For anyone looking to build a career or operate a business in Guatemala, understanding the local compensation landscape is fundamental. The cornerstone of this landscape is the *salario mínimo*, or minimum wage. More than just a number, it's a complex, multi-tiered system that reflects the nation's diverse economic structure. As of 2024, the monthly minimum wage, including the mandatory bonus, ranges from approximately Q3,374 to Q3,516 (quetzales), depending on the industry and geographic location. This guide will break down what that means for both employees and employers.
What Is the "Salario Mínimo" in Guatemala?

The *salario mínimo* is the legally mandated lowest remuneration that employers can pay their wage earners for work performed during a given period. It cannot be lowered by collective agreement or an individual contract. Established and regulated by the Guatemalan Ministry of Labor and Social Prevision (Ministerio de Trabajo y Previsión Social), its primary purpose is to protect workers against unduly low pay and ensure a basic, just standard of living that can cover the essential needs of an individual and their family.
Unlike in many countries with a single national rate, Guatemala’s minimum wage is differentiated by economic activity and, more recently, by geographic area, making it crucial to understand which category applies to a specific job.
Current Minimum Wage Rates in Guatemala (2024)
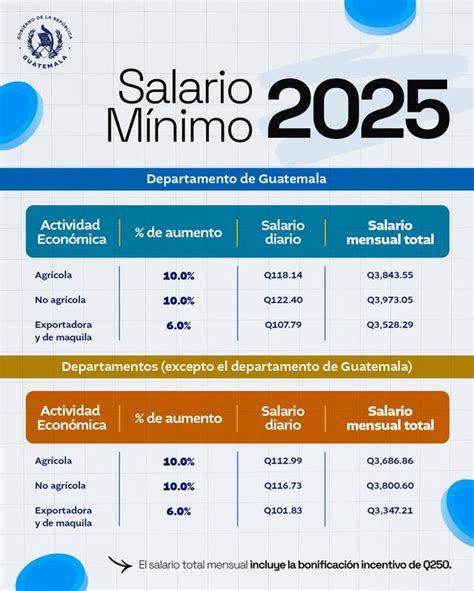
The minimum wage for 2024 was established by Government Agreement No. 307-2023. A key feature is the mandatory, non-taxable "Bonificación Incentivo" (Incentive Bonus) of Q250.00 per month, established by Decree 78-89. This bonus is paid *in addition* to the base minimum wage.
The rates are set for two distinct geographic zones:
1. Department of Guatemala: The capital region.
2. Rest of the Country: All other 21 departments.
Here are the official daily and monthly minimum wage rates for 2024, before the Q250.00 bonus:
| Economic Activity | Geographic Zone | Daily Wage | Monthly Wage | Total Monthly (with Bonus) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| Non-Agricultural (No Agrícola) | Department of Guatemala | Q107.11 | Q3,266.60 | Q3,516.60 |
| | Rest of the Country | Q104.10 | Q3,174.88 | Q3,424.88 |
| Agricultural (Agrícola) | Department of Guatemala | Q104.25 | Q3,179.38 | Q3,429.38 |
| | Rest of the Country | Q101.05 | Q3,081.73 | Q3,331.73 |
| Export & Maquila (Exportadora y de Maquila) | *Nationwide* | Q98.22 | Q2,995.34 | Q3,245.34 |
*Source: Ministerio de Trabajo y Previsión Social de Guatemala, Acuerdo Gubernativo 307-2023.*
*Note: Monthly calculations are based on the official daily rates multiplied by an average of 30.41667 days per month.*
Key Factors That Influence the Minimum Wage

The minimum wage isn't a static figure influenced by market demand alone. It's a regulated rate determined by several key factors.
### Area of Specialization / Economic Sector
This is the primary factor in determining the base wage. The government recognizes three main economic sectors (*circunscripciones económicas*):
1. Non-Agricultural Activities (Actividades No Agrícolas): This is the broadest category, covering the vast majority of jobs in urban areas, including retail, services, construction, administration, and transportation.
2. Agricultural Activities (Actividades Agrícolas): This applies to all work related to farming, livestock, forestry, and other agricultural production.
3. Export and Maquila Activities (Actividad Exportadora y de Maquila): This is a specific category for the apparel and textile industry operating in free trade zones, which is a significant source of formal employment. This sector has a single, nationwide rate intended to maintain its international competitiveness.
### Geographic Location
A significant change implemented in 2023 and continued for 2024 is the regionalization of the minimum wage. Citing differences in the cost of living and economic dynamism, the government established separate rates for the Department of Guatemala (the region including Guatemala City) and the rest of the country. As shown in the table above, the wages for both agricultural and non-agricultural work are slightly higher in the capital department to reflect its higher economic output and living expenses.
### Annual Government and Commission Review
The minimum wage is subject to an annual review process. The National Salary Commission (Comisión Nacional del Salario), a tripartite body composed of representatives from labor unions, employer associations, and the government, convenes each year. They analyze economic indicators like the projected inflation rate, the cost of the *Canasta Básica* (basic food basket), and overall economic growth. Based on these discussions, they provide a recommendation to the President of Guatemala, who makes the final decision via a Government Agreement, which may or may not align with the commission's proposal.
### Level of Education & Years of Experience
While education and experience are critical for advancing *beyond* the minimum wage, they do not directly influence the legal minimum wage rate itself. The *salario mínimo* is a floor, not a ceiling. An entry-level worker with a high school diploma and a senior worker with 20 years of experience in the same non-agricultural role are both legally entitled to *at least* the same minimum wage. However, experience and education are precisely the factors that give an employee the leverage to negotiate a salary significantly higher than the legal minimum.
### Company Type
The type of company—whether it's a small local business, a large national corporation, or a multinational firm—does not change the legal obligation to pay the minimum wage. However, larger corporations and multinational companies often offer starting salaries and benefits packages that are well above the minimum wage to attract and retain top talent. In contrast, smaller enterprises are more likely to offer compensation at or near the legal minimum.
Job Outlook and Economic Context
The minimum wage is a critical economic indicator in Guatemala, as a significant portion of the formal labor force earns wages at or near this level. According to analyses by the Central American Business Intelligence (CABI) and reports from international bodies, the key challenge in Guatemala is not the wage rate itself, but its application. A large informal economy—estimated to encompass over 70% of the workforce—operates outside these legal regulations.
Therefore, the "job outlook" for minimum wage earners is tied to the broader economic goal of formalizing the labor market. Government initiatives, foreign investment, and economic growth in sectors like services, tourism, and manufacturing are key to creating more formal jobs where the minimum wage and associated benefits (like social security and bonuses) are guaranteed.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways

For professionals, job seekers, and business owners in Guatemala, here are the essential takeaways:
- There is no single minimum wage. Your legal minimum earning is determined by your industry (agricultural, non-agricultural, or maquila) and your geographic location (Department of Guatemala vs. the rest of the country).
- The Bonus is Mandatory. The monthly Q250.00 "Bonificación Incentivo" is a separate, non-negotiable part of your compensation on top of the base salary.
- The Minimum Wage is a Floor, Not a Ceiling. It is the starting point for compensation. Your skills, education, experience, and negotiating ability are what will drive your earnings higher throughout your career.
- Know Your Rights and Obligations. Whether you are an employee or an employer, a clear understanding of the current *salario mínimo* regulations is essential for fair and legal employment practices.
Navigating the Guatemalan job market successfully starts with being informed. By understanding these fundamental compensation structures, you can better plan your career path and advocate for your value in the workplace.