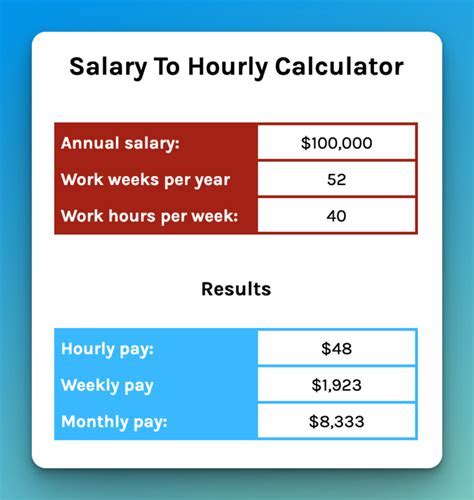
Understanding your earning potential is a cornerstone of career planning. For many, the 40-hour work week is the standard, but how does that translate into an annual salary? While the calculation is simple, the factors determining your actual pay are complex. In the United States, the median annual salary for full-time wage and salary workers was approximately $59,540 in the first quarter of 2024. However, your personal salary can vary dramatically based on your field, location, experience, and education.
This guide will demystify the relationship between hourly work and annual salary. We'll provide the tools to calculate your potential earnings and explore the key variables that will define your financial trajectory in today's job market.
What Does "40 Hours to Salary" Mean?
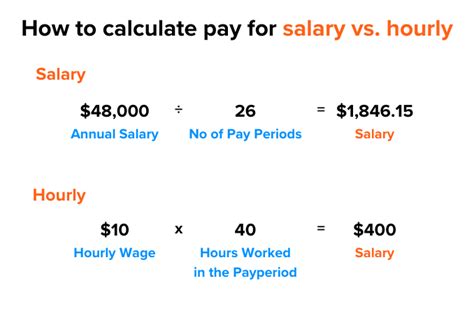
This phrase isn't a job title but a fundamental concept in compensation. It refers to the process of converting an hourly wage into an equivalent annual salary, based on a standard 40-hour work week. Understanding this is crucial for comparing job offers, negotiating pay, and planning your finances.
In the professional world, jobs are typically classified in two ways:
- Hourly (Non-Exempt): You are paid for every hour you work. Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), these positions are eligible for overtime pay (typically 1.5 times the regular rate) for any hours worked beyond 40 in a week.
- Salaried (Exempt): You are paid a fixed annual amount, regardless of the exact hours worked. These positions are "exempt" from overtime pay. A salaried role often implies a professional or managerial level of responsibility.
When a job description lists an hourly rate, or when you're trying to benchmark your worth, converting it to an annual salary based on a 40-hour week provides a clear, apples-to-apples comparison.
Average Salary: The Basic Calculation
Calculating your annual salary from an hourly rate is straightforward. The standard formula assumes you work 40 hours per week for 52 weeks a year.
The Formula: `Hourly Rate × 40 hours/week × 52 weeks/year = Annual Salary`
A simpler shortcut is to multiply the hourly rate by 2,080 (which is 40 x 52).
Example:
Let's use the median hourly wage for all occupations in the U.S., which was $23.11 as of May 2023, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
`$23.11 × 2,080 = $48,068.80 per year`
While this national median provides a baseline, your personal salary will be influenced by a range of critical factors. A typical salary range in the U.S. might span from around $35,000 for many entry-level, lower-skilled roles to well over $150,000 for experienced, highly specialized professionals.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your salary is not just a number; it's a reflection of the value you bring to an employer. Here are the most significant factors that determine your earning potential.
### Level of Education
Your educational background is a primary driver of income. Higher levels of education often signal advanced knowledge and specialized skills, which employers are willing to pay a premium for.
According to the BLS, median usual weekly earnings in 2023 showed a clear correlation with education:
- High School Diploma: $853 ($44,356 annually)
- Bachelor's Degree: $1,432 ($74,464 annually)
- Master's Degree: $1,661 ($86,372 annually)
- Doctoral Degree: $2,083 ($108,316 annually)
A bachelor's degree can nearly double your earning potential compared to a high school diploma, demonstrating the significant return on investment in higher education.
