In our hyper-connected world, the unseen magic of wireless technology powers everything from your smartphone and Wi-Fi to advanced satellite communications and autonomous vehicles. At the heart of this innovation are Radio Frequency (RF) engineers. This demanding and specialized field offers not only intellectually stimulating challenges but also significant financial rewards, with salaries often reaching well into the six-figure range.
If you're considering a career in this dynamic sector, understanding your potential earnings is a critical step. This guide provides a data-driven breakdown of RF engineer salaries, the key factors that influence them, and the promising outlook for this essential profession.
What Does an RF Engineer Do?

RF engineers are the architects of the wireless world. They are a specialized type of electrical engineer who works with devices and systems that transmit or receive radio waves. Their expertise spans the electromagnetic spectrum, and their work is crucial for ensuring seamless, reliable wireless communication.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Designing and Developing: Creating components and systems like antennas, amplifiers, transceivers, and filters.
- Testing and Validation: Conducting rigorous tests to ensure systems meet performance specifications, comply with regulations (like the FCC), and don't interfere with other signals.
- Optimization: Fine-tuning networks (like cellular or Wi-Fi) to improve coverage, capacity, and signal quality.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving complex issues in RF systems, from a single circuit board to a nationwide network.
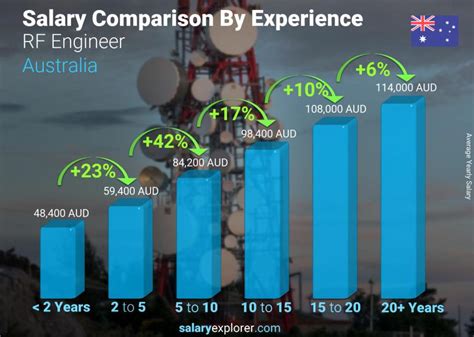
Average RF Engineer Salary
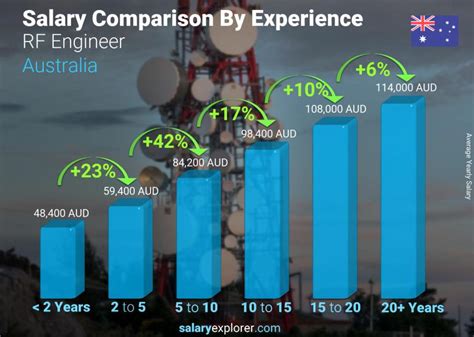
Given the high demand for their specialized skills, RF engineers command competitive salaries. While exact figures vary based on several factors, we can establish a strong baseline from leading data sources.
According to data aggregated from authoritative sources like Salary.com, Payscale, and Glassdoor, the average salary for an RF engineer in the United States typically falls between $115,000 and $125,000 per year.
Of course, this is just the median. The overall salary range is much wider, reflecting differences in experience, location, and specialization:
- Entry-Level RF Engineers (0-2 years of experience) can expect to start in the range of $85,000 to $105,000.
- Senior RF Engineers (10+ years of experience) or those in principal roles can command salaries of $150,000 to $180,000 or more.
Salary.com notes a median salary for an "RF Engineer III" (a mid-to-senior level role) at around $123,500 as of late 2023, while Glassdoor reports a similar total pay average.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as an RF engineer is not a single number but a spectrum influenced by a combination of critical factors. Understanding these drivers is key to maximizing your earning potential.
###
Level of Education
Your educational background sets the foundation for your career trajectory and starting salary.
- Bachelor’s Degree: A Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering (BSEE) is the standard entry-level requirement. Graduates with a solid academic record and relevant internships can secure well-paying entry-level positions.
- Master’s Degree: A Master of Science (M.S.) in Electrical Engineering with a specialization in RF/Microwave Engineering can provide a significant salary advantage, often adding $10,000-$20,000 to your annual earnings. It opens doors to more advanced roles in research and development (R&D) and complex system design, making you a more competitive candidate.
- Ph.D.: A doctorate is typically pursued by those aiming for highly specialized roles in cutting-edge research, academia, or as a principal scientist at a large corporation. A Ph.D. can command the highest salaries in the field.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the most significant factor in salary growth. Your value to an employer increases as you move from theoretical knowledge to proven, hands-on expertise.
- Entry-Level (0-3 Years): At this stage, you are typically focused on testing, data analysis, and supporting senior engineers. Your primary goal is to learn and apply fundamental concepts.
- Mid-Career (4-9 Years): You are now a fully proficient engineer, capable of designing components, managing small projects, and troubleshooting complex issues independently. Salaries see a substantial jump during this period.
