For individuals with a passion for both technology and healthcare, a career as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) offers a stable, rewarding, and increasingly vital role. These are the professionals who ensure that the life-saving and diagnostic medical devices in our hospitals and clinics are functioning perfectly. But beyond job satisfaction, what is the financial potential of this career?
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of a Biomedical Equipment Technician's salary, with median annual earnings often falling between $57,000 and $65,000, and top earners with specialized skills exceeding $97,000 per year. We will explore the factors that shape this income, from experience and location to specialization, giving you a clear picture of your earning potential in this dynamic field.
What Does a Biomedical Equipment Technician Do?
A Biomedical Equipment Technician, also known as a Medical Equipment Repairer or Biomedical Engineering Technician, is an essential part of the modern healthcare ecosystem. They are the highly skilled professionals responsible for the installation, maintenance, calibration, repair, and inspection of a wide array of medical devices.
Their work ensures that everything from patient monitors and infusion pumps to complex MRI machines and life-support ventilators is safe, accurate, and ready for patient use. By blending expertise in electronics, mechanics, and physiology, BMETs directly contribute to patient safety and the quality of care provided by clinical staff.
Average Biomedical Equipment Technician Salary
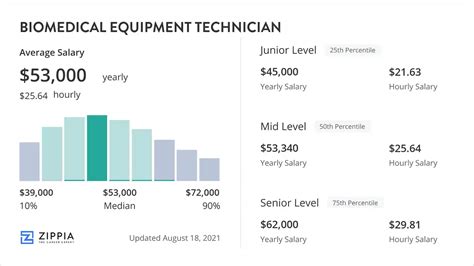
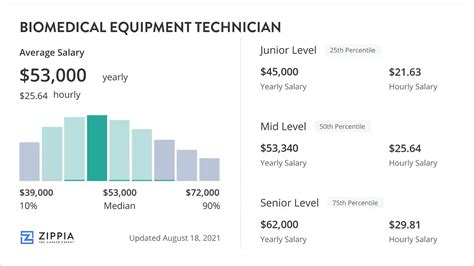
When analyzing salary data, it's crucial to look at multiple authoritative sources to get a complete picture. The figures for a BMET can vary slightly based on the methodology used by each data aggregator.
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the most comprehensive government data. In its May 2022 report (the most recent available), the median annual wage for "Medical Equipment Repairers" was $57,800. The salary spectrum is broad: the lowest 10% earned less than $37,860, while the highest 10% earned more than $97,550.
- Salary.com, which aggregates real-time employer-reported data, lists a slightly higher median salary for a "Biomedical Equipment Technician II" at $64,303 as of late 2023. Their typical range falls between $57,000 and $73,000.
- Payscale, which uses user-reported salary data, shows an average base salary of around $56,000 per year.
These figures confirm a solid median income with significant room for growth. The difference between an entry-level technician and a highly experienced, specialized senior technician can be substantial. Let's explore the factors that drive that growth.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary as a BMET is not a fixed number. It is influenced by a combination of your qualifications, career choices, and market forces. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your earning potential.
### Level of Education
The most common entry point into the BMET field is an Associate of Applied Science (A.A.S.) in Biomedical Equipment Technology or a related electronics technology degree. However, education can directly impact your starting salary and long-term career trajectory.
- Associate's Degree: This is the industry standard and will qualify you for most entry-level (BMET I) and mid-level (BMET II) positions.
- Bachelor's Degree: A Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in Biomedical Engineering Technology or a similar field can provide a competitive advantage. Graduates may command a higher starting salary and are often better positioned for leadership roles, such as a BMET Supervisor, Clinical Engineering Manager, or specialized roles working for equipment manufacturers.
- Certifications: Professional certifications are a powerful tool for salary negotiation. The most recognized certification is the Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET), offered by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI). Earning your CBET demonstrates a verified level of competence and often leads to an immediate salary increase and greater job opportunities.
### Years of Experience
Experience is arguably the single most significant factor in salary growth. The BMET career path has a well-defined progression, typically categorized by levels, each with a corresponding increase in responsibility and pay.
