Embarking on a career in medicine is a journey of immense dedication, rigorous training, and profound impact. While the ultimate earning potential for a physician is significant, the path to get there involves a critical, multi-year training period known as residency. During this time, your salary—more accurately, your stipend—is a key factor in your financial planning.
So, what can you expect to earn as a medical resident? While the hours are long and the learning curve is steep, the compensation is structured to support you through this intensive training. On average, medical residents in the United States earn approximately $67,400 per year, according to the Medscape 2023 Resident Salary & Debt Report. This figure serves as a solid baseline, but the actual amount you earn can vary based on several important factors.
Let's dive into the details of what a medical resident does, what they earn, and the key variables that influence their salary.
What Does a Medical Resident Do?

A medical resident is a physician who has graduated from medical school with an M.D. or D.O. degree and is now undergoing specialized postgraduate training in a hospital or clinic. This is not an entry-level job in the traditional sense; it is a mandatory, hands-on apprenticeship required for obtaining a license to practice medicine independently.
Under the supervision of senior physicians (known as attending physicians), residents are on the front lines of patient care. Their responsibilities are extensive and include:
- Diagnosing illnesses and developing treatment plans.
- Admitting patients and managing their ongoing care.
- Performing procedures relevant to their specialty.
- Responding to medical emergencies.
- Working long hours, including nights, weekends, and holidays, often exceeding 80 hours per week.
Residency is a period of intense learning and professional growth, where theoretical knowledge from medical school is forged into practical, life-saving skill.
Average Medical Resident Salary
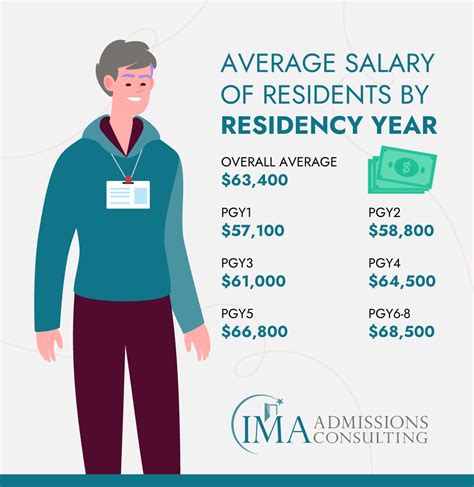
The salary for a medical resident is best understood as a stipend paid by their teaching hospital. It is not a market-driven salary reflecting their full qualifications but rather a standardized wage that covers living expenses during their training years.
Based on the most current data, here is a breakdown of typical resident compensation:
- Overall Average Salary: $67,400 per year, as reported by the Medscape 2023 Resident Salary & Debt Report.
- Typical Salary Range: Most resident salaries fall within a range of $60,000 to $75,000. According to Salary.com, the average First Year Resident Physician salary is $64,481 as of late 2023.
It is crucial to remember that this stipend increases incrementally each year you advance in your residency program.
Key Factors That Influence Salary

While resident salaries don't fluctuate as dramatically as salaries for fully licensed physicians, several factors create modest but meaningful differences in compensation.
###
Years of Experience (Postgraduate Year)
This is the single most significant factor determining a resident's salary. "Experience" here refers to your Postgraduate Year (PGY). A resident in their first year of training (PGY-1) will earn less than a resident in their third year (PGY-3) or a chief resident (often PGY-4 or higher). Hospitals have a set, tiered pay scale based on the PGY level.
According to the AAMC (Association of American Medical Colleges) 2022-2023 Survey of Resident/Fellow Stipends, the average stipend steadily increases with each year of training:
- PGY-1: $61,500
- PGY-2: $63,800
- PGY-3: $66,400
- PGY-4: $69,200
- PGY-5: $71,800
###
Geographic Location
Where you complete your residency matters. Hospitals in regions with a higher cost of living typically offer higher stipends to help offset those expenses. For example, residency programs in major metropolitan areas in the Northeast (like New York or Boston) or on the West Coast (like California) tend to pay more than programs in the South or Midwest.
However, it's essential to analyze the salary in the context of living costs. A $70,000 stipend in New York City may leave you with less disposable income than a $64,000 stipend in a smaller Midwestern city.
###
Institution Type
The type of hospital or medical center where you train can also influence your salary. Large, private university-affiliated medical centers may have different funding structures and pay scales compared to public county hospitals or community-based programs. Much of the funding for graduate medical education (GME) comes from the federal government (specifically the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services), which helps standardize pay to a degree, but institutional budgets and regional economic factors still create variations.
###
Area of Specialization
This is a key point of distinction: during residency, your chosen specialty has a minimal impact on your salary. Unlike in post-residency careers, where a neurosurgeon earns vastly more than a pediatrician, a first-year neurosurgery resident and a first-year pediatrics resident at the same hospital will earn nearly identical salaries. Their pay is determined by their PGY level, not their future specialty.
Some surgical subspecialties that require more years of training will naturally lead to higher PGY-level pay in the later years of residency, but the base salary for any given year is largely standardized across all specialties within an institution.
###
Level of Education
For medical residents, this factor is standardized. All residents have completed a doctorate in medicine (M.D. or D.O.). Therefore, the degree itself does not cause salary variations among residents. The influential factor, as noted above, is the number of years completed in their postgraduate training program.
Job Outlook

While the residency period is financially modest, the long-term career outlook for physicians is exceptionally strong. After completing residency and becoming board-certified, your professional and financial prospects expand dramatically.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment for physicians and surgeons will grow by 3% from 2022 to 2032. This growth is driven by several factors, including the needs of a large and aging population, an increased emphasis on team-based healthcare, and the need to replace a significant number of physicians nearing retirement age. This steady demand ensures that the hard work and financial sacrifices made during residency lead to a stable and secure long-term career.
Conclusion

For aspiring physicians, the residency years are a critical investment in your future. While a resident's salary may seem modest compared to the immense responsibility and long hours, it's important to view it as a structured stipend designed to support you through a finite period of advanced training.
Key Takeaways:
- Expect an Average Stipend: The average resident earns around $67,400, with pay primarily determined by your year of training (PGY level).
- Salary Grows with You: Your income will increase predictably with each year you advance in your residency program.
- Location Matters: Cost of living in different geographic regions will influence your stipend.
- The Long-Term View is Bright: Residency is the gateway to a rewarding, in-demand, and financially lucrative career as a fully-licensed physician.
While the financial path of a resident requires careful budgeting and planning, it is a necessary and temporary phase on the way to one of the most respected and impactful professions in the world.