As a career analyst and expert content writer, here is a comprehensive, in-depth article answering the query "tudor dixon salary".
Decoding the Paycheck: A Deep Dive into a Governor's Salary and Career

### Introduction
Recent online searches for "Tudor Dixon salary" reflect a growing public curiosity about the earnings of prominent political figures. While the specific personal income of a private citizen and former candidate like Tudor Dixon is not public information, her 2022 campaign for Governor of Michigan shines a light on a related and fascinating question: What does it mean to hold one of the highest public offices in the country, and what is the salary for such a demanding role?
Serving as a state governor is a pinnacle of public service, involving immense responsibility and round-the-clock dedication. The compensation for this role varies dramatically across the United States, with salaries ranging from $70,000 to over $250,000 per year. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of a governor's salary, the factors that shape it, and the unique career path it represents.
What Does a State Governor Do?

A state governor is the chief executive officer of their state, holding a position analogous to the U.S. President at the federal level. The role is multifaceted and carries significant authority. Key responsibilities include:
- Executing State Laws: The governor is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws passed by the state legislature.
- Managing the Executive Branch: They oversee a vast network of state agencies, departments, and employees, appointing cabinet members and other officials.
- Preparing the State Budget: The governor proposes an annual or biennial budget to the legislature, setting financial priorities for the state.
- Serving as Commander-in-Chief: They lead the state's National Guard and can deploy it during emergencies, such as natural disasters or civil unrest.
- Legislative Influence: Governors can propose legislation, veto bills passed by the legislature, and call special legislative sessions.
- Acting as a State Figurehead: They represent the state at national and international events, promote its economic interests, and serve as a leader for its citizens.
Average State Governor Salary
Unlike most professions, a governor's salary is not determined by market forces but is set by state law. Therefore, there is no "entry-level" or "senior" salary in the traditional sense; there is one salary for the office holder.
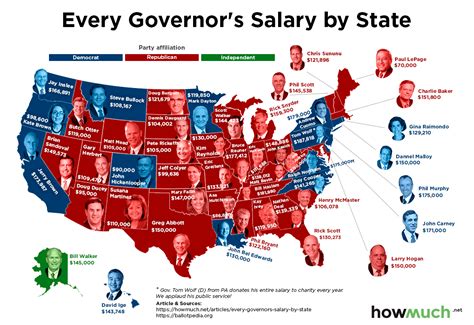
According to 2023 data compiled by Ballotpedia, the average salary for a governor in the United States is approximately $148,900. However, this average masks a very wide range.
- Salary Range: The annual salaries for governors span from $70,000 in Maine to $250,000 in New York.
- Median Salary: The median salary, a midpoint that reduces the effect of outliers, is closer to $150,000.
It's important to note that some governors may choose to voluntarily reduce their salary or donate it to charity as a symbolic gesture.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

The salary of a governor is unique in that it is not influenced by personal experience or education in the same way as a private-sector job. Instead, it is determined by a combination of legal, economic, and political factors specific to each state.
###
State Law and Geographic Location
The single most significant factor determining a governor's salary is the state they govern. Each state's constitution or statutes explicitly sets the compensation for its top executive. This creates the vast disparity seen across the country. For example, the Governor of New York earns more than three times the salary of the Governor of Maine. This is a direct reflection of laws passed by state legislatures, often reflecting the state's size, economy, and historical precedents.
Examples of Governor Salaries by State (2023 Data from Ballotpedia):
- Top 5: New York ($250,000), California ($229,146), Pennsylvania ($213,675), Tennessee ($209,628), Illinois ($205,700).
- Bottom 5: Maine ($70,000), Arizona ($95,000), Nebraska ($105,000), Kansas ($110,885), Oregon ($111,500).
###
State Economy and Population
There is a strong correlation between the size of a state's economy and its population and the salary it pays its governor. States with larger populations and higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP), such as California, New York, and Illinois, tend to have higher-paid governors. This reflects the greater complexity of managing a larger government bureaucracy, a bigger budget, and a more diverse population. A higher salary can also be seen as necessary to attract qualified candidates capable of managing a large and complex entity.
###
Role of Independent Compensation Commissions
To remove the political sensitivity of legislators voting on their own—and other officials'—pay raises, many states have established independent citizen commissions. These commissions are tasked with studying and setting the salaries for elected officials, including the governor. Their recommendations are often based on analyses of a state's economic health, the salaries of governors in comparable states, and compensation for top executives in the private and non-profit sectors. This process aims to make salary-setting a more data-driven and impartial exercise.
###
Comprehensive Compensation: Beyond the Salary
A governor's official salary is only one part of their total compensation package. The perks and benefits associated with the office are substantial and should be considered part of their overall remuneration. These often include:
- Official Residence: Most governors are provided with an official mansion, complete with household staff, maintenance, and security.
- Transportation: Access to a state-owned vehicle, and in some larger states, an aircraft for official travel.
- Expense Account: A budget to cover costs associated with official duties, travel, and hosting dignitaries.
- Security Detail: A full-time security team for the governor and their family.
- Retirement and Health Benefits: Comprehensive benefits packages comparable to other state employees.
When these non-salary benefits are factored in, the total value of a governor's compensation is significantly higher than the base salary figure.
Job Outlook

The job outlook for a state governor is unlike any other profession. There are only 50 governorships in the United States, making it one of the most exclusive and competitive positions in the country.
- No Growth: The number of jobs is fixed and does not grow. Openings only arise when a governor's term ends, they choose not to seek re-election, are term-limited, or leave office for other reasons.
- Extreme Competition: Elections for governor are highly competitive and expensive, requiring immense fundraising capabilities, political savvy, and public support.
- Career Pathway: There is no single path to becoming a governor. Successful candidates often come from backgrounds in law, business, or have extensive prior political experience, serving in roles such as a U.S. Senator, member of Congress, state legislator, or attorney general. Experience in the private sector, like Tudor Dixon's background in the steel industry, can also be a springboard for a political career.
Conclusion

While a specific query about "Tudor Dixon salary" leads to private information, it opens a window into the professional world of public service at the highest level. The role of a state governor is a demanding, high-stakes career defined by public trust and immense responsibility.
Key Takeaways:
- Salary is Public but Varies Widely: A governor's salary is set by law and ranges from $70,000 to $250,000, largely dependent on the state's geography and economy.
- Compensation Extends Beyond Salary: The official salary is supplemented by significant benefits, including an official residence, transportation, and security.
- An Exceptionally Competitive Field: With only 50 positions available, the path to becoming a governor is not a traditional career ladder but a highly competitive and political endeavor.
For anyone inspired by public service, understanding the mechanics of a governor's role and compensation provides a realistic perspective on the peak of state-level political life. It is a career driven less by financial reward and more by the desire to lead and make a lasting impact on millions of lives.