- Senior / Principal (10+ Years): With a decade or more of experience, you are a subject matter expert. You are likely leading system architecture design, mentoring junior engineers, and shaping the technical strategy for major projects. This level commands the highest compensation packages, including significant bonuses and stock options.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries are often adjusted to reflect the cost of living and the concentration of tech and defense companies in a given area. Tech hubs with a high demand for RF talent consistently offer the highest pay.
Top-paying states and metropolitan areas for RF engineers include:
- California: San Jose (Silicon Valley), San Diego, and Los Angeles are epicenters for tech, aerospace, and defense.
- Massachusetts: The Boston-Cambridge area is a major hub for R&D, defense, and communications technology.
- Texas: Austin and Dallas are rapidly growing tech centers with a strong presence in telecommunications and semiconductor manufacturing.
- Colorado: Boulder and Denver have a robust aerospace and telecommunications industry.
- Maryland/Virginia: The proximity to Washington D.C. drives high demand in the defense and government contracting sectors.
Engineers in these high-cost-of-living areas can expect to earn 15-30% above the national average.
###
Company Type
The type of company you work for directly impacts your compensation structure and overall benefits.
- Large Tech & Telecom Giants (e.g., Apple, Qualcomm, Verizon): These companies typically offer very high base salaries, generous bonuses, and excellent benefits packages to attract top talent for consumer electronics and network infrastructure.
- Defense & Aerospace Contractors (e.g., Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon): These firms provide competitive salaries and incredible job stability. Roles here often require security clearances, which can further increase earning potential.
- Semiconductor Companies (e.g., Broadcom, Qorvo, Skyworks): These companies design and manufacture the core RF chips (RFICs) that power modern devices. This is a highly specialized and lucrative sector.
- Startups: While base salaries might be slightly lower than at established giants, startups often offer significant equity or stock options. This presents a high-risk, high-reward scenario where a successful company launch can lead to a massive financial windfall.
###
Area of Specialization
Within the broad field of RF engineering, certain high-demand specializations can lead to premium salaries.
- 5G/6G Technology: Engineers working on the rollout and development of next-generation cellular networks are in extremely high demand.
- Antenna Design: This is a fundamental and always-critical skill for everything from iPhones to fighter jets.
- MMIC/RFIC Design: Designing Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuits and Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits is a highly complex skill that puts engineers at the forefront of hardware innovation.
- Satellite Communications (SatCom): With the growth of constellations like Starlink and renewed investment in space, RF engineers with SatCom experience are highly sought after.
- Phased-Array and Radar Systems: Expertise in these areas is crucial for aerospace, defense, and autonomous vehicle applications.
Job Outlook

The future for RF engineers is bright and stable. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for Electrical and Electronics Engineers will grow by 5% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
However, this number doesn't tell the whole story for RF specialists. The relentless expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), the global deployment of 5G, the race to develop 6G, and continued advancements in aerospace and defense technology will fuel a persistent, strong demand for engineers with RF expertise. As long as the world demands faster, more reliable wireless connectivity, RF engineers will remain essential.
Conclusion

A career as an RF engineer is a pathway to becoming a key player in the technology that defines our modern era. The profession is intellectually challenging, critically important, and, as the data shows, financially rewarding.
Key Takeaways:
- Strong Earning Potential: Expect a six-figure salary to be the norm, with significant growth potential throughout your career.
- Experience is King: Your salary will see its largest increases as you gain hands-on, practical experience.
- Invest in Education: A Master's degree is a powerful tool for unlocking higher-level roles and a bigger paycheck.
- Location and Specialization Matter: Strategically choosing where you work and what you specialize in can dramatically accelerate your earnings.
For students and professionals with a passion for physics, problem-solving, and communication technology, the field of RF engineering offers a secure and prosperous future at the leading edge of innovation.