A career as a special education teacher is one of the most rewarding paths you can choose, offering the profound satisfaction of helping students with diverse learning needs achieve their full potential. But beyond the intrinsic rewards, it's also a stable profession with a solid earning potential. If you're considering this vital role, understanding the financial landscape is a crucial step in your career planning.
So, what can you expect to earn? While the national median salary for special education teachers is approximately $67,730 per year, this figure is just the starting point. Your actual income can vary significantly based on your education, location, experience, and specialization. This guide will break down the salary you can anticipate and the key factors that will shape your earning power throughout your career.
What Does a Special Education Teacher Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's important to understand the scope of the role. A special education teacher is a certified educator who works with children and youth who have a variety of disabilities. Their responsibilities are both challenging and deeply impactful, and typically include:
- Assessing Students: Evaluating students' skills to determine their needs and developing teaching plans.
- Developing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs): Creating tailored, legally mandated plans that outline specific goals and services for each student.
- Adapting Lessons: Modifying the general education curriculum to meet the unique needs of their students.
- Teaching and Mentoring: Providing direct instruction and support in various subjects, as well as on social and life skills.
- Collaborating: Working closely with parents, general education teachers, school counselors, and administrators to create a supportive learning environment for the student.
The dedication and specialized skill set required for this work are directly reflected in the profession's compensation structure.
Average Special Education Teacher Salary
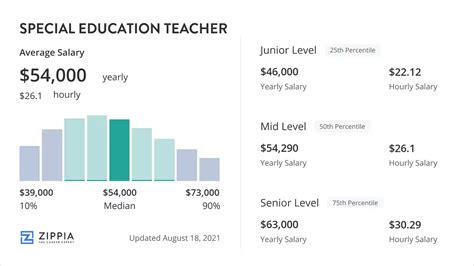
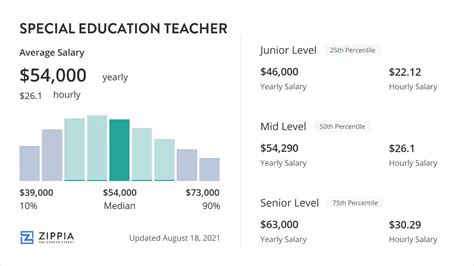
Salary data shows a promising financial outlook for special education teachers. While figures vary slightly between sources due to different data collection methods, they paint a consistent picture.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for Special Education Teachers, All Other, was $67,730 in May 2023. The BLS also provides median salaries for specific levels:
- Secondary School: $67,640
- Kindergarten and Elementary School: $65,530
- Middle School: $65,480
- Preschool: $67,070
Salary aggregators, which use real-time, user-reported data, provide a broader look at the salary range. For instance:
- Salary.com reports that the typical salary range for a special education teacher in the U.S. falls between $54,302 and $76,101 as of May 2024.
- Payscale shows a similar average base salary and notes that the lowest 10% of earners make around $45,000, while the top 10% can earn over $84,000.
This range highlights that while the median provides a solid benchmark, several factors will determine whether you earn at the lower or higher end of the scale.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary is not a static number. It's a dynamic figure influenced by a combination of professional and environmental factors. Understanding these elements can empower you to maximize your earning potential.
### Level of Education
In the field of education, your level of academic achievement has a direct and significant impact on your pay. Most school districts use a "step and lane" salary schedule. "Steps" correspond to years of experience, while "lanes" correspond to educational attainment.
- Bachelor's Degree: A bachelor's degree in special education is the minimum requirement for licensure in most states and will place you in the starting salary lane.
- Master's Degree: Obtaining a Master's degree (M.Ed. or M.A. in Special Education) is one of the most effective ways to increase your salary. Moving into the "Master's" or "Master's+30" lane on a district's salary schedule can result in an annual salary increase of several thousand dollars. Many districts also offer tuition reimbursement programs to encourage teachers to pursue advanced degrees.
### Years of Experience
Experience is highly valued and directly rewarded. As you gain more years in the classroom, you advance up the "steps" of the salary schedule. This provides a clear, predictable path for income growth.
- Entry-Level (0-5 years): An early-career special education teacher can expect to earn a salary at the lower end of the national range. According to Payscale, an entry-level teacher earns an average of around $51,000.
- Mid-Career (5-10 years): With significant experience, teachers see a notable increase in earnings as they climb the salary ladder.
- Experienced (10+ years): Veteran teachers with a decade or more of experience, especially those with an advanced degree, command salaries at the highest end of the spectrum, often exceeding $80,000 in high-paying districts.
### Geographic Location
Where you work is arguably the most significant factor influencing your salary. Teacher pay varies dramatically from state to state and even between districts within the same state, largely due to differences in state funding and local cost of living.
According to 2023 BLS data, the top-paying states for special education teachers (across all levels) are:
1. New York: Average annual salary of $99,750
2. California: Average annual salary of $95,780
3. Oregon: Average annual salary of $90,790
4. Washington: Average annual salary of $86,400
5. Massachusetts: Average annual salary of $85,690
It's crucial to balance a high salary against the cost of living in these areas. A higher salary in an expensive metropolitan area like New York City or San Francisco may not have the same purchasing power as a more moderate salary in a lower-cost region.
### School Type and Work Setting
The vast majority of special education teachers (around 90%) work in public elementary and secondary schools, according to the BLS. However, salaries can differ based on the work environment.
- Public Schools: Generally offer the most competitive salaries and benefits, governed by state and union-negotiated salary schedules.
- Private Schools: Salaries at private schools are often lower than in public schools. However, they may offer other benefits like smaller class sizes or greater autonomy.
- Charter Schools: Compensation at charter schools can vary widely. Some may offer competitive salaries to attract top talent, while others may offer less than traditional public schools.
- Other Settings: Special education teachers also work in residential facilities, hospitals, and government agencies, where pay scales are determined by the specific institution.
### Area of Specialization
While most salary data is aggregated, specializing in a high-need area can provide a competitive edge and potential for additional compensation. Districts facing critical shortages may offer stipends or signing bonuses for teachers with certifications in areas such as:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders (EBD)
- Severe and Multiple Disabilities
- Visual or Hearing Impairments
Holding dual certifications (e.g., in special education and a core subject like math or science) can also make you a more valuable and sought-after candidate.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for special education teachers is very strong. The BLS projects that employment in this field will show little or no change from 2022 to 2032. However, this statistic doesn't tell the whole story.
The BLS also projects about 19,700 openings for special education teachers each year, on average, over the decade. These openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who transfer to different occupations or exit the labor force, such as to retire.
In practical terms, there is a persistent nationwide shortage of qualified special education teachers. This high demand translates into excellent job security and opportunities for qualified professionals, especially in underserved rural and urban areas.
Conclusion

Choosing a career as a special education teacher is a commitment to making a tangible difference in the lives of students. The financial compensation for this vital work is solid and comes with a clear and reliable path for growth.
Your salary journey will be shaped by your proactive decisions—pursuing an advanced degree, gaining experience, and considering high-paying geographic locations. With strong demand and excellent job security, special education offers a career path that is not only emotionally fulfilling but also financially stable and rewarding. For those with a passion for advocacy and education, it remains one of the most impactful professions available today.