### Years of Experience
Experience is a direct measure of your proven ability to perform a role successfully. As you accumulate experience, you develop greater expertise, efficiency, and leadership skills, making you more valuable. Salary aggregators illustrate this trend clearly.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Professionals at the start of their careers are learning the ropes and typically earn at the lower end of the salary scale for their profession.
- Mid-Career (5-9 years): With a solid track record, these professionals can command significantly higher salaries and are often trusted with more complex projects.
- Senior/Late-Career (10+ years): Decades of experience often lead to leadership, strategic, or high-level specialist roles that occupy the top tier of the pay scale. For example, Payscale data shows that a Senior Software Engineer with 10+ years of experience can earn over 40% more than an entry-level one.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters—a lot. Salaries are heavily adjusted based on the local cost of living and the demand for talent in a specific region. A job in a major metropolitan hub like New York City or San Francisco will almost always pay more than the exact same job in a rural area.
For example, the BLS reports that the San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA metropolitan area has the highest annual mean wage across all occupations ($102,330 as of May 2023), while many nonmetropolitan areas in the Southeast have mean wages closer to $45,000. When considering a job, always factor in the local cost of housing, taxes, and transportation.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for can have a major impact on your compensation package.
- Large Corporations (500+ employees): These companies often have structured compensation bands and can typically offer higher salaries and more comprehensive benefits packages (health insurance, 401(k) matching, bonuses).
- Startups: While cash salaries might be lower than at large corporations, startups often compensate with stock options, which can have a high potential upside if the company succeeds. The work environment is often faster-paced and offers more opportunities for rapid growth.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Driven by mission rather than profit, non-profits generally offer lower salaries. However, they can provide immense job satisfaction and other non-monetary benefits.
- Government: Government jobs (federal, state, and local) are known for their stability, strong benefits, and pensions, though their salaries may not always match the top-tier private sector roles.
### Area of Specialization
Perhaps the most powerful factor is your chosen industry and specialization. Demand for specific skill sets creates vast differences in earning potential. According to the BLS Occupational Outlook Handbook, median pay varies dramatically by field (May 2023 data):
- Technology: Computer and Information Systems Managers ($169,510)
- Healthcare: Physicians and Surgeons (>$239,200)
- Finance: Personal Financial Advisors ($99,580)
- Education: High School Teachers ($65,220)
- Hospitality: Food Service Managers ($63,970)
Specializing in a high-demand, high-skill area like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, or specialized medicine is the most direct path to a top-tier salary.
Job Outlook

The overall health of the job market plays a role in salary trends. When the economy is growing, employers compete for talent, driving wages up. The BLS projects that total employment in the U.S. is expected to grow by 4.7 million jobs from 2022 to 2032.
The fastest-growing sectors are projected to be healthcare support and computer and mathematical occupations, indicating that specializing in these fields will likely lead to strong job security and salary growth in the coming decade. Furthermore, the rise of remote and hybrid work is changing how location impacts salary, a trend that will continue to evolve.
Conclusion

Converting a 40-hour work week to an annual salary is a simple calculation, but the number you arrive at is the result of a complex interplay of personal and market forces. To maximize your earning potential, you must think strategically about your career path.
Here are the key takeaways:
1. Know the Math: Use the `Hourly Rate × 2,080` formula to quickly compare compensation.
2. Invest in Yourself: Education and continuous skill development have a clear and direct impact on your income.
3. Gain Experience: Your value grows as you build a track record of success and expertise.
4. Be Strategic About Location & Industry: Choosing a high-growth field in a thriving economic region can dramatically accelerate your earnings.
By understanding these factors, you can move from simply calculating a salary to actively shaping it. Use this knowledge to negotiate effectively, plan your career, and build a financially secure and rewarding professional life.