In an era defined by technological innovation and environmental challenges, the field of agricultural engineering stands at a crucial intersection. These professionals blend biology, mechanics, and environmental science to solve the world's most pressing problems in food production, resource management, and sustainability. But beyond its significant impact, a career as an agricultural engineer offers substantial financial rewards.
For those considering this dynamic profession, a key question arises: what is the earning potential? The answer is promising. A qualified agricultural engineer can expect a competitive salary that typically ranges from $60,000 for entry-level positions to well over $130,000 for experienced specialists in high-demand sectors.
This article provides a data-driven look at agricultural engineer salaries, exploring the key factors that influence your pay and the future outlook for this vital career.
What Does an Agricultural Engineer Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it’s important to understand the role. Agricultural engineers are the architects of modern agriculture. They are problem-solvers who apply engineering principles to food, fiber, and fuel production. Their responsibilities are diverse and impactful, often including:
- Designing advanced machinery: Creating and improving tractors, harvesters, and robotic systems to enhance efficiency and reduce labor.
- Developing irrigation and water management systems: Ensuring sustainable water use for crop production, especially in arid regions.
- Engineering food processing solutions: Designing equipment and facilities for storing, processing, and transporting agricultural products safely and efficiently.
- Managing agricultural environments: Creating systems for animal housing, waste management, and soil conservation to minimize environmental impact.
- Innovating with technology: Integrating GPS, drones, sensors (IoT), and data analytics into farming practices, a field known as precision agriculture.
Average Agricultural Engineer Salary
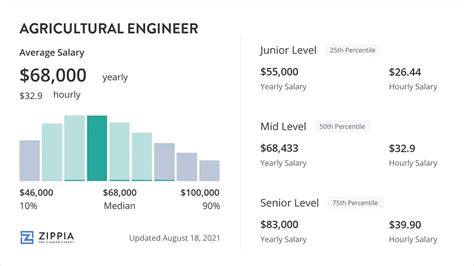
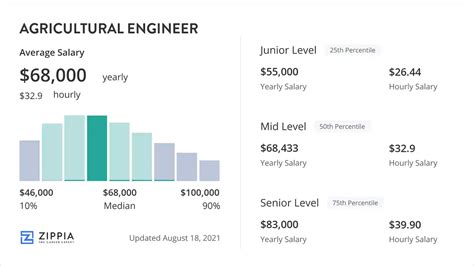
The compensation for agricultural engineers is strong, reflecting the specialized skills and knowledge required for the role.
According to the most recent data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for agricultural engineers was $83,260 in May 2023.
However, a median salary only tells part of the story. The full salary spectrum reveals the potential for significant growth over a career:
- Lowest 10%: Earned less than $57,430 (typical for entry-level or intern positions).
- Lower Quartile (25%): Earned $67,730.
- Upper Quartile (75%): Earned $103,130.
- Highest 10%: Earned more than $131,340 (representing senior, specialized, or management roles).
Data from reputable salary aggregators reinforces this range. Salary.com reports a median base salary of $89,689 as of late 2023, while Payscale.com shows an average base salary of around $73,500, with total pay increasing significantly with bonuses and profit-sharing. This variation highlights that your specific compensation will depend on a number of critical factors.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your final salary is not a single number but a result of your unique qualifications, choices, and environment. Here are the primary factors that will shape your earning potential.
### Level of Education
A bachelor’s degree in agricultural engineering or a related engineering field is the standard entry requirement. However, advanced education can unlock higher-paying roles, particularly in research, development, and academia.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Qualifies you for most entry-level to mid-career engineering positions in design, production, and management.
- Master’s Degree (M.S.): A master's degree can lead to more specialized and senior roles, particularly in research and development (R&D) or technical consulting. It often provides a starting salary boost and can accelerate your path to leadership.
- Doctorate (Ph.D.): A Ph.D. is typically required for university-level teaching and leading advanced research projects, either in academia or for large private corporations. These positions are among the highest-paid in the field.
### Years of Experience
Experience is one of the most significant drivers of salary growth in any engineering discipline. As you accumulate practical skills and a track record of successful projects, your value to employers increases dramatically.
