A career as a Federal Air Marshal (FAM) is one of the most unique and critical roles in federal law enforcement. Offering a blend of national security, extensive travel, and high-stakes responsibility, it’s a path that attracts dedicated and highly skilled individuals. But beyond the mission, what is the earning potential for this demanding profession?
The answer is compelling. A Federal Air Marshal's salary is structured to reflect the role's significant demands, with entry-level positions often starting above $50,000 and senior, experienced agents earning well over $130,000 annually, depending on a variety of factors. This article will provide a data-driven breakdown of what you can expect to earn and what influences that figure.
What Does a Federal Air Marshal Do?

Federal Air Marshals are the primary law enforcement entity within the Transportation Security Administration (TSA). Their core mission is to protect the nation's civil aviation system from criminal and terrorist activities. Operating as covert, armed federal officers, they blend in with passengers on commercial flights, both domestic and international.
Key responsibilities include:
- Detecting and deterring hostile acts targeting U.S. aircraft, passengers, and crews.
- Performing risk assessments and identifying potential threats.
- Responding to in-flight security incidents with decisive action.
- Coordinating with federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies on aviation security matters.
It is a demanding job that requires constant vigilance, physical fitness, and the ability to work long, irregular hours across different time zones.
Average Federal Air Marshal Salary
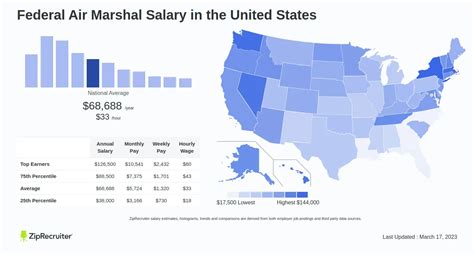
Unlike private-sector jobs, the salary for a Federal Air Marshal is not based on negotiation but is determined by the federal government's structured pay system. FAMs are paid according to a specialized pay band system that corresponds to the General Schedule (GS) scale used by most federal employees.
According to official TSA and OPM (Office of Personnel Management) data, new Federal Air Marshals are typically hired at the SV-G pay band, which is equivalent to the GS-11 grade.
- Typical Starting Salary: The base pay for a GS-11 employee in 2024 starts at $62,107.
- Law Enforcement Availability Pay (LEAP): FAMs are required to work substantial amounts of unscheduled duty and are compensated with LEAP, which adds an additional 25% to their base salary. This brings a starting salary to approximately $77,633.
- Locality Pay: This is where the salary can increase significantly. The government adds a percentage to your base pay (including LEAP) based on the cost of living in your assigned duty station. This can range from 16.82% for the "Rest of U.S." to over 44% for high-cost areas.
Taking all factors into account, a typical salary range for a Federal Air Marshal looks like this:
- Entry-Level (G Pay Band / GS-11): Approximately $90,000 to $105,000+ per year (including LEAP and locality pay for major metropolitan areas).
- Mid-Career (H Pay Band / GS-12): Approximately $105,000 to $125,000+ per year.
- Senior/Supervisory (I Pay Band / GS-13): Approximately $125,000 to $150,000+ per year.
Salary aggregators reflect this reality. Salary.com reports the average Air Marshal salary in the United States to be around $93,501, with a typical range falling between $83,301 and $104,801. This aligns closely with the government pay scale for mid-career professionals in moderately high-cost locations.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While the pay band system is standardized, several key factors determine your exact salary and career earnings trajectory.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is the most direct factor influencing a FAM's salary. The federal pay system is designed to reward longevity and performance. Within each pay band (G, H, I), there are multiple "steps." An employee typically advances to the next step after a set period of satisfactory service (e.g., one year), resulting in a predictable salary increase.
Furthermore, experience is the primary driver for promotions to higher pay bands. Moving from the G band to the H band (equivalent to a promotion from GS-11 to GS-12) represents a significant jump in base pay and overall compensation.
###
Geographic Location
Locality pay has a massive impact on your total earnings. The federal government recognizes that a salary that provides a comfortable living in Des Moines, Iowa, is not sufficient for someone living in San Francisco, California. The OPM publishes annual locality pay tables for dozens of metropolitan areas.
Let's compare the potential starting salary (Base + LEAP) for a new FAM (GS-11, Step 1) in different locations for 2024:
- Base Salary + LEAP: $77,633
- Duty Station: Houston, TX (34.60% Locality Pay): Total Salary ≈ $104,494
- Duty Station: New York, NY (38.99% Locality Pay): Total Salary ≈ $107,903
- Duty Station: San Francisco, CA (45.41% Locality Pay): Total Salary ≈ $112,891
*(Source: OPM 2024 Salary Tables)*
As you can see, your assigned field office can change your annual salary by over $20,000 from the outset.
###
Area of Specialization
While most Federal Air Marshals serve as generalists on flight missions, opportunities for specialization arise with experience and promotion. These specialized roles typically correspond to higher pay bands (H or I bands).
Examples include:
- Supervisory Federal Air Marshal: Leading a team of FAMs and managing administrative and operational duties.
- Instructor: Training new recruits and current officers at the Federal Air Marshal Service Academy.
- Liaison Officer: Working with other federal agencies (like the FBI or CIA) or international partners on intelligence and security initiatives.
- Investigative Roles: Working in a field office on longer-term security investigations.
Securing one of these positions is a key pathway to reaching the top of the pay scale.
###
Level of Education
In the federal system, education doesn't directly add a percentage to your salary once you are hired. However, it plays a crucial role in your initial qualification. To qualify for the G pay band (GS-11), candidates typically need either:
- A bachelor's degree and one year of specialized experience equivalent to the GS-9 level.
- A master's degree (or equivalent graduate degree) or two full years of progressively higher-level graduate education.
- Three years of progressively responsible experience.
Therefore, a higher level of education can help you qualify for a higher starting pay grade and make you a more competitive candidate for promotions down the line, indirectly boosting your career earnings.
###
Company Type
This is a straightforward factor for this career. Federal Air Marshals work for a single "company": the U.S. Federal Government, under the Transportation Security Administration (TSA), which is part of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). There are no private-sector equivalents. Your employer is fixed, and your salary is governed exclusively by federal pay regulations.
Job Outlook

The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not track data for Federal Air Marshals specifically. However, it groups them within the broader category of "Police and Detectives." For this group, the BLS projects a job growth of 3% between 2022 and 2032, which is about average for all occupations.
However, hiring for federal law enforcement is less dependent on economic growth and more on government funding, national security priorities, and attrition rates (i.e., the number of agents retiring). The Federal Air Marshal Service is a highly competitive and sought-after career. While openings may fluctuate from year to year, the ongoing need to secure the nation's transportation infrastructure ensures a consistent demand for qualified candidates.
Conclusion

A career as a Federal Air Marshal is a commitment to public service that comes with a strong and transparent compensation package. Your salary is not a mystery but a clear formula based on your pay grade, experience, and duty location.
Key Takeaways:
- Structured and Predictable Pay: Your salary is determined by the federal pay scale (GS-equivalent), with non-negotiable but transparent step increases.
- Substantial Supplements: Law Enforcement Availability Pay (LEAP) adds 25% to your base salary, and locality pay can add another 17% to 45% or more.
- Experience is King: Your long-term earning potential is directly tied to your years of service and your ability to earn promotions to higher pay bands.
- Location Matters: Your assigned duty station can significantly impact your take-home pay by tens of thousands of dollars per year.
For those who meet the rigorous standards and are driven by a mission to protect, the Federal Air Marshal Service offers not only a challenging and rewarding career but also a stable and lucrative financial future.