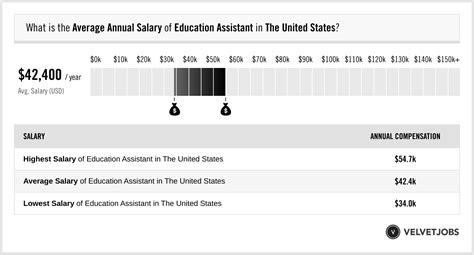
Choosing a career in education is often driven by a passion for helping others learn and grow. As an Education Assistant—also known as a Teacher's Aide, Paraeducator, or Instructional Assistant—you play a vital and direct role in student success. But passion for the job should be complemented by a clear understanding of your financial prospects.
So, what can you expect to earn in this rewarding field? While salaries are influenced by several key factors, most Education Assistants in the U.S. can expect to earn an annual salary ranging from approximately $28,000 to over $42,000. This guide will break down the salary data, explore the factors that can increase your pay, and provide a clear picture of what to expect as you build your career.
What Does an Education Assistant Do?

Before we dive into the numbers, it's important to understand the scope of the role. An Education Assistant works under the supervision of a licensed teacher to provide instructional, clerical, and administrative support. Their responsibilities are diverse and impactful, often including:
- Reinforcing lessons by working with students one-on-one or in small groups.
- Providing extra support to students with special needs, learning disabilities, or language barriers.
- Supervising students in various settings like the classroom, cafeteria, or playground.
- Preparing instructional materials and setting up classroom equipment.
- Assisting with administrative tasks such as grading assignments and recording attendance.
In essence, you are the teacher's right-hand professional, helping to create a positive and effective learning environment where every student can thrive.
Average Education Assistant Salary
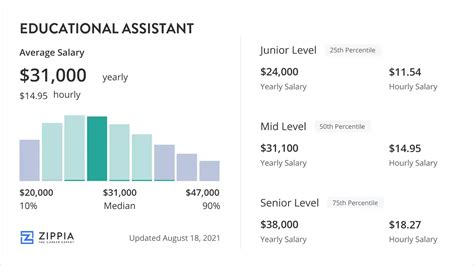
To get a precise understanding of earnings, we turn to authoritative data.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for teacher assistants was $31,040, or $14.92 per hour, in May 2023. The median wage is the point at which half the workers in the occupation earned more than that amount and half earned less.
The BLS also provides a broader spectrum of earnings:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $24,290
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $47,690
Salary aggregator websites, which collect real-time, user-reported data, often show a slightly higher average, reflecting different sample sets and recent market changes.
- Salary.com reports that the average Teacher Aide salary in the United States is around $34,301 as of late 2023, with a typical range falling between $28,967 and $41,102.
- Glassdoor lists a national average base pay of approximately $35,000 per year.
This data illustrates that while the median is around $31,000, there is clear potential to earn significantly more. The key lies in understanding the factors that drive salary upwards.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your final paycheck is not a fixed number; it's a dynamic figure shaped by your qualifications, location, and professional choices. Here’s a breakdown of the most critical factors.
### Level of Education
While a high school diploma or GED is the minimum requirement for many entry-level positions, pursuing further education is a direct path to higher earnings.
- Associate's Degree: Many school districts offer a higher starting salary for candidates with an Associate's degree, particularly in education or child development. This credential demonstrates a foundational knowledge of educational principles and classroom management.
- Bachelor's Degree: Holding a Bachelor's degree—even in an unrelated field—can make you a more competitive candidate and place you on a higher pay scale. If your degree is in education, it may open doors to specialized roles or future teaching opportunities.
- Certifications: Obtaining specific credentials, such as a Paraeducator Certification, Child Development Associate (CDA), or even First Aid and CPR, can boost your resume and your earning potential.
### Years of Experience
As with most professions, experience is highly valued. School districts typically have tiered pay scales that reward longevity and expertise.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): New assistants can expect to start at the lower end of the salary range, often between $28,000 and $32,000.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With a few years of experience, you become more adept at classroom management and instructional support. According to data from Payscale, hourly wages can climb steadily, and annual salaries often move into the mid-to-high $30,000s.
- Experienced (10+ years): Veteran assistants with a decade or more of experience are invaluable assets. They often take on mentorship roles and are compensated accordingly, pushing their earnings into the low-to-mid $40,000s or higher, especially in high-paying districts.
### Geographic Location
Where you work is one of the single biggest determinants of your salary. Pay for education assistants varies dramatically by state and even by metropolitan area, largely due to differences in cost of living, state education funding, and the strength of teacher/staff unions.
According to BLS data, the top-paying states for teacher assistants are:
1. California
2. Washington
3. District of Columbia
4. Massachusetts
5. Alaska
Working in a major metropolitan area within these states, such as San Francisco, Seattle, or Boston, can further increase your earning potential compared to rural areas. Conversely, states with a lower cost of living often have salaries that fall below the national median.
### Company Type (Work Setting)
The type of institution you work for also plays a role in compensation and benefits.
- Public Schools: These are the most common employers. Salaries are determined by district-wide pay scales and are often publicly available. Public school employees typically have access to strong benefits packages, including health insurance and state pension plans.
- Private Schools: Pay at private schools can vary widely. Elite, well-funded independent schools may offer salaries competitive with or higher than public schools. Other smaller, tuition-dependent private schools might offer lower base pay.
- Charter Schools: As publicly funded but independently operated schools, charter school salaries can be more variable. Some may offer competitive pay to attract talent, while others may have more limited budgets.
- Childcare Centers & Early Childhood Programs: These settings may offer slightly lower pay than K-12 schools but provide valuable experience, especially for those specializing in early childhood education.
### Area of Specialization
Specializing in a high-need area is one of the most effective ways to increase your value and your salary.
- Special Education: This is the most significant area of specialization. Assistants who work with students with moderate to severe physical, emotional, or learning disabilities require specialized training and immense patience. As such, they are often compensated with a "stipend" or placed on a higher pay scale.
- Bilingual/ESL Support: In districts with large populations of English Language Learners (ELLs), bilingual assistants are in high demand and can command a higher wage. Fluency in a language like Spanish, Mandarin, or Vietnamese can be a major professional advantage.
- Subject-Specific Roles: In some middle or high schools, assistants may be hired to support specific subjects like science (assisting in labs) or technology, which may come with slightly higher pay.
Job Outlook

The demand for dedicated Education Assistants remains steady. The BLS projects a job growth of 1% for teacher assistants from 2022 to 2032.
While this growth rate is slower than the average for all occupations, it is essential to look beyond the percentage. Due to the large size of this occupation, the 1% growth still translates into approximately 37,700 job openings each year, on average. These openings arise from the need to replace workers who retire or transition to different occupations, ensuring a consistent need for new talent. Job prospects are often best for those with an associate's degree or experience working with special education students.
Conclusion

A career as an Education Assistant is a unique opportunity to make a tangible difference in the lives of students every single day. While the median salary may seem modest at first glance, it is by no means a fixed ceiling.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring Education Assistants:
- National Average: Expect a median salary around $31,000 - $35,000, with a broad potential range from the high $20s to the high $40s.
- Invest in Yourself: Furthering your education with an associate's degree or specialized certifications is a direct investment in your earning potential.
- Location Matters: Research salaries in your state and local districts, as geography is a primary driver of pay.
- Specialize for Success: Pursuing roles in special education or bilingual support can significantly increase your salary and job security.
By strategically building your experience, education, and skills, you can not only find immense personal fulfillment in your work but also build a financially stable and rewarding career.