Embarking on the path to becoming a physician is a long and challenging journey, culminating in a critical training period known as residency. While the ultimate earning potential for a fully licensed physician is substantial, the salary during these formative years is a common point of curiosity and concern. For those considering this demanding yet rewarding career, understanding the compensation structure is essential.
A medical resident's salary, more accurately called a stipend, typically ranges from $60,000 to $80,000 per year, depending on a variety of key factors. This article will break down what a medical resident does, analyze the average salary, and explore the elements that influence their annual earnings.
What Does a Medical Resident Do?

A medical resident is a physician who has graduated from medical school with an M.D. or D.O. degree and is now undergoing supervised, hands-on training in a specific medical specialty. This is not an academic role; it is a full-time job at a hospital or clinic where the resident is directly responsible for patient care.
Residency is the bridge between being a medical student and a fully independent, licensed physician. Key responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing illnesses and managing patient treatment plans.
- Performing medical procedures under the supervision of senior physicians.
- Working long hours, including overnight and weekend shifts (on-call).
- Continuously studying to pass medical board exams and stay current on medical advancements.
- Rotating through various departments to gain comprehensive experience.
Because this is a required training position, compensation is structured as a stipend to cover living expenses while the resident gains invaluable practical experience.
Average Medical Resident Salary
The compensation for medical residents has seen a steady increase to keep pace with inflation and the rising cost of living. While it is a modest figure compared to the salary of a fully licensed physician, it is a livable wage that grows incrementally each year.
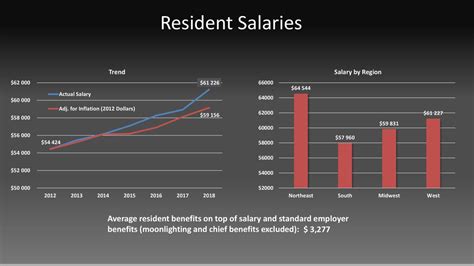
According to the Medscape Resident Salary & Debt Report 2023, the average salary for medical residents in the U.S. is $67,400. This figure represents a notable increase from previous years, reflecting a growing awareness of the financial pressures on physicians-in-training.
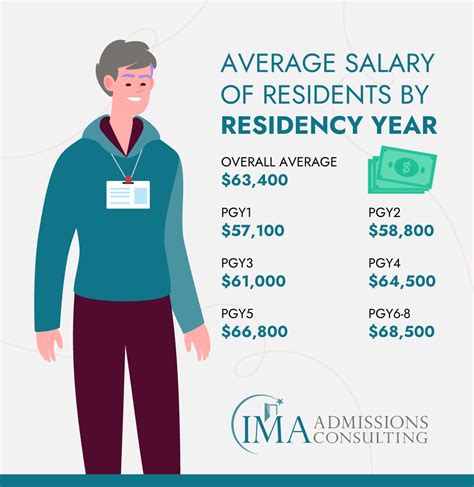
Resident salaries are primarily structured by the post-graduate year (PGY) of training. As residents gain experience and take on more responsibility, their stipend increases. Based on data from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) 2023 Report on Resident/Fellow Stipends and Benefits, the national average stipends by PGY level are:
- PGY-1 (First Year): $64,217
- PGY-2 (Second Year): $66,634
- PGY-3 (Third Year): $69,178
- PGY-4 (Fourth Year): $71,885
- PGY-5 (Fifth Year): $74,621
- PGY-6 and above (Fellows): $77,000 - $82,000+
*Source: AAMC 2023 Report on Resident/Fellow Stipends and Benefits*
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the post-graduate year is the primary driver of a resident's stipend, several other factors create significant variation in pay.
###
Post-Graduate Year (PGY) and Experience
As shown in the AAMC data above, experience is the most direct factor influencing a resident's salary. A PGY-1 resident, or intern, is in their first year of training and earns the base-level stipend. With each subsequent year, the resident’s clinical skills, diagnostic abilities, and level of autonomy grow, warranting a corresponding increase in their stipend. A PGY-4 resident in a surgical specialty, for example, has far more responsibility than an intern and is compensated accordingly.
###
Geographic Location
Where a resident trains has a major impact on their salary, primarily due to variations in the cost of living. Residency programs in major metropolitan areas or states with a high cost of living, like California and New York, tend to offer higher stipends to help their trainees manage expenses.
For instance, Medscape's 2023 report notes that residents in the Northeast region of the U.S. report slightly higher average salaries. Conversely, programs in states with a lower cost of living may offer stipends that are closer to the national average, but the resident’s purchasing power might be greater.
###
Type of Institution
The type of hospital or institution hosting the residency program can also play a role. There are three main types:
- University-Affiliated Hospitals: These are often large, academic medical centers that may have more resources and standardized pay scales set by the university.
- Community Hospitals: These programs can sometimes offer more competitive stipends to attract top candidates, especially if they are not in a major metropolitan hub.
- Government/VA Hospitals: Federal institutions often have their own clear, structured pay scales that are competitive and transparent.
According to Salary.com, which aggregates real-time data, the institution's size and budget can directly influence the salary range it offers its residents.
###
Area of Specialization
During residency, the stipend difference between specialties is generally minimal, as most institutions standardize pay by PGY level regardless of the program. However, some minor variations can exist, particularly in highly demanding fields or programs looking to be more competitive.
The real impact of specialization is seen immediately *after* residency. The salary for a newly minted family physician will be vastly different from that of a neurosurgeon or cardiologist. Furthermore, residents who pursue a fellowship (additional sub-specialty training after residency) often receive a higher stipend than senior residents. For example, a PGY-6 cardiology fellow will earn significantly more than a PGY-3 internal medicine resident.
Job Outlook

The long-term career outlook for physicians and surgeons is exceptionally strong. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for physicians and surgeons will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032.
This steady growth is driven by several factors, including:
- An aging U.S. population that requires more medical care.
- Ongoing advancements in medical technology and treatments.
- A projected wave of physician retirements, creating openings for new doctors.
While the residency years are demanding and the pay is modest, they are a required investment in a stable, secure, and financially lucrative career. The demand for well-trained physicians remains consistently high across nearly all specialties.
Conclusion

For aspiring physicians, the residency years represent a period of intense growth, learning, and hard work. While the salary of a medical resident is a stipend designed to cover living costs rather than build significant wealth, it is a crucial and structured part of the medical journey.
Key Takeaways:
- A Livable, Growing Stipend: Residents can expect to earn a starting salary in the low-to-mid $60,000s, which increases with each year of training.
- Location and Institution Matter: Your annual pay can be influenced by the cost of living in your city and the type of hospital where you train.
- A Sound Investment: The modest pay during residency is a short-term trade-off for a career with an outstanding job outlook and significant long-term earning potential.
Residency is a temporary phase of financial sacrifice that lays the foundation for a deeply rewarding career dedicated to helping others, backed by excellent professional and financial security.