 30% guideline. This indicates that the rent is likely affordable on your salary, leaving you with sufficient income for other financial goals.
Key Factors That Influence Your Rent-to-Salary Ratio
Your rent-to-salary ratio isn't static; it's a dynamic figure heavily influenced by your career decisions. Here’s how different factors can dramatically impact your earning potential and, consequently, your housing affordability.
### Level of Education and Years of Experience
It's a foundational principle of career progression: higher education and more experience typically lead to higher salaries. This directly improves your rent-to-salary ratio by increasing the "salary" part of the equation, giving you more flexibility in the housing market.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), median usual weekly earnings in 2023 show a clear correlation with education:
- High School Diploma: $878
- Bachelor's Degree: $1,490
- Master's Degree: $1,739
- Doctoral Degree: $2,168
Similarly, experience pays. An entry-level professional will earn significantly less than a senior-level manager or director in the same field. As your salary grows with promotions and experience, a rent payment that once seemed high can become a much smaller percentage of your income.
### Geographic Location
Location is arguably the most significant factor influencing your rent-to-salary ratio. A high salary in a low-cost-of-living (LCOL) area can provide an excellent quality of life, while the same salary in a high-cost-of-living (HCOL) city could feel restrictive.
Consider a Marketing Manager with a national average salary of around $138,735, according to Salary.com (as of late 2023). Let's see how the ratio changes in two different cities:
| Metric | New York, NY (HCOL) | Kansas City, MO (LCOL) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Median Marketing Mgr Salary | ~$170,165 ($14,180/mo) | ~$128,495 ($10,708/mo) |
| Average Rent (1-BR) | ~$4,000/mo | ~$1,250/mo |
| Rent-to-Salary Ratio | ~28.2% | ~11.7% |
*(Salary data from Salary.com, Rent data from Zumper/RentCafe)*
As the table shows, even with a higher salary in New York, the rent takes up a much larger portion of income. The professional in Kansas City has a vastly superior rent-to-salary ratio, freeing up thousands of dollars each month for savings, investment, or other lifestyle goals. The rise of remote work has made this calculation a central part of many professionals' career strategies.
### Industry and Company Type
The industry you work in and the type of company you work for create vast differences in compensation. Industries like technology, finance, and biotechnology are known for offering higher-than-average salaries, which can help offset the cost of living in expensive urban centers.
According to BLS data on median wages by industry, workers in sectors like Information Technology and Finance consistently earn more than those in Hospitality or Retail Trade.
Furthermore, a large, publicly-traded corporation (e.g., a FAANG company) will generally offer a more lucrative compensation package (including salary, bonuses, and stock options) than a small non-profit or a startup in its early stages. Choosing a high-growth, high-paying industry is a direct strategy for improving your financial standing and rent-to-salary ratio.
### Area of Specialization
Within any given industry, specialization pays. A generalist may have broad opportunities, but a specialist with in-demand, niche skills can command a premium salary. For example:
- A Software Engineer is a valuable role.
- A Software Engineer specializing in AI and Machine Learning for the fintech industry is an even more valuable—and higher-paid—role.
According to Payscale, professionals with specialized skills in areas like data science, cybersecurity, and cloud computing often see a significant salary premium. By investing in certifications and skills that are in high demand, you can increase your income without necessarily changing industries, thereby improving your rent-to-salary ratio.
Job Outlook and Strategic Planning

Thinking about your rent-to-salary ratio is a form of strategic career planning. The BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook projects which fields are set to grow. For example, employment in computer and information technology occupations is projected to grow 15% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations.
By targeting a career in a high-growth, high-demand field, you not only secure your job prospects but also position yourself for stronger salary growth over time. This forward-looking approach ensures that your income will keep pace with or exceed inflation and rising housing costs, keeping your financial health in check.
Conclusion: A Tool for Empowered Career Decisions
The rent-to-salary ratio is more than just a budgeting rule; it's a powerful lens through which to view your career. It forces you to ask critical questions: Does this salary offer work in this city? Is this industry a path to long-term financial stability? Should I negotiate for more, or consider a remote role?
For anyone planning their professional future, here are the key takeaways:
- Aim for 30% or Less: Use the 30% rule as a starting guideline to assess housing affordability.
- Your Career Choices are Your Leverage: Your education, experience, industry, and location are the most powerful tools you have for improving your ratio.
- Think Holistically: A high salary in an expensive city may not be better than a good salary in an affordable one. Calculate the ratio to be sure.
- Plan for the Future: Choose career paths and specializations with strong growth outlooks to ensure your salary—and your financial freedom—continues to grow.
By keeping the rent-to-salary ratio in mind, you can move beyond simply earning a paycheck and begin strategically building a career that truly supports the life you want to live.