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Engineers fresh out of college typically earn in the lower range, often between $60,000 and $75,000. They focus on learning, supporting senior engineers, and handling less complex tasks.
- Mid-Career (3-9 years): With several years of experience, engineers can manage projects, work more independently, and start to specialize. Their salaries often move into the $75,000 to $100,000 range.
- Senior/Lead Engineer (10+ years): Highly experienced professionals who lead teams, manage complex, high-budget projects, or act as subject matter experts command top-tier salaries, often exceeding $110,000 and reaching well into the $130,000+ range, consistent with the BLS top 10% data.
### Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries can vary significantly based on state and metropolitan area due to local demand, cost of living, and the concentration of agricultural industries.
According to the BLS, some of the top-paying states for agricultural engineers include:
1. California: A hub for high-tech agriculture and food processing.
2. Maryland: Home to federal agencies and research institutions.
3. Nebraska: A center for agricultural machinery manufacturing and research.
4. Minnesota: Strong in both food production and agricultural technology.
5. Iowa: A core state for crop science and agricultural equipment companies.
Working in a major agricultural hub or a region with a high concentration of engineering firms will generally result in a higher salary than in a region with less demand.
### Company Type
The type of organization you work for has a direct impact on your compensation and benefits. The BLS identifies several key employment sectors with varying pay scales:
- Federal Government: Often one of the highest-paying sectors, employing engineers in agencies like the USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS). These roles offer excellent benefits and job security.
- Engineering and Architectural Services: Consulting firms that design systems and solve problems for a variety of clients often pay competitively to attract top talent.
- Food Manufacturing: Large corporations involved in food and beverage processing require engineers to optimize production lines and ensure safety, offering robust salary packages.
- Agricultural Machinery Manufacturing: Working for major equipment manufacturers (e.g., John Deere, CNH Industrial) is a classic path for agricultural engineers and offers strong, stable salaries.
- Academia: While starting salaries may be modest, senior professors at major research universities can earn substantial incomes, especially when supplemented by grants and consulting work.
### Area of Specialization
Modern agriculture is highly specialized, and your chosen focus can significantly influence your pay. In-demand, high-tech fields command a premium.
- Precision Agriculture & Data Science: Engineers who can work with drones, IoT sensors, GPS mapping, and data analytics are in extremely high demand and can command top-tier salaries.
- Food and Bioprocess Engineering: Specialists who design efficient and safe food processing systems are vital to the global supply chain and are compensated accordingly.
- Environmental and Water Resource Engineering: With increasing global focus on sustainability and water scarcity, engineers who specialize in irrigation, drainage, and environmental remediation are highly valued.
- Power Systems & Machinery Design: The traditional core of the profession remains lucrative, especially for those innovating with robotics, automation, and alternative fuels.
Job Outlook

The future for agricultural engineers is bright. The BLS projects that employment for agricultural engineers will grow by 4% from 2022 to 2032, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.
While this may seem like modest growth, the context is key. The world’s population continues to grow, demanding more efficient and sustainable food production methods. This creates a consistent, long-term need for engineers who can:
- Increase crop yields with less environmental impact.
- Automate farm operations.
- Develop new forms of biofuels.
- Conserve precious water and soil resources.
This sustained demand means that qualified agricultural engineers with modern skill sets will continue to find excellent career opportunities.
Conclusion

A career as an agricultural engineer is more than just a job; it’s an opportunity to be at the forefront of solving critical global challenges. The profession is intellectually stimulating, professionally rewarding, and financially sound.
Key Takeaways:
- Solid Earning Potential: With a median salary of $83,260 and a path to earning over $130,000, this career offers excellent financial stability and growth.
- You Control Your Growth: Your salary is directly influenced by your choices in education, specialization, and continuous learning.
- Experience Pays: Demonstrable skills and a strong project portfolio are the surest way to advance to higher salary bands.
- Demand is Stable and Evolving: The need for agricultural innovation is constant, ensuring a stable job market for those with skills in high-tech areas like precision agriculture and sustainability.
For prospective students and professionals with a passion for technology, biology, and making a tangible impact, agricultural engineering offers a fertile ground for a prosperous and fulfilling career.