Teaching in Utah offers a unique opportunity to shape the future in one of the nation's fastest-growing states. For those considering this vital profession, understanding the financial landscape is a critical step. While passion drives educators, compensation is a key factor in career sustainability. So, what can you expect to earn as a teacher in the Beehive State?
The financial picture for Utah teachers is one of significant recent progress and promising potential. With salaries influenced by a variety of factors, compensation can range from approximately $48,000 for new teachers to over $90,000 for experienced, highly-educated professionals in high-paying districts. This guide will break down the salary you can expect and the key factors that will shape your earning potential throughout your career.
What Does a Utah Teacher Do?

A teacher's role extends far beyond delivering lectures at the front of a classroom. They are mentors, curriculum designers, and facilitators of learning. Core responsibilities include:
- Instruction: Developing and executing engaging lesson plans that align with Utah's state curriculum standards.
- Classroom Management: Creating a safe, inclusive, and productive learning environment for a diverse group of students.
- Assessment: Evaluating student progress through assignments, projects, and standardized tests, and providing constructive feedback.
- Collaboration: Working closely with other educators, administrators, and support staff to improve student outcomes.
- Communication: Maintaining open and regular communication with parents and guardians regarding their child's academic and social development.
It's a dynamic and demanding profession that requires a deep commitment to student success.
Average Utah Teacher Salary
When analyzing teacher salaries, it's helpful to look at data from several authoritative sources to get a complete picture.
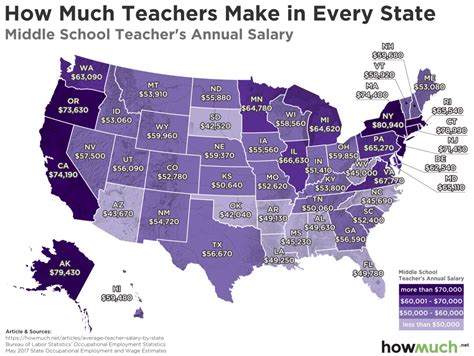
According to Salary.com, the average salary for a public school teacher in Utah is $61,048 as of May 2024. However, the typical range is quite broad, generally falling between $50,967 and $72,995.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides more granular data from May 2023, breaking it down by educational level:
- Elementary School Teachers (Utah): The mean annual wage is $65,160.
- Middle School Teachers (Utah): The mean annual wage is $67,110.
- Secondary (High School) Teachers (Utah): The mean annual wage is $68,810.
These figures highlight that entry-level positions (the bottom 10-25%) typically start in the $48,000-$55,000 range, while the top 10% of earners, often those with advanced degrees and decades of experience, can surpass $90,000 annually.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your base salary is not a single, static number. It is determined by a structured system used by nearly every school district in the state. Here are the most significant factors that will impact your earnings.
### Level of Education
School districts in Utah use a "salary schedule" that typically includes different columns, or "lanes," based on your educational attainment. Moving into a new lane results in a significant pay increase.
- Bachelor's Degree: This is the minimum requirement and places you in the starting lane.
- Master's Degree: Earning a master's degree is one of the most effective ways to increase your salary. This can result in an annual pay bump of $3,000 to $7,000 or more, depending on the district.
- Doctorate or Additional Credits: Further lanes often exist for educators who have earned a doctorate or a specific number of credits beyond a master's degree, offering the highest earning potential on the schedule.
### Years of Experience
The salary schedule also includes rows, or "steps," that correspond to your years of credited teaching experience. With each year you teach, you advance one step, which comes with a built-in, automatic raise. For example, a teacher in their first year will earn considerably less than a 15-year veteran with the same degree, simply due to their position on the salary schedule. This structure rewards loyalty and provides a predictable path for income growth.
### Geographic Location
Where you teach in Utah matters significantly. Districts in metropolitan areas with a higher cost of living and stronger tax bases often offer more competitive salaries than those in rural communities.
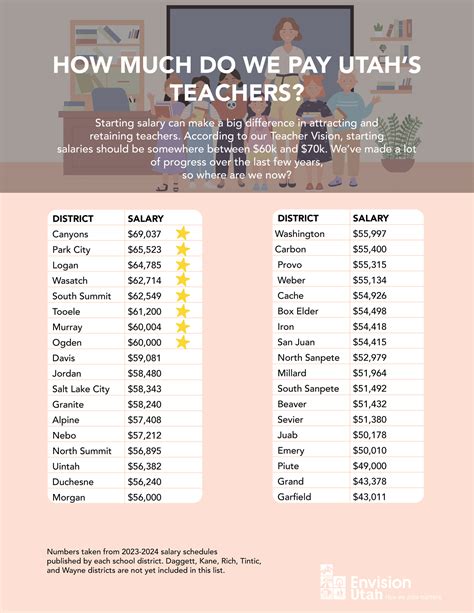
- High-Paying Districts: Districts along the Wasatch Front, such as Park City School District, Canyons School District, and Salt Lake City School District, are consistently among the highest-paying in the state. For instance, Park City is known for offering some of the most competitive teacher salaries in the nation.
- Average and Rural Districts: While salaries have been rising statewide thanks to legislative action, districts in more rural or less affluent areas may have lower starting salaries and a lower salary ceiling. However, the lower cost of living in these areas can sometimes offset the difference in pay.
### School Type
The type of school where you work also plays a role in your compensation structure.
- Public Schools: The vast majority of teachers work in traditional public schools, where salaries are transparent and dictated by the district's public salary schedule.
- Charter Schools: As public schools, charters are funded by the state but often have more autonomy. Their salary structures can be more flexible and may or may not follow a traditional step-and-lane schedule. Some may offer performance-based bonuses.
- Private Schools: Private school salaries are highly variable and are not bound by state schedules. Elite preparatory schools may offer very competitive pay, while smaller, parochial schools may offer less than their public school counterparts.
### Area of Specialization
Your teaching subject or specialty can unlock additional earning opportunities, often through stipends. Districts frequently offer extra pay to attract and retain teachers in high-need areas. These can include:
- STEM Subjects: Teachers certified in science, technology, engineering, and math are in high demand.
- Special Education (SPED): SPED-certified teachers almost always receive a stipend due to the specialized skills and demands of the role.
- Extracurriculars: Taking on additional duties, such as coaching a sports team, leading the debate club, or directing the school play, comes with supplemental pay that can add several thousand dollars to your annual income.
Job Outlook

The career outlook for teachers in Utah is very strong. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for high school, middle school, and elementary school teachers is projected to grow nationally, but the demand in Utah is particularly robust.
Utah's consistently high birth rate and rapid population growth create a constant need for qualified educators to staff new and existing schools. This sustained demand provides excellent job security and has spurred the state legislature to continue investing in teacher pay to remain competitive.
Conclusion

A career in teaching in Utah is a stable, rewarding path with a clear and predictable trajectory for salary growth. While it may not be the highest-paid profession, recent statewide initiatives have made compensation more competitive than ever.
For prospective teachers, the key takeaways are:
- Your Salary Will Grow: Through the step-and-lane system, your pay will automatically increase with experience and further education.
- Education is a Direct Investment: Earning a master's degree is a surefire way to boost your lifetime earnings.
- Location and Specialization Matter: Strategically choosing where you teach and what you specialize in can significantly impact your income.
With a strong job outlook and a clear system for advancement, Utah presents an encouraging and viable landscape for dedicated individuals ready to make a difference in the classroom.