- Entry-Level (BMET I / 0-2 years): Technicians at this level typically earn in the lower end of the salary range, often from $40,000 to $52,000. They perform routine maintenance, safety checks, and basic repairs under supervision.
- Mid-Career (BMET II / 3-9 years): After gaining a few years of experience and demonstrating proficiency, technicians advance to BMET II. They work more independently and handle more complex equipment. Salaries typically move into the median range of $55,000 to $70,000.
- Senior/Experienced (BMET III / 10+ years): A senior BMET is an expert, often specializing in high-impact equipment and mentoring junior technicians. Their earnings are in the top tier, frequently ranging from $70,000 to over $90,000, especially with specialized skills.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for BMETs vary significantly by state and even by metropolitan area due to differences in cost of living and the concentration of healthcare facilities.
According to the BLS, the top-paying states for medical equipment repairers are:
1. California: Average annual salary of $82,360
2. Washington: Average annual salary of $78,540
3. Oregon: Average annual salary of $78,160
4. Nevada: Average annual salary of $76,170
5. District of Columbia: Average annual salary of $72,550
Major metropolitan areas with large hospital networks and medical research centers, such as those in the Boston, San Francisco, and Seattle areas, typically offer higher wages to attract and retain top talent.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a direct impact on your salary and job responsibilities.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Systems: This is the largest employer of BMETs. Pay is generally stable and follows the experience-based levels described above.
- Third-Party Independent Service Organizations (ISOs): These companies are contracted by hospitals to service their equipment. Pay can be very competitive, and the roles often involve travel to multiple client sites, which may include travel stipends or higher base pay.
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Working directly for a manufacturer like GE Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, or Philips is often one of the highest-paying avenues. These roles, often called Field Service Engineers, require specialization in the manufacturer’s proprietary technology and can command salaries well above the national average.
- Medical and Diagnostic Laboratories: These facilities also employ BMETs to maintain complex analytical equipment, offering competitive pay for specialized knowledge.
### Area of Specialization
General BMETs are masters of a wide range of devices, but specializing in high-cost, high-complexity systems is a clear path to a higher salary. As you advance in your career, developing expertise in one of the following areas can significantly boost your income:
- Diagnostic Imaging: Servicing MRI, CT, PET scanners, and X-ray systems.
- Anesthesiology and Respiratory: Maintaining ventilators, anesthesia machines, and other life-support equipment.
- Sterilization Equipment: Managing autoclaves and other central sterile processing technology.
- Laboratory Equipment: Repairing and calibrating complex blood analyzers and other diagnostic lab instruments.
Job Outlook

The future for Biomedical Equipment Technicians is bright. The BLS projects that employment for medical equipment repairers will grow by 5% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This growth is driven by two key trends:
1. An Aging Population: An older population requires more medical care, increasing the demand for and use of sophisticated medical devices.
2. Technological Advancement: As medical technology becomes more complex, the need for skilled technicians to install, maintain, and repair it will continue to grow.
The BLS estimates there will be about 5,600 job openings for medical equipment repairers each year, on average, over the decade, making it a career with excellent job security.
Conclusion

A career as a Biomedical Equipment Technician offers a unique blend of technical challenge and meaningful contribution to public health. The salary potential is strong and stable, with a clear and achievable path to significant income growth.
Key Takeaways:
- Solid Starting Point: Expect a median salary in the range of $57,000 to $65,000, with significant upward potential.
- Growth is in Your Control: You can actively increase your salary by gaining experience, pursuing certifications like the CBET, and choosing to work in high-demand geographic locations or for top-paying employers like OEMs.
- Specialize to Excel: Developing expertise in high-tech areas like diagnostic imaging or life-support systems will make you a more valuable and higher-paid professional.
- A Secure Future: With a positive job outlook driven by an aging population and advancing technology, the demand for skilled BMETs is set to remain strong for years to come.
For those looking for a hands-on, problem-solving career that makes a real difference, the role of a Biomedical Equipment Technician is an excellent choice with rewarding financial prospects.