Decoding the Dollars: A Comprehensive Guide to Air Marshal Salary
For those drawn to a career that blends the intensity of federal law enforcement with the critical mission of national security, the role of a Federal Air Marshal (FAM) is a compelling choice. Operating at 30,000 feet, these covert agents are the last line of defense in aviation security. But beyond the immense responsibility, what is the financial potential of this career?
A career as a Federal Air Marshal offers a competitive and structured salary, with entry-level agents potentially earning between $50,000 and $75,000 annually depending on their location, and senior or supervisory agents capable of earning well over $150,000. This article will break down the components of an Air Marshal's salary, the factors that drive earnings, and the overall outlook for this elite profession.
What Does an Air Marshal Do?

A Federal Air Marshal is a highly-trained federal law enforcement officer working for the Transportation Security Administration (TSA). Their primary mission is to protect the nation's civil aviation system from hostile acts. They fly incognito on commercial aircraft, blending in with passengers while remaining prepared to detect, deter, and defeat any terrorist or criminal threat.
Beyond their in-flight duties, Air Marshals also participate in ground-based investigative work, liaise with other law enforcement agencies, and contribute to national security task forces. It is a demanding role that requires exceptional judgment, rigorous physical and firearms proficiency, and the ability to operate with complete discretion.
Average Air Marshal Salary
Unlike private-sector jobs, the salary for a Federal Air Marshal is not based on negotiation but is determined by a structured government pay system. FAMS uses the Transportation Security Administration's "SV" pay scale, which is a broadband system linked to the federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay scale.
New Federal Air Marshals are typically hired at the SV-G pay band. According to the TSA, the base salary range for this starting band is approximately $46,428 to $71,987 per year.
However, this base pay is only part of the story. The most significant addition is Locality Pay, which adjusts an agent's salary upwards based on the cost of living in their assigned duty station. This can increase base pay by 16% to 44%.
When factoring in locality pay and potential overtime, the real-world earnings are higher.
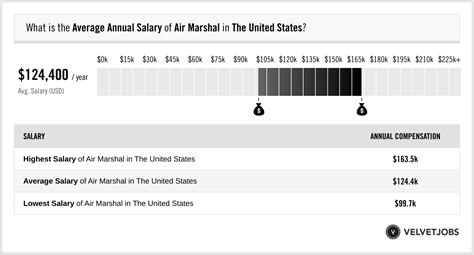
- Salary.com reports that the average Federal Air Marshal salary in the United States is approximately $100,551, with a typical range falling between $91,440 and $111,048.
- Glassdoor estimates the total pay for a Federal Air Marshal is around $118,500 per year on average, including base salary and additional pay like overtime and cash bonuses.
This data illustrates that while the starting base pay is defined, an agent's total compensation quickly climbs into a much higher bracket as they gain experience and benefit from location-based adjustments.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Several key factors determine an Air Marshal's exact salary and career earnings potential. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone considering this path.
### Years of Experience
Experience is the primary driver of salary growth for a Federal Air Marshal. The FAMS career path is structured for clear progression through the SV pay bands. After demonstrating proficiency and meeting time-in-grade requirements, agents can be promoted from the entry-level G band to the H and I bands.
- Journey-Level Agent (SV-H/I Band): This is the full performance level for a non-supervisory Air Marshal. Reaching this level brings a significant salary increase, with potential earnings, including locality pay, often exceeding $100,000 per year.
- Senior & Supervisory Roles (SV-J/K Band and above): Agents who advance into management roles, such as Supervisory Federal Air Marshal or Assistant Federal Air Marshal in Charge (AFAMIC), move into the highest pay bands. In these leadership positions, salaries can reach up to the federal cap of $187,300 (as of 2024), depending on locality.
### Geographic Location
As mentioned, geographic location is a critical salary factor due to the OPM's Locality Pay system. An Air Marshal based in a high-cost-of-living area will earn substantially more than an agent with the same experience level based in a lower-cost area.
For example, an agent based in the San Francisco-Oakland-San Jose area (44.15% locality pay adjustment) will have a much higher total salary than an agent based in a location that falls under the "Rest of U.S." category (16.82% locality pay adjustment). Major hubs like New York, Los Angeles, Washington D.C., and Chicago also have high locality pay rates, making them more lucrative duty stations.
### Company Type
As a federal law enforcement position, the sole employer for an Air Marshal is the U.S. government, specifically the TSA. This is a defining factor for compensation. Unlike the private sector, there is no "shopping around" for a higher salary at a competitor.
However, this comes with distinct advantages:
- Transparency: Salaries are determined by a public, transparent pay scale.
- Stability: Federal jobs offer unparalleled job security compared to private industry.
- Excellent Benefits: Federal employees receive a comprehensive benefits package, including excellent health insurance, life insurance, and a three-tiered retirement plan (FERS) consisting of a pension, Thrift Savings Plan (TSP), and Social Security benefits.
### Area of Specialization
Within FAMS, specialization often leads to advancement and, therefore, a higher salary. While the core mission is in-flight security, agents can pursue specialized roles that align with promotions to higher pay bands. These specializations can include:
- Training and Instruction: Becoming a firearms or tactics instructor.
- Management and Leadership: Moving into supervisory roles managing teams of agents.
- Special Operations: Participating in high-level threat assessment teams or joint operations with other federal agencies.
Pursuing these advanced roles is the primary way an agent can specialize and significantly increase their long-term earning potential.
### Level of Education
While a bachelor's degree is highly preferred and makes a candidate more competitive, the minimum requirement to become an Air Marshal is often a combination of education and experience. An applicant can typically qualify with three years of progressively responsible general experience or a bachelor's degree.
A degree does not automatically place a new hire in a higher pay band. However, a degree in a relevant field such as Criminal Justice, Homeland Security, or International Relations can be a significant advantage during the highly competitive selection process and for long-term career advancement into management and policy-making roles.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) groups Federal Air Marshals within the broader category of "Police and Detectives." For this group, the BLS projects a job growth of 3% between 2022 and 2032, which is about average for all occupations.
However, the demand for Federal Air Marshals is less tied to economic cycles and more to national security priorities and federal funding. Given the enduring threat of terrorism and crime in the aviation domain, the need for a well-trained, professional FAMS force is expected to remain constant. The position is highly competitive, and the TSA is always seeking highly qualified candidates to fill positions due to attrition and retirement.
Conclusion

A career as a Federal Air Marshal is far more than just a job; it is a commitment to public service and national security. From a financial perspective, it offers a solid and reliable path to a six-figure income with outstanding federal benefits.
Key Takeaways:
- Starting Salary: Expect to start in the SV-G pay band, with a total annual income (including locality pay) between $50,000 and $75,000.
- Earnings Growth: Salary progression is structured and transparent, driven primarily by experience, performance, and promotions to higher pay bands (H, I, J, and K).
- Top Potential: Seasoned, journey-level agents can comfortably earn over $100,000, while senior leaders can reach salaries exceeding $150,000.
- Location Matters: Your duty station's locality pay rate is a major factor in your total compensation.
For individuals with integrity, resilience, and a deep sense of duty, the role of a Federal Air Marshal provides not only a path to financial stability but also the profound reward of safeguarding the American public.