Pursuing a career in special education is a calling, driven by a passion for helping students with diverse learning needs achieve their full potential. While the intrinsic rewards are immense, it's also a professional career with significant responsibilities that command a respectable salary. If you're considering this vital path, understanding your potential earnings is a crucial step.
So, what can you expect to earn? While the national median salary for a special education teacher hovers around $63,890 per year, your actual income can range from approximately $48,000 for entry-level positions to well over $100,000 for experienced educators in high-paying districts. This guide will break down the numbers, the factors that influence them, and the bright future of this essential profession.
What Does a Special Education Teacher Do?

Before diving into the financials, it's important to appreciate the scope of the role. A special education teacher is a highly skilled educator who works with students who have a wide range of learning, mental, emotional, and physical disabilities. Their core responsibilities go far beyond standard teaching and include:
- Assessing students' skills to determine their needs and strengths.
- Developing and implementing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), which are legally mandated documents outlining each student's specific goals and the support needed to meet them.
- Adapting general education lessons and teaching various subjects, such as reading, writing, and math, to students with mild and moderate disabilities.
- Collaborating closely with parents, general education teachers, school counselors, and administrators to create a supportive learning environment.
- Teaching life skills and social skills to help students become more independent.
It is a demanding, multifaceted role that requires patience, creativity, and a deep commitment to student advocacy.
Average Special Education Teacher Salary
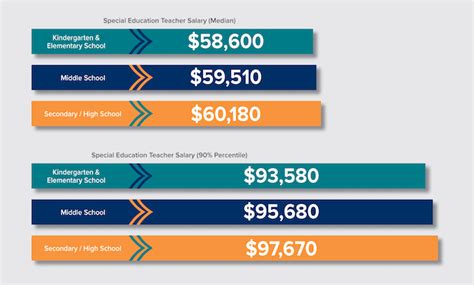
The salary for a special education teacher is competitive within the education sector and reflects the specialized skills required. Let's look at the data from several authoritative sources.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for special education teachers was $63,890 as of May 2023. This is the midpoint, meaning half of all special education teachers earned more than this, and half earned less. The BLS also provides a broader look at the pay scale:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $48,320
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $103,110
Salary aggregator websites provide similar figures, often updated more frequently with user-submitted data:
- Salary.com reports a median salary of $66,975 as of May 2024, with a typical range falling between $52,821 and $83,040.
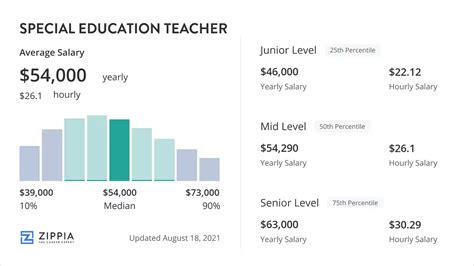
- Payscale shows an average salary of approximately $54,800, but highlights the significant impact of experience on pay over time.
This data clearly shows that while there is a solid starting baseline, there is substantial room for financial growth throughout your career.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary is not a single number but a calculation based on several key variables. Understanding these factors is essential for maximizing your earning potential.
### Level of Education
In the field of education, your level of academic achievement directly correlates with your pay. Nearly all school districts use a "step and lane" salary schedule. "Steps" refer to years of experience, while "lanes" refer to educational attainment.
- Bachelor's Degree: This is the minimum requirement for a teaching license in most states. Teachers in this "lane" will be on the lower end of the pay scale.
- Master's Degree: Earning a master's degree (e.g., an M.Ed. in Special Education) will move you to a higher-paying "lane" on the salary schedule. This can result in an immediate salary increase of several thousand dollars per year and will continue to compound over your career.
- Doctorate (Ph.D. or Ed.D.): While less common for K-12 teachers, a doctorate places you in the highest possible pay lane, often leading to the most lucrative teaching salaries within a district.
### Years of Experience
Experience is the second half of the salary schedule equation. As you gain more years of service in a school district (the "steps"), your salary automatically increases annually.
- Entry-Level (0-5 years): According to Payscale, an entry-level special education teacher can expect to earn an average of around $49,000.
- Mid-Career (5-10 years): With solid experience, your salary will grow, potentially reaching an average of $60,000 or more.
- Experienced (10-20+ years): Veteran teachers with advanced degrees can earn significantly more, often placing them in the $75,000 to $95,000+ range, especially in well-funded districts.
### Geographic Location
Where you teach has one of the most significant impacts on your salary, largely due to differences in state education funding and cost of living. The BLS identifies the following states as the top-paying for special education teachers:
1. Oregon: Annual mean wage of $91,920
2. New York: Annual mean wage of $91,090
3. California: Annual mean wage of $90,150
4. Washington: Annual mean wage of $86,300
5. Maryland: Annual mean wage of $83,380
Conversely, states with lower costs of living and different funding structures, such as Mississippi, Oklahoma, and Arkansas, tend to offer lower average salaries.
### School Type
The type of institution you work for also plays a role. The BLS data from May 2023 shows the median salaries for special education teachers across different school types:
- Public Elementary and Secondary Schools: $65,550
- Private Elementary and Secondary Schools: $60,780
- Other Educational Services (e.g., specialty centers): $51,020
Generally, public school districts offer higher salaries and more robust benefits packages due to union representation and public funding structures.
### Area of Specialization
Within the broad field of special education, certain high-need specializations can make you a more sought-after candidate and potentially lead to stipends or other financial incentives. While your base salary is tied to the district schedule, expertise in these areas can boost your overall compensation and job security. High-need areas include:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders (EBD)
- Severe and Profound Disabilities
- Deaf and Hard of Hearing
- Visual Impairments
Furthermore, federal programs like the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program can provide significant financial relief (up to $17,500) for highly qualified special education teachers who work in low-income schools for five consecutive years.
Job Outlook

The demand for qualified special education teachers remains consistently high. While the BLS projects a slight decline of 1% in the total number of positions from 2022 to 2032, this figure doesn't tell the whole story.
The Bureau notes that thousands of job openings are expected each year. These openings arise from the need to replace teachers who are retiring or leaving the profession for other reasons. The national shortage of qualified educators, especially in special education, means that skilled and certified teachers have excellent job security and are highly sought after by school districts across the country.
Conclusion

A career as a special education teacher offers a clear path to a stable, professional income with significant opportunities for growth. While the national median salary provides a solid benchmark, your earning potential is ultimately in your hands.
To maximize your salary, focus on these key takeaways:
- Invest in Education: Pursuing a master's degree is the most direct way to increase your lifetime earning potential.
- Location Matters: Research salaries in different states and districts, balancing pay with cost of living.
- Gain Experience: Your value and salary will grow steadily with each year you dedicate to the profession.
- Consider High-Need Specializations: Developing expertise in a critical area can open doors to unique opportunities and financial incentives.
More than just a salary, a career in special education provides the profound satisfaction of making a tangible, positive impact on students' lives every single day. For the right individual, it is a profession that is as financially viable as it is personally fulfilling.