For ambitious accounting and finance professionals, the role of a Controller represents a significant milestone—a position of leadership, strategic importance, and substantial financial reward. If you're charting a course toward this prestigious role, one of your primary questions is likely: "What can I expect to earn?" The answer is encouraging. A Controller's salary often ranges from $120,000 to well over $220,000 annually, reflecting the role's critical importance to an organization's financial health.
This guide will provide a data-driven look at the average controller salary, break down the key factors that influence your pay, and explore the promising career outlook for this essential profession.
What Does a Controller Do?

Before diving into the numbers, it's essential to understand the scope of the role. A Controller is the lead accountant of an organization, responsible for the integrity and accuracy of all accounting operations. They are the tactical and technical leaders of the finance department, ensuring that the financial engine of the company runs smoothly and in compliance with regulations.
Key responsibilities typically include:
- Financial Reporting: Preparing and analyzing internal and external financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- General Ledger Management: Overseeing all activities in the general ledger to ensure accuracy and timeliness.
- Oversight of Accounting Functions: Managing core departments like Accounts Payable (AP), Accounts Receivable (AR), and Payroll.
- Internal Controls: Designing and implementing robust internal controls to safeguard company assets and ensure compliance (e.g., Sarbanes-Oxley or SOX).
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Assisting the CFO with the creation of budgets and financial forecasts.
- Audits and Compliance: Acting as the primary point of contact for external auditors and ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal tax laws.
A Controller ensures the books are clean, the data is reliable, and the company is audit-ready at all times.
Average Controller Salary: What the Data Shows
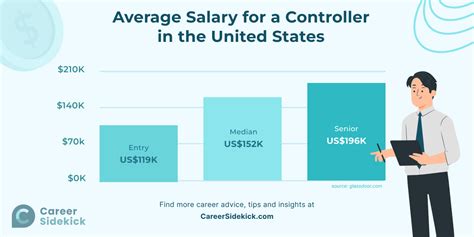
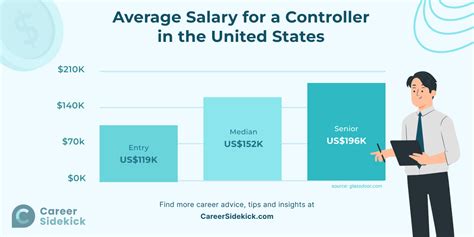
The average controller salary varies based on the data source, but a clear picture of high earning potential emerges across the board. It's important to look at multiple sources to get a well-rounded view.
- According to Salary.com, the median salary for a Controller in the United States is $169,475 as of late 2023, with a typical range falling between $144,354 and $197,114.
- Payscale reports a median salary of $121,500, with a range generally spanning from $85,000 for early-career controllers to over $168,000 for those with extensive experience.
- Glassdoor's data, which aggregates user-submitted salaries, shows an average base pay of approximately $156,000 per year, with total pay (including bonuses and profit sharing) often reaching over $180,000.
It's also useful to consult the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). While the BLS doesn't track "Controllers" as a distinct category, it groups them under the broader profession of Financial Managers. For this group, the BLS reports a median annual wage of $156,010 as of May 2023. The top 10% of financial managers earned more than $239,200.
This data clearly shows that a six-figure salary is standard for a Controller, with significant room for growth based on several key factors.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

Your specific salary as a Controller isn't determined by a single number. It's a complex calculation influenced by your qualifications, where you work, and the nature of your role. Here’s how the primary factors break down.
###
Level of Education
A solid educational foundation is non-negotiable. A bachelor's degree in accounting or finance is the standard minimum requirement. However, advanced credentials are what truly unlock higher earning potential.
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA): The CPA license is the gold standard in the accounting world. It is highly sought after for Controller positions and can significantly increase your salary. Many companies, especially larger or publicly traded ones, list a CPA as a firm requirement for the role.
- Master's Degree (MBA or Master's in Accounting): A Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a finance concentration or a Master's in Accounting demonstrates advanced business acumen and specialized knowledge. This is particularly valuable for controllers who aspire to move into a CFO role and can command a higher salary.
###
Years of Experience
Experience is perhaps the single most significant factor in determining salary. The career path to a Controller role is progressive, with compensation rising at each stage.
- Assistant Controller / Senior Accountant (3-7 years of experience): Professionals in these roles are building their skills and typically earn between $80,000 and $120,000.
- Controller (7-15 years of experience): This is the standard level, where professionals have a proven track record of managing accounting functions. Salaries align with the national averages previously mentioned, typically $120,000 to $180,000.
- Senior or Corporate Controller (15+ years of experience): At this level, you may be overseeing the accounting for a large corporation, a public company, or an entire group of companies. These top-tier roles command salaries well in excess of $200,000, plus substantial bonuses.
###
Geographic Location
Where you work matters. Salaries for controllers vary significantly by state and metropolitan area to account for differences in the cost of living and demand for financial talent. Major financial hubs and high-cost-of-living areas typically offer the highest salaries.
According to BLS data for Financial Managers, top-paying states include:
- New York: Average annual salary of $222,090
- New Jersey: Average annual salary of $197,300
- California: Average annual salary of $187,030
- Massachusetts: Average annual salary of $185,570
Salaries in states with a lower cost of living will generally be closer to or slightly below the national median.
###
Company Type
The size and type of the company you work for have a massive impact on compensation.
- Company Size (Revenue): A Controller at a small business or startup with under $25 million in revenue will earn significantly less than a Controller at a Fortune 500 company with billions in revenue. Professional staffing firm Robert Half's Salary Guide often breaks down salaries by company revenue, showing a clear correlation between company size and pay.
- Public vs. Private: Controllers at publicly traded companies almost always earn more than their counterparts at private companies. This is due to the increased complexity and risk associated with SEC reporting, Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance, and shareholder accountability.
- Industry: The industry also plays a role. High-growth, complex sectors like technology (especially SaaS), pharmaceuticals, and financial services often pay a premium for controllers with specialized industry knowledge.
###
Area of Specialization
Within the Controller title, specialized expertise can make you a more valuable and higher-paid asset. Controllers who can master complex, in-demand accounting areas are highly compensated. Examples include:
- Technical Accounting: Deep expertise in complex areas like revenue recognition (ASC 606), lease accounting (ASC 842), or mergers and acquisitions.
- Cost Accounting: Essential in manufacturing, where managing and analyzing inventory and production costs is critical to profitability.
- International Accounting: Knowledge of IFRS and experience managing finances for a multinational corporation with foreign subsidiaries.
Job Outlook

The future is bright for aspiring controllers. The BLS projects that employment for Financial Managers will grow by 16% from 2022 to 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
This robust demand is driven by several factors:
- The growing complexity of the global economy.
- An increasing need for robust financial reporting and regulatory compliance.
- The rising importance of data analysis to guide business strategy.
This positive outlook ensures that the Controller role will remain a stable, in-demand, and lucrative career path for years to come.
Conclusion: A Rewarding Path Forward

Becoming a Controller is a challenging yet immensely rewarding journey. The role offers not only significant financial compensation but also a central position in shaping a company's financial destiny.
Key Takeaways for Your Career:
- Aim High: A six-figure salary is the standard, with top earners reaching well over $200,000.
- Invest in Credentials: A CPA is the most powerful tool for maximizing your salary and job opportunities.
- Gain Diverse Experience: Build a strong foundation in all areas of accounting and seek out complex challenges.
- Be Strategic: Your choice of industry, company size, and location will have a major impact on your long-term earnings.
For any dedicated finance professional, the path to Controller is a clear and attainable goal. By focusing on continuous learning and strategic career moves, you can position yourself to achieve the high salary and professional fulfillment this critical role offers.